Tan Sri Dr. Noor Hisham, Malaysia’s Director-General of Health, estimates that 3.9 million individuals, or 20% of Malaysia’s adult population, are diabetes patients. According to the National Health and Morbidity Survey Report, the percentage of adult Malaysians with diabetes has significantly increased, going from 11.2% in 2011 to 13.4% in 2015 and 18.3% in 2019. Nevertheless, more than 30% of Malaysians are unaware they have been diagnosed with diabetes. The gender split of the 1.7 million diabetes patients in 2020 was 57.02% female and 42.98% male.
The majority of individuals don’t realize they have diabetes until they start experiencing common symptoms, which include eating more, drinking more, urinating more, or losing weight. This is because there aren’t any evident signs of diabetes in the early stages. They cannot control blood sugar in time, as they are not discovered in time and lead to comorbidities. Early treatment is required in cases with metabolic abnormalities and the three-hypers – high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and high blood sugar – in order to prevent diabetes and other cardiovascular diseases.
Younger Diabetics
Diabetes has evolved from a common disease to a severe societal issue with numerous comorbidities and complicated variables as Malaysia enters an aging society. In Malaysia, the rise of young diabetics is another significant issue. More than 7 million people are predicted to have diabetes by 2025, with a 31.5% prevalence among Malaysian adults across the country.
Young-onset diabetes (YOD) refers to type 2 diabetics who age below 40. Many countries have found that YOD prevalence has been rising drastically in recent years; however, the factors are yet to be confirmed. Studies have shown that Africans and Asians have a higher YOD prevalence than other ethnic groups.
Diet Control and Exercise
Other than medical treatment, diet control and exercising frequently are also crucial to recovering from type 2 diabetes. Younger type 2 diabetic patients are more likely to be out of control than the elderly, due to the rapid aging of insulin cells and more consequential complications.
Continuous Monitoring of Blood Sugar Levels
Weight management is the key to preventing diabetes and three-hypers. Nowadays, the number of overweight and obese individuals is rising. Thus, it is significant for us to lose weight in order to achieve a healthy lifestyle and reduce the demand for medication intake.
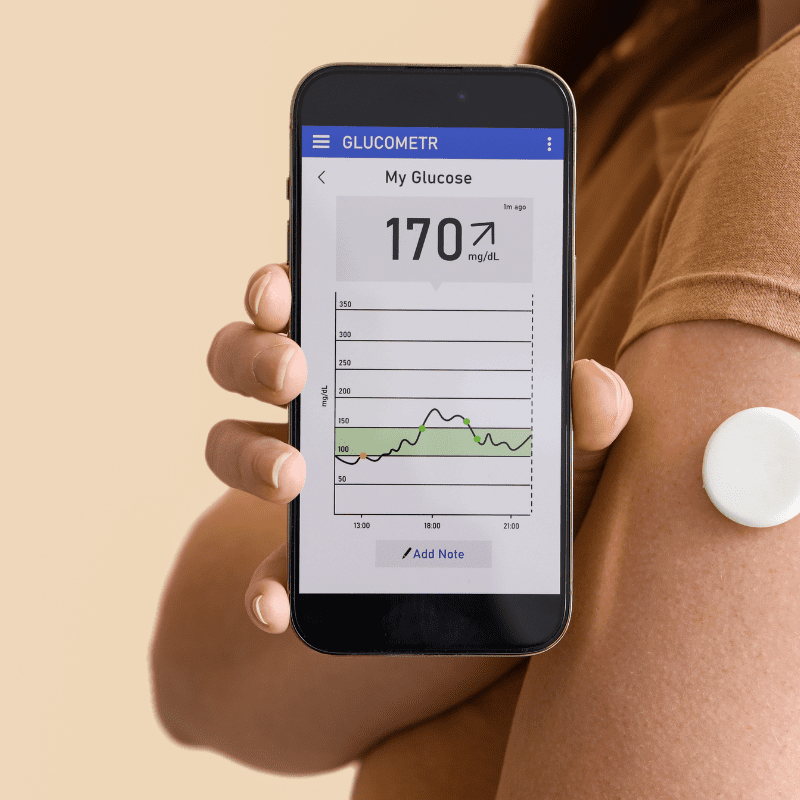
In addition, monitoring blood sugar levels continuously can help us improve diabetes. In the past, insulin intake was the only way to cure diabetes. However, research in recent years has shown that drugs, injections, oral incretins, or even continuous blood sugar level monitoring can help us improve type 2 diabetes.
