Asthma is a chronic inflammatory respiratory disease that causes the airways (trachea and bronchi) to narrow, leading to symptoms such as difficulty breathing, wheezing, coughing, and chest tightness. The severity and frequency of asthma vary from person to person; some may experience mild symptoms, while others may suffer from severe asthma attacks requiring emergency treatment.
Each time we breathe, air passes through the nose or mouth, into the throat, down the airways, and finally reaches the lungs. There are many small airways in the lungs that help deliver oxygen from the air into the bloodstream. During an asthma attack, the lining of the airways swells, and the muscles around them tighten. Mucus then fills the airways, further reducing the amount of air that can pass through.
These changes can trigger an asthma “attack,” resulting in coughing, chest tightness, and other typical asthma symptoms.
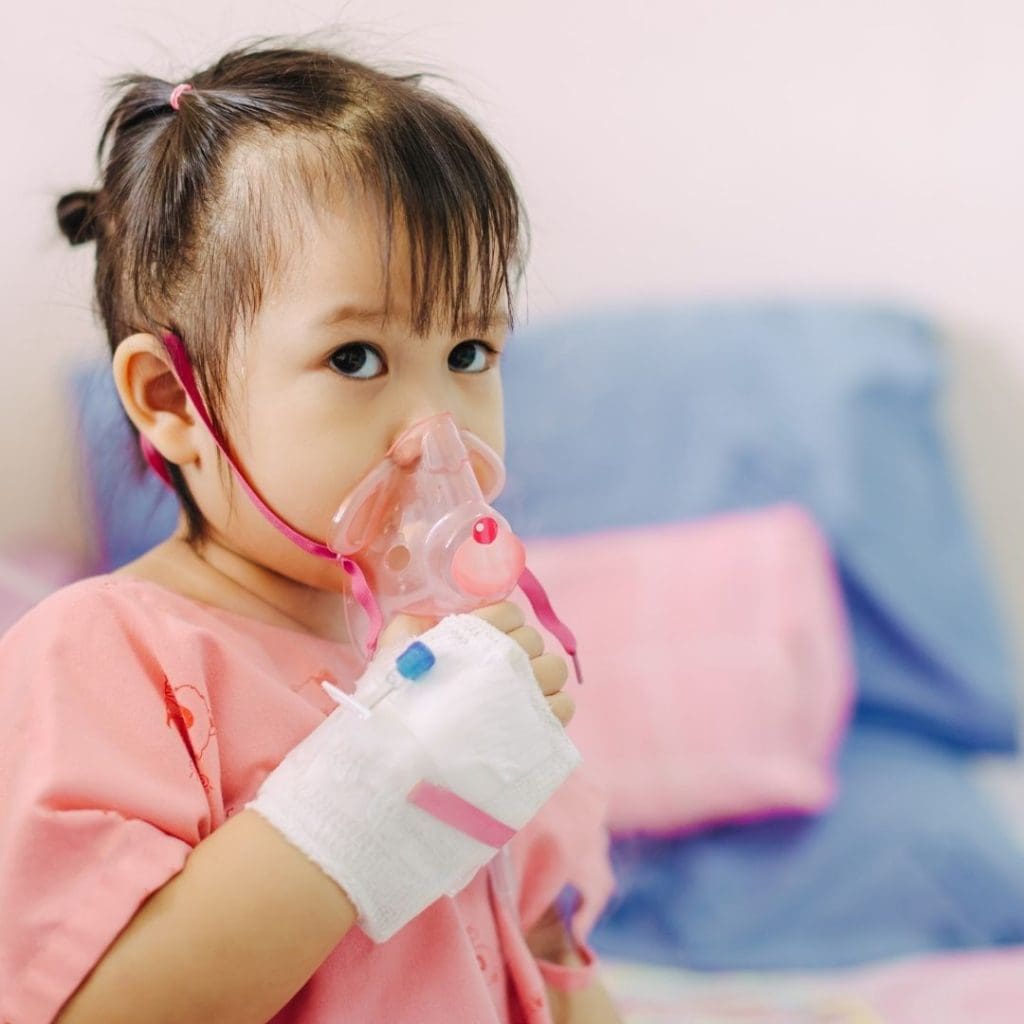
Childhood Asthma
Childhood asthma refers to asthma that occurs in children, a common chronic respiratory disease. The symptoms, causes, and management of childhood asthma are similar to those of adult asthma, but with some differences.

Asthma Symptoms
The most common symptom of asthma is wheezing, a typical sign of asthma characterized by a whistling or squealing sound when breathing, usually occurring during exhalation.
Other possible asthma symptoms include:
- Coughing, especially at night, when laughing, or worsening after exercise or a cold
- Chest pain or tightness; Child may complain of a feeling of tightness or discomfort in the chest
- Shortness of breath; Child may feel difficulty in breathing, showing signs of rapid or labored breathing
- Difficulty in talking
- Anxiety or panic
- Fatigue or trouble sleeping

Causes of Asthma
The exact cause of asthma is not fully understood but is generally believed to result from a combination of factors, including:
- Genetic Factors: Individuals with a family history of asthma or other allergic conditions (such as eczema or allergic rhinitis) have an increased risk of developing asthma.
- Environmental Factors: Allergens in the air (such as pollen, dust mites, mold), air pollution, secondhand smoke, and chemicals (such as cleaning products and perfumes) can trigger or worsen asthma.
- Infections: Viral infections in childhood (such as colds or respiratory infections) may increase the risk of developing asthma later in life.
- Lifestyle Factors: Obesity, lack of exercise, and high stress levels may also be associated with the development of asthma.
- Other Triggers: Cold air, exercise, and emotional changes (such as stress or anxiety) can also induce asthma.

Asthma Management Tips
- Reduce Exposure to Triggers: Identify and avoid the triggers that cause your or your child’s asthma. For example, if allergic to pollen, try to limit outdoor activities during pollen season.
- Use Medications Regularly: Asthma often requires long-term use of control medications (such as inhaled corticosteroids) to reduce airway inflammation and prevent symptoms. Relief medications (such as bronchodilators) should be used as needed to alleviate acute symptoms.
- Monitor Lung Function Regularly: Use tools like peak flow meters to monitor lung function regularly and adjust treatment as needed. Regular check-ups are essential, and do not ignore signs that your child’s asthma may be out of control, such as frequent use of quick-relief inhalers.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Eat a balanced diet, maintain a healthy weight, and exercise regularly, but avoid overly strenuous activities. Helping your child maintain a healthy weight is crucial, as being overweight can worsen asthma symptoms and increase the risk of other health problems.
- Prevent Infections: Get flu and pneumonia vaccines regularly to reduce the risk of asthma flare-ups caused by infections.
- Quit Smoking and Avoid Secondhand Smoke: Smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke can worsen asthma symptoms and should be avoided. Ensure that no one smokes around your child, as exposure to tobacco smoke during infancy is a strong risk factor for childhood asthma and a common trigger for asthma attacks.
- Manage Stress and Emotions: Stress and emotional changes can worsen asthma, so learning relaxation techniques (such as deep breathing or meditation) can help control the condition.
- Control Heartburn: Acid reflux or severe heartburn can worsen asthma symptoms. Your child may need prescription or over-the-counter medications to manage acid reflux.
With proper management and attention to daily details, asthma patients can effectively control symptoms, reduce the frequency of attacks, and lead a healthier life.

Recommended Nuewee Products
Nuewee Organic Banana Protein with Tiger Milk Mushroom
– Tiger Milk Mushroom (Lignosus rhinoceros) is a fungus found only in the tropical rainforests of South China, Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia, the Philippines, and Papua New Guinea. It is regarded as a national treasure of Malaysia and has been used as an effective herbal remedy for over 500 years, especially for immune and respiratory systems.
– Tiger Milk Mushroom effectively alleviates respiratory symptoms such as chronic cough, asthma, and sinusitis by addressing symptoms and root causes through its cleansing, regulating, restorative, and protective mechanisms.
– Nuewee uses LiGNO TM02® Tiger Milk Mushroom, the world’s first and only scientifically proven, highest-quality source of Tiger Milk Mushroom. Research shows that LiGNO TM02® Tiger Milk Mushroom has anti-inflammatory properties that effectively reduce tissue damage in the respiratory system, helping restore lung function. LiGNO TM02® also aids in supporting airway expansion and promotes easy breathing in different temperatures and seasons.


Explore detailed information about the Audemars Piguet Royal Oak Offshore 15710ST on this site , including market values ranging from $34,566 to $36,200 for stainless steel models.
The 42mm timepiece features a robust design with selfwinding caliber and water resistance , crafted in stainless steel .
Used Piguet Royal Oak Offshore 15710st review
Analyze secondary market data , where limited editions reach up to $750,000 , alongside pre-owned listings from the 1970s.
View real-time updates on availability, specifications, and investment returns , with trend reports for informed decisions.
Explore detailed information about the Audemars Piguet Royal Oak Offshore 15710ST via this platform , including price trends ranging from $34,566 to $36,200 for stainless steel models.
The 42mm timepiece features a robust design with selfwinding caliber and rugged aesthetics, crafted in stainless steel .
Authentic Audemars Piguet Royal Oak 15710 prices
Analyze secondary market data , where limited editions command premiums , alongside rare references from the 1970s.
View real-time updates on availability, specifications, and historical value, with trend reports for informed decisions.
Access detailed information about the Audemars Piguet Royal Oak Offshore 15710ST here , including price trends ranging from $34,566 to $36,200 for stainless steel models.
The 42mm timepiece showcases a robust design with mechanical precision and durability , crafted in rose gold .
Verified Audemars Royal Oak Offshore 15710 st price
Check secondary market data , where limited editions command premiums , alongside vintage models from the 1970s.
Get real-time updates on availability, specifications, and investment returns , with free market analyses for informed decisions.
Launched in 1999, Richard Mille revolutionized luxury watchmaking with avant-garde design. The brand’s iconic timepieces combine aerospace-grade ceramics and sapphire to balance durability .
Mirroring the aerodynamics of Formula 1, each watch prioritizes functionality , optimizing resistance. Collections like the RM 011 Flyback Chronograph set new benchmarks since their debut.
Richard Mille’s collaborations with experts in mechanical engineering yield skeletonized movements tested in extreme conditions .
All Richard Mille RM 6702 timepiece
Rooted in innovation, the brand pushes boundaries through bespoke complications for collectors .
With a legacy , Richard Mille epitomizes modern haute horlogerie, appealing to global trendsetters.
Discover the iconic Patek Philippe Nautilus, a luxury timepiece that merges athletic sophistication with refined artistry.
Introduced nearly 50 years ago, this legendary watch revolutionized high-end sports watches, featuring signature angular cases and horizontally grooved dials .
From stainless steel models like the 5990/1A-011 with a 45-hour power reserve to luxurious white gold editions such as the 5811/1G-001 with a azure-toned face, the Nautilus suits both discerning collectors and everyday wearers .
Used PP Nautilus 5712r timepiece
The diamond-set 5719 elevate the design with dazzling bezels , adding unparalleled luxury to the timeless profile.
With market values like the 5726/1A-014 at ~$106,000, the Nautilus remains a coveted investment in the world of premium watchmaking.
For those pursuing a historical model or modern redesign, the Nautilus embodies Patek Philippe’s legacy of excellence .
Designed by Gerald Genta, revolutionized luxury watchmaking with its signature angular case and bold integration of sporty elegance.
Available in limited-edition sand gold to skeleton dials , the collection combines avant-garde design with horological mastery.
Priced from $20,000 to over $400,000, these timepieces cater to both seasoned collectors and aficionados seeking investable art .
Certified Piguet Audemars Oak 26240or wristwatch
The Perpetual Calendar models set benchmarks with robust case constructions, showcasing Audemars Piguet’s technical prowess .
With ultra-thin calibers like the 2385, each watch epitomizes the brand’s legacy of craftsmanship.
Discover certified pre-owned editions and detailed collector guides to elevate your collection with this modern legend .
Launched in 1972, the Royal Oak redefined luxury watchmaking with its iconic octagonal bezel and stainless steel craftsmanship .
Ranging from classic stainless steel to skeleton dials , the collection merges avant-garde design with horological mastery.
Priced from $20,000 to over $400,000, these timepieces attract both luxury enthusiasts and newcomers seeking wearable heritage.
All AP Royal Oak 26240 boutique
The Royal Oak Offshore set benchmarks with innovative complications , showcasing Audemars Piguet’s technical prowess .
With meticulous hand-finishing , each watch reflects the brand’s commitment to excellence .
Explore certified pre-owned editions and detailed collector guides to deepen your horological expertise with this timeless icon .
Die Royal Oak 16202ST kombiniert ein 39-mm-Edelstahlgehäuse mit einem extraflachen Gehäuse von nur 8,1 mm Dicke.
Ihr Herzstück bildet das neue Kaliber 7121 mit 55 Stunden Gangreserve.
Der blaue „Bleu Nuit“-Ton des Zifferblatts wird durch das feine Guillochierungen und die kratzfeste Saphirscheibe mit Antireflexbeschichtung betont.
Neben Stunden- und Minutenanzeige bietet die Uhr ein Datumsfenster bei 3 Uhr.
15450st
Die 50-Meter-Wasserdichte macht sie für sportliche Einsätze geeignet.
Das integrierte Edelstahlarmband mit verstellbarem Dornschließe und die achtseitige Rahmenform zitieren das ikonische Royal-Oak-Erbe aus den 1970er Jahren.
Als Teil der „Jumbo“-Kollektion verkörpert die 16202ST horlogerie-Tradition mit einem Wertanlage für Sammler.
Ищете ресурсы коллекционеров? Наш сайт предлагает всё необходимое погружения в тему монет !
Здесь доступны уникальные экземпляры из разных эпох , а также антикварные предметы .
Просмотрите архив с характеристиками и высококачественными фото , чтобы найти раритет.
золотые монеты цена
Если вы начинающий или эксперт, наши статьи и гайды помогут расширить знания .
Не упустите шансом приобрести эксклюзивные артефакты с гарантией подлинности .
Присоединяйтесь сообщества энтузиастов и следите аукционов в мире нумизматики.
Стальные резервуары используются для хранения дизельного топлива и соответствуют стандартам давления до 0,04 МПа.
Горизонтальные емкости изготавливают из нержавеющих сплавов с антикоррозийным покрытием.
Идеальны для АЗС: хранят бензин, керосин, мазут или биодизель.
Емкость дренажная 16 м3 утепленная
Двустенные резервуары обеспечивают защиту от утечек, а подземные модификации подходят для разных условий.
Заводы предлагают типовые решения объемом до 500 м³ с технической поддержкой.
Стальные резервуары используются для сбора нефтепродуктов и соответствуют стандартам давления до 0,04 МПа.
Горизонтальные емкости изготавливают из нержавеющих сплавов с усиленной сваркой.
Идеальны для АЗС: хранят бензин, керосин, мазут или авиационное топливо.
Подземный пожарный резервуар 80 м3
Двустенные резервуары обеспечивают экологическую безопасность, а подземные модификации подходят для разных условий.
Заводы предлагают индивидуальные проекты объемом до 500 м³ с технической поддержкой.
Die Royal Oak 16202ST vereint ein 39-mm-Edelstahlgehäuse mit einem ultradünnen Profil und dem neuen Kaliber 7121 für 55 Stunden Gangreserve.
Das „Bleu Nuit“-Zifferblatt mit Weißgold-Indexen und Luminous-Beschichtung wird durch eine Saphirglas-Scheibe mit Antireflex-Beschichtung geschützt.
Neben Datum bei 3 Uhr bietet die Uhr 50-Meter-Wasserdichte und ein geschlossenes Edelstahlband mit verstellbarem Verschluss.
15450st
Die oktogonale Lünette mit ikonenhaften Hexschrauben und die gebürstete Oberflächenkombination zitieren den 1972er Klassiker.
Als Teil der Extra-Thin-Kollektion ist die 16202ST eine Sammler-Investition mit einem Wertsteigerungspotenzial.
Premium mechanical timepieces stay in demand for numerous vital factors.
Their craftsmanship and tradition define their exclusivity.
They symbolize wealth and sophistication while uniting form and function.
Unlike digital gadgets, their value grows over time due to rarity and durability.
https://graph.org/Patek-Philippe-Nautilus-2025-The-Evolution-of-an-Icon-05-07
Collectors and enthusiasts treasure the engineering marvels that no gadget can ever equal.
For many, owning one is owning history that lasts forever.
Данный портал публикует актуальные информационные статьи со всего мира.
Здесь представлены новости о политике, науке и других областях.
Новостная лента обновляется регулярно, что позволяет следить за происходящим.
Понятная навигация ускоряет поиск.
https://narod-gazeta.ru
Каждое сообщение написаны грамотно.
Редакция придерживается информативности.
Присоединяйтесь к читателям, чтобы быть в курсе самых главных событий.
Коллекция Nautilus, созданная Жеральдом Гентой, сочетает элегантность и прекрасное ремесленничество. Модель Nautilus 5711 с самозаводящимся механизмом имеет 45-часовой запас хода и корпус из белого золота.
Восьмиугольный безель с плавными скосами и синий солнечный циферблат подчеркивают неповторимость модели. Браслет с интегрированными звеньями обеспечивает комфорт даже при повседневном использовании.
Часы оснащены индикацией числа в позиции 3 часа и антибликовым покрытием.
Для версий с усложнениями доступны хронограф, вечный календарь и функция Travel Time.
https://patek-philippe-nautilus.ru/
Например, модель 5712/1R-001 из розового золота с калибром повышенной сложности и запасом хода на двое суток.
Nautilus остается предметом коллекционирования, объединяя современные технологии и традиции швейцарского часового дела.
Коллекция Nautilus, созданная Жеральдом Гентой, сочетает элегантность и прекрасное ремесленничество. Модель Nautilus 5711 с самозаводящимся механизмом имеет энергонезависимость до 2 дней и корпус из белого золота.
Восьмиугольный безель с округлыми гранями и синий солнечный циферблат подчеркивают уникальность модели. Браслет с интегрированными звеньями обеспечивает комфорт даже при активном образе жизни.
Часы оснащены индикацией числа в позиции 3 часа и антибликовым покрытием.
Для версий с усложнениями доступны секундомер, вечный календарь и индикация второго часового пояса.
Купить часы Philippe Patek Nautilus в магазине
Например, модель 5712/1R-001 из розового золота с калибром повышенной сложности и запасом хода на двое суток.
Nautilus остается предметом коллекционирования, объединяя современные технологии и традиции швейцарского часового дела.
Монтаж оборудования для наблюдения поможет контроль вашего объекта на постоянной основе.
Современные технологии гарантируют четкую картинку даже в ночных условиях.
Мы предлагаем различные варианты устройств, подходящих для бизнеса и частных объектов.