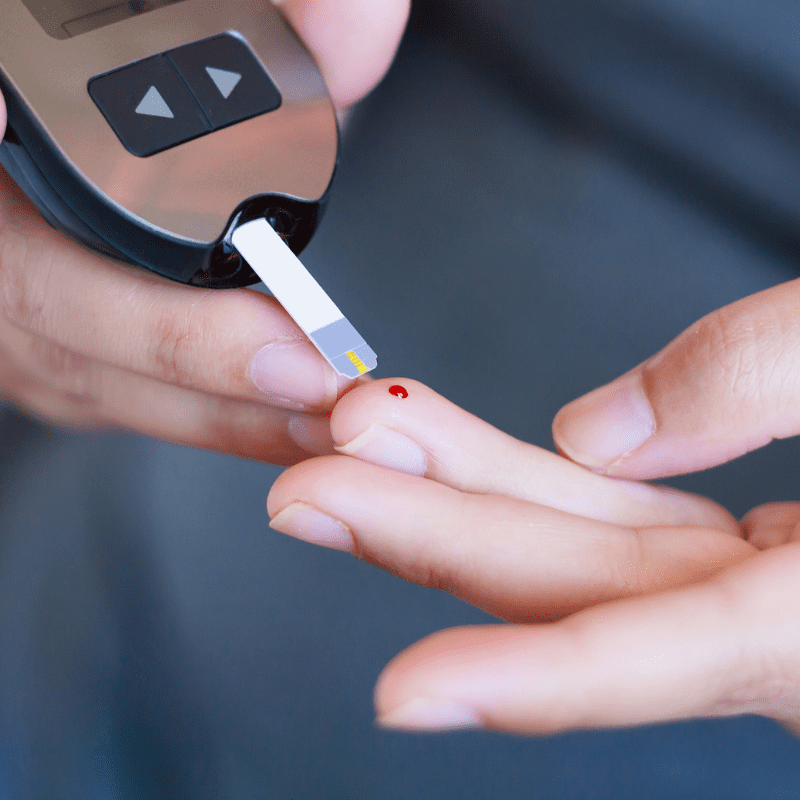
What is A Blood Sugar Detector?
Medical staff will install an automated blood sugar detector under the skin by using a thin blood sugar-sensing needle. It can automatically monitor the blood sugar level in the subcutaneous tissue fluid and record it on the receiver via Bluetooth. By recording data such as diet content, exercise pace, and medical records, patients are able to notice the concentration of blood sugar at any time. A home blood sugar test apparatus has similar properties to an automatic blood sugar level detector, too. In actuality, blood sugar levels can only be monitored manually, in contrast to an automated blood sugar meter. Patients cannot detect changes in blood sugar without spilling a drop of blood on the monitoring device.
In addition, every diabetic patient has to have their medication dosage precisely adjusted by a specialist. Therefore, an autonomous blood sugar level meter can help clinicians by properly tracking patient blood sugar variations. Patients can also alter or enhance their lifestyle by being aware of blood sugar variations.
5 Types of Diabetic Patients
- New patients with frequent and recurring hypoglycemia.
- Blood sugar fluctuates greatly, especially at midnight.
- Those with diet control but not an ideal glycosylated hemoglobin level.
- Changes in exercise intensity, illness, or infection.
- Glycosylated hemoglobin levels increased unexpectedly.
Diabetic patients who lack blood sugar control may experience various complications. For instance, cerebrovascular disease, cardiovascular disease, retinopathy, peripheral vascular disease, neuropathy, and a weakened immune system.
Relationship between Hepatitis C and Diabetes
Diabetes is the main Hepatitis C comorbidities. Studies have shown that the prevalence of hepatitis C in diabetic patients is about 2-3 times that of the general population. The risk of hepatitis C infection leading to diabetes has even increased by 11 times.
Hepatitis C causes chronic inflammation throughout the body and blood vessels, although it mainly infects liver cells. Studies have found that the hepatitis C virus can cause insulin resistance, increase blood sugar, blood pressure, and blood lipids, and also cause damage to endothelial cells, eventually leading to cardiovascular disease, stroke, and other diseases.


Ищете ресурсы для нумизматов ? Наш сайт предлагает исчерпывающие материалы погружения в тему нумизматики!
У нас вы найдёте уникальные экземпляры из исторических периодов, а также драгоценные предметы .
Изучите архив с подробными описаниями и высококачественными фото , чтобы найти раритет.
цена монет Австрии
Если вы начинающий или эксперт, наши статьи и руководства помогут расширить знания .
Не упустите возможностью приобрести лимитированные монеты с сертификатами.
Присоединяйтесь сообщества энтузиастов и будьте в курсе аукционов в мире нумизматики.
Explore the iconic Patek Philippe Nautilus, a luxury timepiece that blends sporty elegance with refined artistry.
Launched in 1976 , this cult design redefined high-end sports watches, featuring distinctive octagonal bezels and horizontally grooved dials .