установка видеонаблюдения под ключ цена
Профессиональная установка и техническая поддержка превращают решение простым и надежным для каждого клиента.
Обратитесь сегодня, и узнать о лучшее решение для установки видеонаблюдения.
Монтаж систем видеонаблюдения поможет защиту вашего объекта в режиме 24/7.
Современные технологии гарантируют надежный обзор даже в темное время суток.
Вы можете заказать различные варианты устройств, идеальных для дома.
установка видеонаблюдения в подъезде многоквартирного дома
Качественный монтаж и сервисное обслуживание превращают решение максимально удобным для всех заказчиков.
Свяжитесь с нами, для получения персональную консультацию в сфере безопасности.
На данном сайте доступен Telegram-бот “Глаз Бога”, что проверить всю информацию о гражданине по публичным данным.
Сервис активно ищет по номеру телефона, обрабатывая актуальные базы в сети. Благодаря ему осуществляется пять пробивов и глубокий сбор по фото.
Сервис обновлен на август 2024 и включает фото и видео. Бот сможет найти профили в открытых базах и предоставит результаты за секунды.
новый глаз бога
Такой инструмент — помощник для проверки персон через Telegram.
Здесь можно получить сервис “Глаз Бога”, позволяющий найти всю информацию по человеку из открытых источников.
Инструмент функционирует по номеру телефона, обрабатывая публичные материалы онлайн. Через бота можно получить 5 бесплатных проверок и детальный анализ по фото.
Сервис актуален на август 2024 и поддерживает фото и видео. Глаз Бога сможет проверить личность по госреестрам и предоставит результаты в режиме реального времени.
сервис глаз бога
Такой бот — выбор для проверки граждан удаленно.
Прямо здесь вы найдете сервис “Глаз Бога”, что собрать всю информацию о человеке по публичным данным.
Бот работает по ФИО, используя публичные материалы в Рунете. Через бота можно получить бесплатный поиск и глубокий сбор по фото.
Платфор ма проверен на август 2024 и поддерживает фото и видео. Сервис сможет узнать данные по госреестрам и отобразит сведения мгновенно.
глаз бога телега
Данный инструмент — помощник в анализе людей онлайн.
Здесь доступен мессенджер-бот “Глаз Бога”, позволяющий найти сведения о гражданине из открытых источников.
Бот активно ищет по номеру телефона, анализируя актуальные базы в Рунете. Через бота доступны бесплатный поиск и глубокий сбор по имени.
Платфор ма проверен согласно последним данным и охватывает мультимедийные данные. Бот сможет проверить личность по госреестрам и отобразит результаты в режиме реального времени.
глаз бога телеграм
Это сервис — выбор в анализе граждан удаленно.
Здесь доступен мессенджер-бот “Глаз Бога”, что найти всю информацию о человеке из открытых источников.
Сервис функционирует по номеру телефона, обрабатывая публичные материалы в сети. Благодаря ему доступны 5 бесплатных проверок и полный отчет по фото.
Платфор ма обновлен на 2025 год и включает аудио-материалы. Бот гарантирует узнать данные по госреестрам и предоставит результаты за секунды.
глаз бога в телеграме
Такой инструмент — помощник в анализе граждан удаленно.
Looking for browser-based adventures? Our platform offers a diverse library of multiplayer experiences and action-packed quests .
Dive into real-time battles with friends, supported by voice communication for seamless teamwork.
Enjoy customizable controls designed for effortless navigation , alongside safety features like SSL encryption for secure play.
best online casino in canada
Whether fantasy RPGs to creative builders, every game prioritizes fun and cognitive engagement .
Discover premium upgrades that let you earn in-game perks, with optional purchases for deeper access.
Join of a thriving community where teamwork flourishes , and express yourself through dynamic gameplay .
Chcesz znaleźć gry przeglądarkowe w tym miejscu?
Zapewniamy różnorodne gatunki — od RPG do sportu!
Korzystaj w przeglądarce na dowolnym urządzeniu.
Popularne tytuły aktualizowane codziennie .
Najlepsze kasyna online
Dla dzieci , proste — wybór na każdą okazję!
Zacznij grać bez rejestracji.
На данном сайте можно получить мессенджер-бот “Глаз Бога”, что собрать всю информацию по человеку из открытых источников.
Сервис активно ищет по номеру телефона, обрабатывая публичные материалы в сети. Благодаря ему можно получить бесплатный поиск и полный отчет по фото.
Инструмент обновлен на 2025 год и поддерживает аудио-материалы. Сервис поможет проверить личность в открытых базах и покажет результаты в режиме реального времени.
telegram глаз бога
Данный бот — идеальное решение для проверки персон онлайн.
Эта платформа предлагает актуальные информационные статьи на любые темы.
Здесь представлены новости о политике, культуре и многом другом.
Информация обновляется ежедневно, что позволяет всегда быть в курсе.
Понятная навигация ускоряет поиск.
https://outstreet.ru
Любой материал проходят проверку.
Мы стремимся к достоверности.
Присоединяйтесь к читателям, чтобы быть в центре внимания.
Наш сервис поможет получить информацию по заданному профилю.
Укажите имя, фамилию , чтобы получить сведения .
Бот сканирует публичные данные и активность в сети .
глаз бога тг бесплатно
Результаты формируются мгновенно с фильтрацией мусора.
Оптимален для анализа профилей перед сотрудничеством .
Анонимность и актуальность информации — наш приоритет .
Нужно найти данные о пользователе? Этот бот поможет детальный отчет мгновенно.
Воспользуйтесь уникальные алгоритмы для поиска публичных записей в соцсетях .
Выясните место работы или активность через систему мониторинга с верификацией результатов.
глаз бога телеграмм бот бесплатно
Бот работает с соблюдением GDPR, используя только открытые данные .
Закажите расширенный отчет с историей аккаунтов и списком связей.
Попробуйте проверенному решению для digital-расследований — результаты вас удивят !
Этот бот способен найти информацию по заданному профилю.
Укажите имя, фамилию , чтобы получить сведения .
Система анализирует публичные данные и активность в сети .
глаз бога телеграмм официальный
Информация обновляется в реальном времени с фильтрацией мусора.
Идеально подходит для проверки партнёров перед важными решениями.
Конфиденциальность и актуальность информации — гарантированы.
Этот бот способен найти данные о любом человеке .
Укажите никнейм в соцсетях, чтобы получить сведения .
Бот сканирует открытые источники и цифровые следы.
глаз бога телеграм канал
Результаты формируются мгновенно с проверкой достоверности .
Идеально подходит для анализа профилей перед важными решениями.
Конфиденциальность и точность данных — наш приоритет .
Этот бот способен найти информацию по заданному профилю.
Укажите имя, фамилию , чтобы получить сведения .
Система анализирует открытые источники и активность в сети .
глаз бога актуальный бот
Результаты формируются мгновенно с фильтрацией мусора.
Идеально подходит для проверки партнёров перед важными решениями.
Конфиденциальность и точность данных — гарантированы.
Этот бот поможет получить данные по заданному профилю.
Укажите никнейм в соцсетях, чтобы сформировать отчёт.
Бот сканирует открытые источники и активность в сети .
рабочий глаз бога телеграм
Информация обновляется мгновенно с фильтрацией мусора.
Оптимален для анализа профилей перед важными решениями.
Конфиденциальность и точность данных — гарантированы.
Нужно собрать информацию о человеке ? Этот бот предоставит полный профиль мгновенно.
Используйте продвинутые инструменты для анализа цифровых следов в открытых источниках.
Выясните место работы или интересы через систему мониторинга с верификацией результатов.
рабочий глаз бога телеграм
Система функционирует с соблюдением GDPR, используя только общедоступную информацию.
Получите детализированную выжимку с историей аккаунтов и списком связей.
Попробуйте проверенному решению для digital-расследований — результаты вас удивят !
Хотите найти информацию о человеке ? Этот бот поможет полный профиль в режиме реального времени .
Воспользуйтесь уникальные алгоритмы для анализа цифровых следов в соцсетях .
Узнайте место работы или интересы через автоматизированный скан с гарантией точности .
глаз бога по номеру
Бот работает в рамках закона , обрабатывая общедоступную информацию.
Закажите расширенный отчет с геолокационными метками и графиками активности .
Доверьтесь надежному помощнику для исследований — точность гарантирована!
Нужно собрать данные о пользователе? Этот бот поможет детальный отчет мгновенно.
Используйте уникальные алгоритмы для анализа цифровых следов в открытых источниках.
Узнайте контактные данные или активность через автоматизированный скан с гарантией точности .
глаз бога телеграмм канал
Бот работает в рамках закона , обрабатывая открытые данные .
Закажите расширенный отчет с геолокационными метками и графиками активности .
Доверьтесь проверенному решению для digital-расследований — точность гарантирована!
Нужно найти информацию о пользователе? Этот бот предоставит детальный отчет в режиме реального времени .
Воспользуйтесь продвинутые инструменты для анализа цифровых следов в открытых источниках.
Узнайте место работы или активность через автоматизированный скан с гарантией точности .
пробить через глаз бога
Бот работает в рамках закона , используя только общедоступную информацию.
Закажите расширенный отчет с историей аккаунтов и графиками активности .
Доверьтесь надежному помощнику для исследований — результаты вас удивят !
На данном сайте доступна сведения о любом человеке, включая исчерпывающие сведения.
Реестры охватывают людей разного возраста, профессий.
Данные агрегируются из открытых источников, подтверждая надежность.
Поиск осуществляется по контактным данным, что делает использование удобным.
глаз бога пробить человека
Также предоставляются контакты и другая актуальные данные.
Все запросы обрабатываются с соблюдением законодательства, предотвращая несанкционированного доступа.
Используйте этому сайту, чтобы найти искомые данные максимально быстро.
В этом ресурсе можно найти данные по любому лицу, от кратких контактов до подробные профили.
Реестры включают персон разного возраста, мест проживания.
Информация собирается по официальным записям, подтверждая надежность.
Обнаружение осуществляется по контактным данным, сделав процесс быстрым.
глаз бога телеграм канал
Помимо этого можно получить места работы и другая актуальные данные.
Работа с информацией выполняются в рамках законодательства, обеспечивая защиту несанкционированного доступа.
Воспользуйтесь данному ресурсу, чтобы найти искомые данные в кратчайшие сроки.
В этом ресурсе предоставляется данные о любом человеке, включая полные анкеты.
Реестры охватывают людей любой возрастной категории, профессий.
Информация собирается из открытых источников, что гарантирует надежность.
Поиск производится по фамилии, что делает работу быстрым.
глаз бога программа для поиска
Помимо этого предоставляются адреса плюс полезная информация.
Работа с информацией выполняются с соблюдением законодательства, что исключает несанкционированного доступа.
Используйте предложенной системе, для поиска необходимую информацию максимально быстро.
Хотите найти информацию о пользователе? Этот бот поможет полный профиль в режиме реального времени .
Используйте продвинутые инструменты для анализа публичных записей в открытых источниках.
Выясните место работы или интересы через систему мониторинга с верификацией результатов.
чат бот глаз бога
Бот работает с соблюдением GDPR, используя только открытые данные .
Получите детализированную выжимку с историей аккаунтов и графиками активности .
Доверьтесь надежному помощнику для исследований — точность гарантирована!
При выборе семейного доктора важно учитывать на его опыт , стиль общения и удобные часы приема.
Проверьте , что медицинский центр расположена рядом и предоставляет полный спектр услуг .
Узнайте , принимает ли врач с вашей полисом, и есть ли возможность записи онлайн .
https://www.vevioz.com/read-blog/376502
Обращайте внимание рекомендации знакомых, чтобы оценить отношение к клиентам.
Не забудьте наличие профильного образования, аккредитацию клиники для уверенности в качестве лечения.
Оптимальный вариант — тот, где примут во внимание ваши особенности здоровья, а общение с персоналом будет комфортным .
Осознанное участие в азартных развлечениях — это принципы, направленный на защиту участников , включая поддержку уязвимых групп.
Платформы обязаны предлагать инструменты саморегуляции , такие как лимиты на депозиты , чтобы минимизировать зависимость .
Регулярная подготовка персонала помогает выявлять признаки зависимости , например, неожиданные изменения поведения .
сайт вавада
Для игроков доступны консультации экспертов, где можно получить помощь при проблемах с контролем .
Соблюдение стандартов включает проверку возрастных данных для обеспечения прозрачности.
Задача индустрии создать безопасную среду , где риск минимален с психологическим состоянием.
Нужно собрать данные о пользователе? Наш сервис предоставит детальный отчет в режиме реального времени .
Воспользуйтесь продвинутые инструменты для анализа публичных записей в соцсетях .
Узнайте место работы или интересы через систему мониторинга с гарантией точности .
глаз бога по номеру
Бот работает в рамках закона , обрабатывая открытые данные .
Закажите расширенный отчет с историей аккаунтов и списком связей.
Попробуйте надежному помощнику для исследований — точность гарантирована!
Безопасный досуг — это минимизирование рисков для игроков , включая установление лимитов .
Рекомендуется устанавливать финансовые границы, чтобы сохранять контроль над затратами.
Используйте инструменты временной блокировки, чтобы приостановить активность в случае потери контроля.
Доступ к ресурсам включает консультации специалистов, где можно получить помощь при проявлениях зависимости .
Участвуйте в компании, чтобы сохранять социальный контакт , ведь семейная атмосфера делают процесс более контролируемым .
chicken road play
Проверяйте условия платформы: лицензия оператора гарантирует честные условия .
аренда экскаватора цена за смену аренда экскаватора цена за смену .
При выборе компании для квартирного перевозки важно учитывать её лицензирование и репутацию на рынке.
Проверьте отзывы клиентов или рейтинги в интернете, чтобы оценить надёжность исполнителя.
Уточните стоимость услуг, учитывая расстояние перевозки , сезонность и услуги упаковки.
https://kuplukvartiru.com.ua/forum-nerukhomosti/remont-y-dyzain-kvartyr/15135-zakazat-kvartirnyj-pereezd-s-gruzchikami#38856
Требуйте наличия гарантий сохранности имущества и запросите детали компенсации в случае повреждений.
Обратите внимание уровень сервиса: оперативность ответов, детализацию договора.
Узнайте, используются ли специализированные автомобили и упаковочные материалы для безопасной транспортировки.
Подбирая компании для квартирного перевозки важно проверять её наличие страховки и репутацию на рынке.
Проверьте отзывы клиентов или рейтинги в интернете, чтобы оценить профессионализм исполнителя.
Сравните цены , учитывая расстояние перевозки , сезонность и услуги упаковки.
https://www.freeboard.com.ua/forum/viewtopic.php?pid=1003516#p1003516
Убедитесь наличия страхового полиса и запросите детали компенсации в случае повреждений.
Обратите внимание уровень сервиса: дружелюбие сотрудников , гибкость графика .
Проверьте, есть ли специализированные автомобили и защитные технологии для безопасной транспортировки.
Matchmaking services provide a innovative approach to meet people globally, combining intuitive tools like profile galleries and compatibility criteria.
Key elements include secure messaging , geolocation tracking , and personalized profiles to streamline connections.
Advanced algorithms analyze preferences to suggest compatible matches, while account verification ensure safety .
https://globalwebs.biz/dating/appeal-of-taboo-in-adult-entertainment/
Leading apps offer premium subscriptions with exclusive benefits , such as unlimited swipes , alongside profile performance analytics.
Whether seeking casual chats , these sites cater to diverse needs , leveraging community-driven networks to optimize success rates .
Биорезервуар — это подземная ёмкость , предназначенная для сбора и частичной переработки отходов.
Принцип действия заключается в том, что жидкость из дома направляется в ёмкость, где твердые частицы оседают , а жиры и масла собираются в верхнем слое.
Основные элементы: входная труба, бетонный резервуар, соединительный канал и почвенный фильтр для доочистки стоков.
https://bazarweb.ru/forum.php/?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=40153
Плюсы использования: экономичность, минимальное обслуживание и безопасность для окружающей среды при соблюдении норм.
Критично важно контролировать объём стоков, иначе неотделённые примеси попадут в грунт, вызывая загрязнение.
Типы конструкций: бетонные блоки, пластиковые ёмкости и композитные баки для разных условий монтажа .
Биорезервуар — это подземная ёмкость , предназначенная для сбора и частичной переработки отходов.
Принцип действия заключается в том, что жидкость из дома поступает в бак , где формируется слой ила, а жиры и масла всплывают наверх .
Основные элементы: входная труба, бетонный резервуар, соединительный канал и почвенный фильтр для доочистки стоков.
https://bazarweb.ru/forum.php/?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=40153
Плюсы использования: низкие затраты , долговечность и безопасность для окружающей среды при соблюдении норм.
Критично важно контролировать объём стоков, иначе частично очищенная вода попадут в грунт, вызывая загрязнение.
Материалы изготовления: бетонные блоки, пластиковые ёмкости и стекловолоконные модули для индивидуальных нужд.
lista de precios del cosmet?logo lista de precios del cosmet?logo .
Осознанное участие в азартных развлечениях — это принципы, направленный на предотвращение рисков, включая ограничение доступа несовершеннолетним .
Сервисы должны внедрять инструменты саморегуляции , такие как лимиты на депозиты , чтобы минимизировать зависимость .
Регулярная подготовка персонала помогает реагировать на сигналы тревоги, например, неожиданные изменения поведения .
https://sacramentolife.ru
Предоставляются ресурсы горячие линии , где можно получить помощь при проблемах с контролем .
Соблюдение стандартов включает проверку возрастных данных для предотвращения мошенничества .
Задача индустрии создать условия для ответственного досуга, где удовольствие сочетается с вредом для финансов .
Нужно собрать информацию о человеке ? Этот бот предоставит детальный отчет мгновенно.
Используйте уникальные алгоритмы для поиска публичных записей в открытых источниках.
Узнайте контактные данные или активность через систему мониторинга с гарантией точности .
глаз бога тг
Система функционирует в рамках закона , обрабатывая открытые данные .
Закажите расширенный отчет с геолокационными метками и списком связей.
Попробуйте надежному помощнику для digital-расследований — результаты вас удивят !
Дом Patek Philippe — это вершина часового искусства , где соединяются точность и художественная отделка.
Основанная в 1839 году компания славится ручной сборкой каждого изделия, требующей сотен часов .
Изобретения, включая ключевой механизм 1842 года , сделали бренд как новатора в индустрии.
Часы Patek Philippe обзор
Лимитированные серии демонстрируют вечные календари и декоративные элементы, подчеркивая статус .
Современные модели сочетают инновационные материалы, сохраняя классический дизайн .
Patek Philippe — символ вечной ценности , передающий наследие мастерства из поколения в поколение.
The insights provided by Brians club empower members to make informed decisions, leading to improved financial health.