For stainless steel variants like the 5990/1A-011 with a 45-hour power reserve to luxurious white gold editions such as the 5811/1G-001 with a azure-toned face, the Nautilus caters to both discerning collectors and casual admirers.
Original Patek Nautilus information
The diamond-set 5719 elevate the design with dazzling bezels , adding unparalleled luxury to the iconic silhouette .
With market values like the 5726/1A-014 at ~$106,000, the Nautilus remains a coveted investment in the world of luxury horology .
For those pursuing a historical model or modern redesign, the Nautilus epitomizes Patek Philippe’s legacy of excellence .
Этот сайт публикует свежие информационные статьи на любые темы.
Здесь вы легко найдёте аналитика, бизнесе и разных направлениях.
Материалы выходят регулярно, что позволяет всегда быть в курсе.
Удобная структура делает использование комфортным.
https://ryazansport.ru
Каждое сообщение оформлены качественно.
Целью сайта является достоверности.
Следите за обновлениями, чтобы быть на волне новостей.
Wagering is becoming an exciting way to enhance your gaming journey. Whether you’re betting on football, our platform offers great opportunities for all players.
With in-play wagering to scheduled events, you can find a wide variety of gambling options tailored to your needs. The easy-to-use design ensures that making wagers is both effortless and safe.
https://gazetablic.com/new/?easybet_south_africa___sports_betting__casino___free_r50_bonus.html
Get started to explore the best betting experience available on the web.
Монтаж систем видеонаблюдения обеспечит безопасность территории на постоянной основе.
Продвинутые системы обеспечивают высокое качество изображения даже при слабом освещении.
Вы можете заказать различные варианты оборудования, подходящих для бизнеса и частных объектов.
videonablyudeniemoskva.ru
Качественный монтаж и консультации специалистов превращают решение простым и надежным для всех заказчиков.
Оставьте заявку, чтобы получить оптимальное предложение для установки видеонаблюдения.
Looking for browser-based adventures? This site offers a diverse library of casual puzzles and strategy challenges.
Dive into cooperative missions with friends, supported by voice communication for seamless teamwork.
Enjoy customizable controls designed for quick mastery, alongside safety features like SSL encryption for secure play.
new zealand online casinos
Whether sports simulations to creative builders, every game balances fun and emotional rewards.
Unlock premium upgrades that let you earn in-game perks, with subscription models for deeper access.
Become part of a thriving community where creativity shines, and express yourself through dynamic gameplay .
Этот бот поможет получить данные по заданному профилю.
Достаточно ввести никнейм в соцсетях, чтобы сформировать отчёт.
Бот сканирует публичные данные и цифровые следы.
глаз бога телеграмм бот ссылка
Результаты формируются в реальном времени с фильтрацией мусора.
Оптимален для анализа профилей перед сотрудничеством .
Анонимность и точность данных — гарантированы.
Хотите собрать данные о человеке ? Наш сервис предоставит детальный отчет мгновенно.
Используйте продвинутые инструменты для анализа публичных записей в соцсетях .
Выясните место работы или активность через систему мониторинга с верификацией результатов.
чат бот глаз бога
Система функционирует в рамках закона , используя только общедоступную информацию.
Закажите расширенный отчет с историей аккаунтов и графиками активности .
Доверьтесь надежному помощнику для digital-расследований — результаты вас удивят !
Нужно найти данные о человеке ? Этот бот поможет детальный отчет мгновенно.
Воспользуйтесь уникальные алгоритмы для анализа публичных записей в открытых источниках.
Узнайте контактные данные или интересы через автоматизированный скан с верификацией результатов.
глаз бога поиск людей
Система функционирует с соблюдением GDPR, используя только открытые данные .
Получите детализированную выжимку с историей аккаунтов и графиками активности .
Попробуйте проверенному решению для digital-расследований — точность гарантирована!
Здесь можно найти данные по любому лицу, включая полные анкеты.
Архивы содержат персон разного возраста, профессий.
Сведения формируются по официальным записям, что гарантирует точность.
Обнаружение выполняется по контактным данным, что обеспечивает работу удобным.
новый глаз бога
Также предоставляются контакты плюс полезная информация.
Обработка данных проводятся в рамках правовых норм, обеспечивая защиту разглашения.
Используйте данному ресурсу, для поиска искомые данные максимально быстро.
Нужно найти данные о пользователе? Этот бот поможет детальный отчет в режиме реального времени .
Используйте уникальные алгоритмы для поиска цифровых следов в соцсетях .
Выясните контактные данные или интересы через автоматизированный скан с гарантией точности .
глаз бога бот бесплатно
Система функционирует с соблюдением GDPR, используя только общедоступную информацию.
Получите детализированную выжимку с геолокационными метками и графиками активности .