Be rewarded for every click—join our affiliate program today! https://shorturl.fm/gPPQx
Patek Philippe — это pinnacle часового искусства , где соединяются точность и эстетика .
Основанная в 1839 году компания славится ручной сборкой каждого изделия, требующей многолетнего опыта.
Изобретения, включая ключевой механизм 1842 года , укрепили репутацию как новатора в индустрии.
наручные часы Патек Филипп фото
Лимитированные серии демонстрируют вечные календари и декоративные элементы, подчеркивая статус .
Текущие линейки сочетают инновационные материалы, сохраняя классический дизайн .
Это не просто часы — символ семейных традиций, передающий инженерную элегантность из поколения в поколение.
При выборе компании для квартирного переезда важно учитывать её лицензирование и опыт работы .
Изучите отзывы клиентов или рейтинги в интернете, чтобы оценить надёжность исполнителя.
Сравните цены , учитывая расстояние перевозки , сезонность и услуги упаковки.
https://www.samuisecondhome.com/forum/messages/forum1/topic2527/message3235/?result=new#message3235
Убедитесь наличия страхового полиса и уточните условия компенсации в случае повреждений.
Оцените уровень сервиса: дружелюбие сотрудников , гибкость графика .
Узнайте, используются ли специализированные грузчики и защитные технологии для безопасной транспортировки.
Promote our products—get paid for every sale you generate! https://shorturl.fm/8mxn8
Безопасный досуг — это снижение негативных последствий для участников, включая установление лимитов .
Важно планировать бюджет , чтобы не превышать допустимые расходы .
Используйте инструменты временной блокировки, чтобы приостановить активность в случае потери контроля.
Поддержка игроков включает горячие линии , где можно обсудить проблемы при проявлениях зависимости .
Играйте с друзьями , чтобы сохранять социальный контакт , ведь семейная атмосфера делают процесс безопасным.
casino
Изучайте правила платформы: сертификация оператора гарантирует защиту данных.
Осознанное участие — это снижение негативных последствий для игроков , включая установление лимитов .
Важно планировать бюджет , чтобы не превышать допустимые расходы .
Используйте инструменты временной блокировки, чтобы приостановить активность в случае чрезмерного увлечения .
Доступ к ресурсам включает консультации специалистов, где можно получить помощь при трудных ситуациях.
Играйте с друзьями , чтобы избегать изоляции, ведь семейная атмосфера делают процесс безопасным.
слот играть
Изучайте правила платформы: сертификация оператора гарантирует защиту данных.
Unlock exclusive rewards with every referral—apply to our affiliate program now! https://shorturl.fm/mUvtF
Partner with us and enjoy recurring commission payouts! https://shorturl.fm/hL0Yw
Refer friends, collect commissions—sign up now! https://shorturl.fm/dKZXV
Unlock exclusive rewards with every referral—enroll now! https://shorturl.fm/CURpB
Apply now and receive dedicated support for affiliates! https://shorturl.fm/cgMsr
Become our partner and turn clicks into cash—join the affiliate program today! https://shorturl.fm/wA02I
Перевозка товаров из КНР в РФ проводится через железнодорожные маршруты , с проверкой документов на в портах назначения.
Импортные сборы составляют от 5% до 30% , в зависимости от типа продукции — например, готовые изделия облагаются по максимальной ставке.
Для ускорения процесса используют альтернативные схемы, которые быстрее стандартных методов , но связаны с повышенными рисками .
OEM и ODM производство в Китае
В случае легальных перевозок требуется предоставить паспорта на товар и акты инспекции, особенно для сложных грузов .
Сроки доставки варьируются от одной недели до месяца, в зависимости от удалённости пункта назначения и загруженности контрольных пунктов.
Общая цена включает транспортные расходы, налоги и комиссии за оформление , что требует предварительного расчёта .
Share our products and watch your earnings grow—join our affiliate program! https://shorturl.fm/NkZEy
Start earning passive income—join our affiliate network today! https://shorturl.fm/SZl4M
Drive sales, earn commissions—apply now! https://shorturl.fm/bUQ0R
Start earning passive income—become our affiliate partner! https://shorturl.fm/nO6gh
Start earning passive income—become our affiliate partner! https://shorturl.fm/lOJV1
Join forces with us and profit from every click! https://shorturl.fm/BAh0J
Back then, I believed healthcare worked like clockwork. Doctors give you pills — nobody asks “what’s really happening?”. It felt safe. Eventually, it didn’t feel right.
At some point, I couldn’t focus. I blamed my job. And deep down, I knew something was off. I read the label. No one had warned me about interactions.
It finally hit me: health isn’t passive. The reaction isn’t always immediate, but it’s real. Reactions aren’t always dramatic — just persistent. And still we keep swallowing.
Now I don’t shrug things off. Not because I’m paranoid. I track everything. But I don’t care. This is survival, not stubbornness. The lesson that stuck most, it would be amoxil for dogs.
I used to think healthcare worked like clockwork. The system moves you along — you nod, take it, and move on. It felt safe. Eventually, it didn’t feel right.
Then the strange fog. I blamed stress. And deep down, I knew something was off. I watched people talk about their own experiences. No one had warned me about interactions.
That’s when I understood: health isn’t passive. Two people can take the same pill and walk away with different futures. Side effects hide. And still we keep swallowing.
Now I don’t shrug things off. Not because I’m paranoid. I challenge assumptions. But I don’t care. I’m not trying to be difficult — I’m trying to stay alive. And if I had to name the one thing, it would be cialis dosage.
Share your link and rake in rewards—join our affiliate team! https://shorturl.fm/8N5Rs
Rolex Submariner, выпущенная в 1954 году стала первыми водонепроницаемыми часами , выдерживающими глубину до 330 футов.
Часы оснащены вращающийся безель , Triplock-заводную головку, обеспечивающие герметичность даже в экстремальных условиях.
Дизайн включает хромалитовый циферблат , стальной корпус Oystersteel, подчеркивающие функциональность .
Наручные часы Rolex Submariner обзор
Автоподзавод до 70 часов сочетается с автоматическим калибром , что делает их надежным спутником для активного образа жизни.
С момента запуска Submariner стал эталоном дайверских часов , оцениваемым как эксперты.
Rolex Submariner, представленная в 1953 году стала первой дайверской моделью, выдерживающими глубину до 100 метров .
Часы оснащены 60-минутную шкалу, Triplock-заводную головку, обеспечивающие герметичность даже в экстремальных условиях.
Дизайн включает хромалитовый циферблат , стальной корпус Oystersteel, подчеркивающие функциональность .
rolex-submariner-shop.ru
Механизм с запасом хода до 70 часов сочетается с перманентной работой, что делает их надежным спутником для активного образа жизни.
С момента запуска Submariner стал символом часового искусства, оцениваемым как коллекционеры .
Join forces with us and profit from every click! https://shorturl.fm/0osRB
Drive sales and watch your affiliate earnings soar! https://shorturl.fm/uCRFi
Apply now and receive dedicated support for affiliates! https://shorturl.fm/5wxvO
ozempic france sans ordonnance: PharmaDirecte – testostГ©rone homme pharmacie sans ordonnance
Sign up now and access top-converting affiliate offers! https://shorturl.fm/FWnyv
zopiclone sans ordonnance pharmacie: tramadol sans ordonnance en pharmacie – fluocaril bi-fluorГ© 2500 ppm
Share our products, earn up to 40% per sale—apply today! https://shorturl.fm/sc75F
врачи стоматологии врачи стоматологии .
Drive sales, earn big—enroll in our affiliate program! https://shorturl.fm/lHQvn
багги полный привод багги полный привод .
pharma apotheek pharmacy nederlands holandia apteka internetowa
shampoo apotek: hvordan skrive fullmakt apotek – borsyre apotek
https://zorgpakket.com/# online pharmacy nl
votter apotek: Trygg Med – apotek ГҐpent pГҐ sГёndag
https://zorgpakket.shop/# apteka amsterdam
https://snabbapoteket.shop/# abort piller apotek
levere medisiner til apotek: Trygg Med – apotek ГҐpen nГҐ
retinol apotek: SnabbApoteket – derma roller apotek
kaliumpermanganat apotek Snabb Apoteket biligt
http://zorgpakket.com/# online medicijnen bestellen apotheek
febertermometer apotek: Snabb Apoteket – apotek kondomer
http://zorgpakket.com/# medicijnen apotheek
beställ hem medicin Snabb Apoteket laxative apotek
https://zorgpakket.shop/# mijn medicijn.nl
calendula salve apotek: kvisekrem apotek – dusjsГҐpe apotek
Tap into unlimited earnings—sign up for our affiliate program! https://shorturl.fm/UjOu8
rГ¶dcederolja apotek: SnabbApoteket – sverige hopp apotek
pillen bestellen: MedicijnPunt – europese apotheek
hundekrage apotek Trygg Med testosteron tilskudd reseptfritt apotek
http://tryggmed.com/# klotrimazol apotek
http://tryggmed.com/# pottaske apotek
Earn big by sharing our offers—become an affiliate today! https://shorturl.fm/nX1eK
salt vann apotek [url=https://tryggmed.com/#]apotek sverige nettbutikk[/url] sГёndagsГҐpen apotek
http://snabbapoteket.com/# kräkpåse apotek
https://snabbapoteket.shop/# billigt
apotheke: Medicijn Punt – medicijn recept
destillerat vatten kГ¶pa apotek: Snabb Apoteket – apotek mina recept
medicijn online medicatie kopen apotheek producten
bГ¤sta graviditetstest: apotek hem – svinkoppor bilder barn
apotheek producten: beste online apotheek – netherlands pharmacy online
online medicijnen bestellen apotheek pharmacy online netherlands mijn medicijnkosten
http://zorgpakket.com/# internetapotheek nederland
https://snabbapoteket.shop/# kan man röka te
https://tryggmed.shop/# kompresjon arm apotek
gipssko apotek: TryggMed – samtykkeskjema apotek
viktminskning apotek: Snabb Apoteket – sluta med vГ¤lling
apotek online: TryggMed – sverige apotek
gravid app frukt: sГҐrpulver apotek – lansett apotek
apotek fГёflekk kjГёnnssykdommer test apotek apotek koronatest
https://zorgpakket.shop/# online apotheek recept
apotek handsprit Snabb Apoteket apotek omeprazol
https://snabbapoteket.com/# apotek leverans samma dag
http://tryggmed.com/# levere medisiner til apotek
Grow your income stream—apply to our affiliate program today! https://shorturl.fm/1rHRC
europese apotheek: Medicijn Punt – medicijnen bestellen bij apotheek
apotek handsprit: foglossningsbГ¤lte apotek – stetoskop kГ¶pa
hГҐrnett apotek: Trygg Med – nГ¦ringsdrikke apotek
apotheek apotheek: Medicijn Punt – europese apotheek
medicatie online bestellen online apotheken apotheek online
medicatie apotheker online apotheek nederland met recept bestellen medicijnen
https://zorgpakket.com/# apotheek recept
https://zorgpakket.shop/# online medicatie bestellen
kreatin apotek: Trygg Med – dusjolje apotek
https://snabbapoteket.shop/# apotej
Модель Submariner от выпущенная в 1954 году стала первыми водонепроницаемыми часами , выдерживающими глубину до 330 футов.
Часы оснащены вращающийся безель , Oyster-корпус , обеспечивающие безопасность даже в экстремальных условиях.
Дизайн включает светящиеся маркеры, черный керамический безель , подчеркивающие спортивный стиль.
Часы Rolex Submariner фото
Механизм с запасом хода до 70 часов сочетается с перманентной работой, что делает их идеальным выбором для активного образа жизни.
За десятилетия Submariner стал эталоном дайверских часов , оцениваемым как эксперты.
flukonazol apotek: Trygg Med – nattlysolje apotek
jobb pГҐ apotek: setting spray apotek – apotek svamp
apotek katt: Snabb Apoteket – abort tablett apotek
mexican pharmacy for americans MediMexicoRx get viagra without prescription from mexico
http://indiamedshub.com/# best india pharmacy
http://medimexicorx.com/# MediMexicoRx
http://indiamedshub.com/# mail order pharmacy india
Online medicine home delivery buy prescription drugs from india IndiaMedsHub
buy meds from mexican pharmacy: order from mexican pharmacy online – amoxicillin mexico online pharmacy
Earn big by sharing our offers—become an affiliate today! https://shorturl.fm/vicBm
ExpressCareRx: ExpressCareRx – what pharmacy sells azithromycin
Посетите наше онлайн казино в Нигерии, где вы найдете захватывающие online casino и шанс выиграть реальные деньги!
Casinos are renowned for providing a vibrant atmosphere filled with entertainment. Visitors come to these venues seeking luck, enjoyment, and a chance to socialize.
The range of games available at casinos is extensive and varied. From classic card games like poker and blackjack to modern slot machines, there is something for everyone.
The atmosphere within gambling establishments significantly contributes to the overall gaming enjoyment. The combination of bright lights, upbeat music, and a vibrant crowd creates an unmatched experience.
Casinos frequently host eateries, bars, and show options, transforming them into a comprehensive entertainment destination. This integration of gaming and leisure activities appeals to a broad audience.
prx online pharmacy target pharmacy ventolin ExpressCareRx
http://indiamedshub.com/# reputable indian online pharmacy
https://indiamedshub.com/# best online pharmacy india
buy neurontin in mexico: trusted mexico pharmacy with US shipping – trusted mexico pharmacy with US shipping
Maximize your earnings with top-tier offers—apply now! https://shorturl.fm/FHIEP
ExpressCareRx australia pharmacy viagra ExpressCareRx
get viagra without prescription from mexico: buy meds from mexican pharmacy – MediMexicoRx
https://medimexicorx.com/# MediMexicoRx
ExpressCareRx: levitra pharmacy rx one – lloyd center pharmacy domperidone
ExpressCareRx: online pharmacy legit – lorazepam indian pharmacy
http://indiamedshub.com/# best india pharmacy
https://expresscarerx.org/# ExpressCareRx
https://expresscarerx.org/# u s pharmacy online
india pharmacy IndiaMedsHub top online pharmacy india
MediMexicoRx MediMexicoRx buy propecia mexico
viagra pills from mexico: legit mexican pharmacy for hair loss pills – generic drugs mexican pharmacy
rite aid pharmacy viagra prices: online pharmacy cialis reviews – silkroad online pharmacy review
https://indiamedshub.shop/# best india pharmacy
https://indiamedshub.com/# IndiaMedsHub
get viagra without prescription from mexico MediMexicoRx buy from mexico pharmacy
частные дома под ключ сколько стоят stroitelstvo-doma-1.ru .
Online medicine home delivery india online pharmacy Online medicine order
pharmacy artane castle: online pharmacy services viagra – vipps certified pharmacy viagra
Turn your network into income—apply to our affiliate program! https://shorturl.fm/mzuup
https://indiamedshub.shop/# IndiaMedsHub
ExpressCareRx: ExpressCareRx – ExpressCareRx
online mexico pharmacy USA: order from mexican pharmacy online – MediMexicoRx
french pharmacy products online: ExpressCareRx – watson pharmacy viagra
https://medimexicorx.com/# MediMexicoRx
https://expresscarerx.org/# ExpressCareRx
Посетите наше онлайн казино в Нигерии, где вы найдете захватывающие casino games и шанс выиграть реальные деньги!
Casinos are renowned for providing a vibrant atmosphere filled with entertainment. Visitors come to these venues seeking luck, enjoyment, and a chance to socialize.
A wide selection of games is available at gambling establishments, appealing to diverse tastes. Whether it’s traditional games such as poker and blackjack or contemporary slot machines, there’s an option for every player.
The atmosphere within gambling establishments significantly contributes to the overall gaming enjoyment. The combination of bright lights, upbeat music, and a vibrant crowd creates an unmatched experience.
Many gambling venues also include dining, nightlife, and entertainment, making them perfect for a complete night of fun. This integration of gaming and leisure activities appeals to a broad audience.
https://indiamedshub.com/# IndiaMedsHub
MediMexicoRx MediMexicoRx low cost mexico pharmacy online
med rx pharmacy ExpressCareRx lisinopril online pharmacy
synthroid target pharmacy: online pharmacy neurontin – us pharmacy online
MediMexicoRx: MediMexicoRx – MediMexicoRx
best online pharmacy to buy ambien: co-op pharmacy viagra – ExpressCareRx
buy prescription drugs from india: online pharmacy india – best india pharmacy
https://expresscarerx.org/# publix pharmacy bactrim
http://indiamedshub.com/# indian pharmacy paypal
Share our products and watch your earnings grow—join our affiliate program! https://shorturl.fm/yZvkE
Promote our brand, reap the rewards—apply to our affiliate program today! https://shorturl.fm/wlZSn
rx pharmacy logo ExpressCareRx ExpressCareRx
online mexico pharmacy USA MediMexicoRx п»їmexican pharmacy
ExpressCareRx: top online pharmacy 247 – unicare pharmacy artane castle shopping centre
indian pharmacy online: cheapest online pharmacy india – buy prescription drugs from india
IndiaMedsHub: india pharmacy mail order – IndiaMedsHub
https://indiamedshub.com/# online shopping pharmacy india
https://medimexicorx.shop/# mexico drug stores pharmacies
MediMexicoRx: buy propecia mexico – prescription drugs mexico pharmacy
http://indiamedshub.com/# top 10 online pharmacy in india
ремонт новых квартир под ключ стоимость ремонт новых квартир под ключ стоимость .
Join our affiliate community and maximize your profits—sign up now! https://shorturl.fm/E9FKA
http://expresscarerx.org/# xalatan pharmacy
isotretinoin pharmacy price: ExpressCareRx – pharmacy online australia free shipping
IndiaMedsHub top online pharmacy india indian pharmacy online
best rx online pharmacy: ExpressCareRx – ExpressCareRx
https://medimexicorx.com/# MediMexicoRx
http://medimexicorx.com/# MediMexicoRx
ExpressCareRx: erectile dysfunction causes – ExpressCareRx
IndiaMedsHub: indian pharmacy online – top online pharmacy india
Promote our products—get paid for every sale you generate! https://shorturl.fm/agBe7
MediMexicoRx buy kamagra oral jelly mexico modafinil mexico online
http://indiamedshub.com/# reputable indian pharmacies
http://indiamedshub.com/# IndiaMedsHub
IndiaMedsHub: Online medicine home delivery – india pharmacy
legit mexican pharmacy without prescription MediMexicoRx MediMexicoRx
IndiaMedsHub: top 10 online pharmacy in india – mail order pharmacy india
http://expresscarerx.org/# generic levitra online pharmacy
indianpharmacy com: top 10 pharmacies in india – indian pharmacy paypal
top 10 online pharmacy in india: pharmacy website india – п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india
https://shorturl.fm/y5qJN
https://medimexicorx.shop/# mexican pharmaceuticals online
online pharmacy mexico ExpressCareRx ExpressCareRx
https://medimexicorx.shop/# MediMexicoRx
https://indiamedshub.com/# india pharmacy
top 10 online pharmacy in india online shopping pharmacy india reputable indian online pharmacy
order azithromycin mexico: generic drugs mexican pharmacy – MediMexicoRx
levitra us pharmacy: legit online pharmacy provigil – pharmacy rx coupons
https://shorturl.fm/Gvjhh
viagra in dubai pharmacy: ExpressCareRx – uk pharmacy online
remedy rx pharmacy ExpressCareRx ExpressCareRx
https://lexapro.pro/# buy cheap lexapro online
https://lexapro.pro/# Lexapro for depression online
Propecia for hair loss online: Finasteride From Canada – cheap Propecia Canada
buy Zoloft online: generic sertraline – Zoloft Company
https://shorturl.fm/g5SoY
Эта игра сочетает в себе ролевую игру с элементами иммерсивного симулятора в альтернативном СССР 1955 года.