Попробуйте проверенному решению для исследований — точность гарантирована!
Подбирая семейного доктора стоит обратить внимание на квалификацию, стиль общения и удобные часы приема.
Проверьте , что клиника расположена рядом и сотрудничает с узкими специалистами.
Спросите, принимает ли врач с вашей страховой компанией , и какова загруженность расписания.
http://www.mhdvmobilu.cz/forum/index.php?topic=158.new#new
Обращайте внимание рекомендации знакомых, чтобы понять уровень доверия .
Важно проверить наличие профильного образования, подтверждающие документы для гарантии безопасности .
Оптимальный вариант — тот, где вас услышат ваши нужды , а процесс лечения будет максимально прозрачным.
В этом ресурсе доступна данные о любом человеке, от кратких контактов до подробные профили.
Архивы включают людей разного возраста, статусов.
Данные агрегируются на основе публичных данных, подтверждая достоверность.
Обнаружение выполняется по фамилии, что делает работу эффективным.
актуальный глаз бога
Также можно получить контакты а также актуальные данные.
Работа с информацией проводятся в рамках норм права, предотвращая утечек.
Воспользуйтесь данному ресурсу, чтобы найти искомые данные максимально быстро.
Нужно найти данные о пользователе? Этот бот предоставит полный профиль в режиме реального времени .
Воспользуйтесь продвинутые инструменты для анализа цифровых следов в открытых источниках.
Выясните место работы или активность через систему мониторинга с гарантией точности .
глаз бога телега
Бот работает с соблюдением GDPR, используя только открытые данные .
Получите расширенный отчет с геолокационными метками и графиками активности .
Доверьтесь надежному помощнику для digital-расследований — результаты вас удивят !
Хотите собрать данные о пользователе? Этот бот предоставит детальный отчет мгновенно.
Воспользуйтесь продвинутые инструменты для анализа публичных записей в открытых источниках.
Выясните контактные данные или активность через систему мониторинга с верификацией результатов.
bot глаз бога telegram
Бот работает с соблюдением GDPR, используя только общедоступную информацию.
Закажите расширенный отчет с историей аккаунтов и списком связей.
Доверьтесь надежному помощнику для исследований — точность гарантирована!
Ответственная игра — это принципы, направленный на защиту участников , включая поддержку уязвимых групп.
Платформы обязаны предлагать инструменты саморегуляции , такие как лимиты на депозиты , чтобы избежать чрезмерного участия.
Обучение сотрудников помогает выявлять признаки зависимости , например, частые крупные ставки.
вавада вход
Для игроков доступны консультации экспертов, где обратиться за поддержкой при проблемах с контролем .
Соблюдение стандартов включает проверку возрастных данных для предотвращения мошенничества .
Ключевая цель — создать безопасную среду , где удовольствие сочетается с вредом для финансов .
При выборе компании для квартирного переезда важно учитывать её наличие страховки и опыт работы .
Изучите отзывы клиентов или рейтинги в интернете, чтобы оценить надёжность исполнителя.
Уточните стоимость услуг, учитывая объём вещей, сезонность и услуги упаковки.
https://www.kinofilms.ua/forum/t/5190510/
Требуйте наличия гарантий сохранности имущества и уточните условия компенсации в случае повреждений.
Оцените уровень сервиса: дружелюбие сотрудников , гибкость графика .
Проверьте, есть ли специализированные автомобили и упаковочные материалы для безопасной транспортировки.
Хотите собрать информацию о пользователе? Наш сервис предоставит детальный отчет в режиме реального времени .
Используйте уникальные алгоритмы для поиска публичных записей в соцсетях .
Узнайте контактные данные или активность через автоматизированный скан с верификацией результатов.
глаз бога узнать номер
Бот работает с соблюдением GDPR, обрабатывая открытые данные .
Закажите детализированную выжимку с геолокационными метками и графиками активности .
Доверьтесь надежному помощнику для digital-расследований — точность гарантирована!
Перевозка товаров из КНР в РФ проводится через железнодорожные каналы, с таможенным оформлением на в портах назначения.
Импортные сборы составляют в диапазоне 15–20%, в зависимости от типа продукции — например, готовые изделия облагаются по максимальной ставке.
Для ускорения процесса используют серые каналы доставки , которые быстрее стандартных методов , но связаны с повышенными рисками .
Доставка грузов из Китая
В случае легальных перевозок требуется предоставить сертификаты соответствия и декларации , особенно для сложных грузов .
Сроки доставки варьируются от нескольких дней до двух недель , в зависимости от вида транспорта и загруженности контрольных пунктов.
Стоимость услуг включает транспортные расходы, таможенные платежи и комиссии за оформление , что влияет на рентабельность поставок.