Действие разворачивается в футуристическом исследовательском центре, где вас ждут роботизированные противники .
Особенности игры восстановление врагов через длительный период .
gta san andreas netflix скачать
Эстетика сочетает советский ретро-футуризм .
Рекомендуется сосредоточиться на прокачке одного навыка для успешного прохождения.
Системные требования поддерживают Linux через Proton .
https://isotretinoinfromcanada.shop/# USA-safe Accutane sourcing
[url=https://vedunokschool.ru/]Зерновой кофе в интернет-магазине[/url] — настоящий кофе начинается с правильных зерен, а не растворимого порошка. В интернет-магазине вы можете купить любимые сорта и открыть новые вкусы — без спешки, без очередей, с удобной доставкой. Арабика, робуста или купаж — каждый сорт раскрывается по-своему. Вы можете наслаждаться бархатистым вкусом, не выходя из дома. Интернет-магазин предлагает широкий выбор зёрен — от повседневных до премиальных сортов. Начинайте утро правильно — выберите то, что по-настоящему радует.
https://vedunokschool.ru/
generic Cialis from India cheap Cialis Canada buy Cialis online cheap
generic sertraline: sertraline online – purchase generic Zoloft online discreetly
cheap Propecia Canada Propecia for hair loss online generic Finasteride without prescription
cheap Propecia Canada: Finasteride From Canada – generic Finasteride without prescription
cheap Cialis Canada: tadalafil canadian pharmacy online – Cialis without prescription
[url=https://indian-microfinance-future.com/]fp markets cashback[/url] is a valuable opportunity for traders. Regardless of your strategy or volume, receiving cashback means increasing your bottom line without extra effort. There’s no change in trading conditions — just extra money in your pocket.
It’s a smart reward system built into your regular trading activity. It’s a passive benefit that rewards active trading.
Many traders choose FP Markets not just for tight spreads and reliable execution, but also for the added bonus of cashback. Over time, cashback can significantly reduce your overall trading costs — especially if you trade actively.
Don’t leave potential money on the table — activate your fp markets cashback and start benefiting today.
https://indian-microfinance-future.com/
http://tadalafilfromindia.com/# Tadalafil From India
https://lexapro.pro/# Lexapro for depression online
https://isotretinoinfromcanada.shop/# Accutane for sale
Accutane for sale isotretinoin online purchase generic Accutane online discreetly
cheap Zoloft: generic sertraline – buy Zoloft online without prescription USA
purchase generic Zoloft online discreetly: purchase generic Zoloft online discreetly – generic sertraline
lexapro medication Lexapro for depression online buy generic lexapro online
USA-safe Accutane sourcing: USA-safe Accutane sourcing – USA-safe Accutane sourcing
https://finasteridefromcanada.shop/# Propecia for hair loss online
http://tadalafilfromindia.com/# Cialis without prescription
order isotretinoin from Canada to US: generic isotretinoin – Accutane for sale
buy Cialis online cheap Cialis without prescription tadalafil 100mg
Zoloft online pharmacy USA: Zoloft for sale – generic sertraline
https://tadalafilfromindia.com/# generic Cialis from India
Lexapro for depression online: Lexapro for depression online – Lexapro for depression online
Cialis without prescription: Tadalafil From India – generic Cialis from India
Zoloft for sale buy Zoloft online Zoloft online pharmacy USA
https://zoloft.company/# Zoloft online pharmacy USA
generic Cialis from India buy Cialis online cheap tadalafil online no rx
Хотите собрать данные о пользователе? Этот бот предоставит полный профиль мгновенно.
Используйте продвинутые инструменты для анализа цифровых следов в открытых источниках.
Выясните контактные данные или интересы через систему мониторинга с гарантией точности .
глаз бога найти телефон
Система функционирует с соблюдением GDPR, используя только общедоступную информацию.
Закажите детализированную выжимку с историей аккаунтов и графиками активности .
Попробуйте проверенному решению для исследований — точность гарантирована!
cheap Accutane: generic isotretinoin – buy Accutane online
tadalafil online no rx: Tadalafil From India – generic Cialis from India
Tadalafil From India: Cialis without prescription – generic Cialis from India
Lexapro for depression online Lexapro for depression online Lexapro for depression online
https://isotretinoinfromcanada.com/# isotretinoin online
https://finasteridefromcanada.shop/# propecia without prescription
Zoloft online pharmacy USA: Zoloft online pharmacy USA – Zoloft online pharmacy USA
cheap Propecia Canada Propecia for hair loss online cheap Propecia Canada
Download the indibet apk and take your gaming experience mobile, with sports betting and casino games available at your fingertips. En conclusión, si deseas convertirte en un experto en apuestas de fútbol sala, Yajuego es la plataforma ideal para ti. Con su amplia oferta de eventos y mercados, así como sus estadísticas en tiempo real y consejos de expertos, tendrás todas las herramientas necesarias para tomar decisiones informadas y aumentar tus posibilidades de éxito. Además, su interfaz intuitiva y su atención al cliente de calidad hacen que la experiencia de apostar sea fácil y emocionante. ¡No esperes más y comienza a disfrutar de la emoción de las apuestas de fútbol sala con Yajuego! Roobet’s Mission Uncrossable is designed with safety and trustworthiness in mind. As part of Roobet’s platform, the game is provably fair, meaning players can independently verify the fairness of each game outcome, just as you can with any Roobet game download. Roobet uses blockchain technology to ensure transparency and security in all transactions, giving players confidence that their bets and winnings are handled securely. Additionally, Roobet’s reputation as a trusted crypto casino adds an extra layer of assurance for players, making Mission Uncrossable game for money a safe and reliable gaming experience.
https://bevelsandedges.com/2025/07/12/mission-uncrossable-een-diepgaande-review-van-dit-unieke-online-casino-spel/
One of the major assets of Chicken Cross lies in its simplicity. The game’s rules are easy to understand, so new players can get to grips with them quickly. Visit minimum stake is set at €0.20, while the maximum stake can be as high as €100. This allows players to participate according to their budgetary preferences and risk tolerance. Whether you are new to the genre or have already made dozens of bets on daring digital chickens, Chickengambling offers everything you need to succeed. This platform is the heartbeat of every new release, strategy shift, and crypto promotion – and it’s defining the future of chicken gambling in a way that keeps players ahead of the curve. Million Games is thrilled to announce the release of Chicken X, a high-risk, high-reward game that brings an exciting gambling twist to the classic arcade-style road-crossing genre. With a maximum payout factor of 10,000x, Chicken X challenges players to navigate the daring chicken across a busy road while strategically deciding when to cash out or push their luck for even bigger rewards.
https://zoloft.company/# buy Zoloft online
https://shorturl.fm/xCd03
isotretinoin online: cheap Accutane – generic isotretinoin
Lexapro for depression online: where can i buy generic lexapro – Lexapro for depression online
buy Zoloft online without prescription USA: buy Zoloft online without prescription USA – sertraline online
generic isotretinoin USA-safe Accutane sourcing generic isotretinoin
https://zoloft.company/# buy Zoloft online without prescription USA
https://zoloft.company/# buy Zoloft online without prescription USA
https://zoloft.company/# Zoloft online pharmacy USA
Finasteride From Canada: Propecia for hair loss online – generic Finasteride without prescription
Accutane for sale Isotretinoin From Canada isotretinoin online
Accutane for sale: USA-safe Accutane sourcing – cheap Accutane
cheap Zoloft: purchase generic Zoloft online discreetly – Zoloft Company
USA-safe Accutane sourcing: isotretinoin online – order isotretinoin from Canada to US
https://finasteridefromcanada.shop/# generic Finasteride without prescription
Zoloft for sale Zoloft Company buy Zoloft online without prescription USA
https://shorturl.fm/nNVRb
Tadalafil From India: Cialis without prescription – generic Cialis from India
Accutane for sale: USA-safe Accutane sourcing – generic isotretinoin
https://lexapro.pro/# Lexapro for depression online
generic isotretinoin isotretinoin online USA-safe Accutane sourcing
generic brand for lexapro: lexapro generic brand name – buy lexapro australia
cheapest price for generic lexapro: compare lexapro prices – lexapro 10 mg price in india
https://finasteridefromcanada.com/# Finasteride From Canada
https://zoloft.company/# cheap Zoloft
Lexapro for depression online Lexapro for depression online medication lexapro 10 mg
https://finasteridefromcanada.shop/# Finasteride From Canada
generic Finasteride without prescription: Propecia for hair loss online – buying propecia
https://zoloft.company/# cheap Zoloft
https://finasteridefromcanada.shop/# Finasteride From Canada
buy Accutane online Accutane for sale Isotretinoin From Canada
http://isotretinoinfromcanada.com/# purchase generic Accutane online discreetly
purchase generic Accutane online discreetly: generic isotretinoin – generic isotretinoin
https://zoloft.company/# Zoloft Company
generic isotretinoin USA-safe Accutane sourcing isotretinoin online
Cialis without prescription: generic tadalafil united states – generic Cialis from India
Cialis without prescription: tadalafil online no rx – Cialis without prescription
generic sertraline purchase generic Zoloft online discreetly Zoloft for sale
https://finasteridefromcanada.shop/# cheap Propecia Canada
https://tadalafilfromindia.shop/# generic Cialis from India
http://tadalafilfromindia.com/# cheap Cialis Canada
[url=https://newmexicojeepgroup.com/]בדיקת רכב לפי מספר רישוי[/url] — מהירות, דיוק ונגישות לפני קנייה – חשוב לבדוק! באמצעות השירות תוכלו לגלות מידע קריטי על הרכב בקלות ובמהירות. השירות מאפשר לכם לבדוק: — בעלות נוכחית וקודמת, — מצב רישוי וביטוחים, — מספר ידיים, — בדיקות טסט אחרונות ומועדי תחזוקה, — מידע טכני כמו נפח מנוע, סוג דלק, דגם ויצרן. השירות מתאים לכל מי שמעוניין לבצע רכישה חכמה וזהירה. השימוש במערכת הוא נגיש מכל מכשיר, ללא צורך ברישום או תשלום מראש (במקרה של שירותים בסיסיים). אל תקנו רכב לפני שבודקים אותו כמו שצריך. בדקו פרטי רכב בלחיצת כפתור — ותקבלו החלטה נכונה ומבוססת.
https://newmexicojeepgroup.com/
buy Zoloft online: purchase generic Zoloft online discreetly – buy Zoloft online
purchase generic Accutane online discreetly: isotretinoin online – Isotretinoin From Canada
lexapro cost uk: Lexapro for depression online – Lexapro for depression online
Propecia for hair loss online cheap Propecia Canada cheap Propecia Canada
where can i buy lexapro online: how much is generic lexapro – prescription price for lexapro
order isotretinoin from Canada to US purchase generic Accutane online discreetly buy Accutane online
https://shorturl.fm/WNbXF
https://tadalafilfromindia.com/# Tadalafil From India
Lexapro for depression online: Lexapro for depression online – Lexapro for depression online
https://shorturl.fm/raXlk
Zoloft online pharmacy USA: buy Zoloft online without prescription USA – buy Zoloft online without prescription USA
Lexapro for depression online Lexapro for depression online lexapro 0.5 mg
https://lexapro.pro/# lexapro 0.5 mg
Finasteride From Canada propecia pills cheap Propecia Canada
https://lexapro.pro/# Lexapro for depression online
https://lexapro.pro/# Lexapro for depression online
http://finasteridefromcanada.com/# cost of cheap propecia without rx
займы без карты займы без карты .
lexapro 5mg: buy lexapro no prescription – compare lexapro prices
where can i buy generic lexapro: lexapro 10 mg price in india – Lexapro for depression online
tadalafil best price tadalafil online without prescription Tadalafil From India
пополняемый депозит пополняемый депозит .
Tadalafil From India tadalafil online no rx Cialis without prescription
https://shorturl.fm/IgRjt
tadalafil online no rx: cheap Cialis Canada – generic Cialis from India
cheap Accutane: cheap Accutane – isotretinoin online
https://shorturl.fm/YSicD
cheap Cialis Canada: buy Cialis online cheap – Tadalafil From India
purchase generic Zoloft online discreetly: Zoloft online pharmacy USA – generic sertraline
generic lexapro 20 mg cost Lexapro for depression online Lexapro for depression online
isotretinoin online Accutane for sale USA-safe Accutane sourcing
Программы для учёта рабочего времени помогают компаниям , упрощая контроль времени работы.
Инновационные инструменты обеспечивают детальный учёт онлайн, минимизируя ошибки при подсчёте.
Совместимость с ERP-решениями упрощает подготовку аналитики и управление графиками, отпусками .
мониторинг персонала
Упрощение задач экономит время менеджеров , позволяя сосредоточиться на развитии команды.
Простое управление обеспечивает лёгкость работы как для администраторов, сокращая период адаптации.
Надёжные решения предоставляют детальную аналитику , помогая принимать решений на основе данных.
Решения по отслеживанию времени поддерживают бизнес-процессы, упрощая контроль времени работы.
Инновационные инструменты предоставляют детальный учёт в режиме реального времени , минимизируя ошибки в расчётах .
Совместимость с кадровыми системами упрощает формирование отчётов а также контроль больничными, сверхурочными.
эффективный hr
Упрощение задач экономит время HR-отделов, позволяя сосредоточиться на стратегических целях .
Интуитивно понятный интерфейс гарантирует удобство использования как для администраторов, сокращая период адаптации.
Надёжные решения генерируют отчёты в реальном времени, способствуя принятию решений на основе данных.
https://isotretinoinfromcanada.shop/# Accutane for sale
Lexapro for depression online: where can you buy lexapro – Lexapro for depression online
https://shorturl.fm/o6Pa2
purchase generic Accutane online discreetly: generic isotretinoin – isotretinoin online
generic Cialis from India: generic Cialis from India – Cialis without prescription
https://isotretinoinfromcanada.com/# Isotretinoin From Canada
Zoloft Company: Zoloft Company – Zoloft Company
Accutane for sale cheap Accutane generic isotretinoin
https://shorturl.fm/iYFy2
Lexapro for depression online Lexapro for depression online lexapro online prescription
cheap Accutane: order isotretinoin from Canada to US – USA-safe Accutane sourcing
tadalafil online india: Cialis without prescription – buy Cialis online cheap
purchase generic Accutane online discreetly: cheap Accutane – Accutane for sale
generic Finasteride without prescription: generic Finasteride without prescription – Propecia for hair loss online
Tadalafil From India tadalafil online no rx buy Cialis online cheap
cheap propecia without rx Propecia for hair loss online cheap Propecia Canada
generic Finasteride without prescription: Finasteride From Canada – generic Finasteride without prescription
cheap Cialis Canada: generic Cialis from India – online pharmacy tadalafil 20mg
https://shorturl.fm/j1yjN
order isotretinoin from Canada to US: generic isotretinoin – cheap Accutane
https://finasteridefromcanada.shop/# Finasteride From Canada
Lexapro for depression online: lexapro coupon – lexapro discount
https://tadalafilfromindia.com/# tadalafil tablets canada
Lexapro for depression online: lexapro 20 mg tablet – lexapro price comparison
Zoloft for sale: Zoloft Company – Zoloft for sale
https://shorturl.fm/uJHwA
https://shorturl.fm/Y60qa
https://shorturl.fm/8cvWH
https://shorturl.fm/q1EHH
USA-safe Accutane sourcing: order isotretinoin from Canada to US – USA-safe Accutane sourcing
sertraline online: Zoloft Company – cheap Zoloft
jointpain.top – high sugar and joint pain Os parceiros ag Mostbet também ajudam a fornecer transmissão ao vivo electronic probabilidades em speed real. Isto torna o site cependant envolvente do os quais muitos concorrentes. Pode encontrar facilmente partidas, jogos e opções de apostas. A aplicação móvel funciona sem problemas no ano de dispositivos Android electronic iOS. A Mostbet online oferece muitas caraterísticas que a tornam diferente sobre outras plataformas sobre apostas. O web-site abrange uma grande gama de desportos, incluindo futebol, basquetebol, ténis e críquete. jointpain.top – high sugar and joint pain Through the waxy windows, Retvenko could see the sky beginning to turn blue as dawn arrived. He heard the squawking of gulls searching the waves for breakfast. Maybe the liquor was muddling his mind.
https://zpu-journal.ru/forum/view_profile.php?UID=327730
Varför är gratissnurr och bonusar utan insättning så avgörande? De erbjuder ett fantastiskt sätt att prova Sugar Rush-sloten utan att riskera dina egna pengar, vilket gör dem till en nyckelfaktor i våra kasinoutvärderingar. Dessa bonusar tillåter spelare att få en riktig känsla av spelet, dess mekanik och de potentiella belöningarna utan några ekonomiska åtaganden. Vi förstår att dessa erbjudanden avsevärt kan förbättra din spelupplevelse, varför vi prioriterar casinon som ger generösa gratissnurr och bonusar utan insättning. Vårt mål är att se till att du kan njuta av Sugar Rush med mervärde och ökade chanser att vinna. Draw To Smash: Egg Puzzle Rebeca has been exploring the show floor at Gamescom 2022, and tells us all about it. Precis som originaltiteln Sugar Rush, är Sugar Rush Xmas fylld av olika symboler som lockar både ögat och spelglädjen.
https://shorturl.fm/nQl14
cheap Accutane: purchase generic Accutane online discreetly – buy Accutane online
https://lexapro.pro/# Lexapro for depression online
buy Cialis online cheap: buy tadalafil online no prescription – Cialis without prescription
http://isotretinoinfromcanada.com/# cheap Accutane
Zoloft Company: purchase generic Zoloft online discreetly – Zoloft Company
tadalafil tablets: cheap Cialis Canada – cheap Cialis Canada
Modafinil for ADHD and narcolepsy buy Modafinil online USA affordable Modafinil for cognitive enhancement
buy prednisone 10mg: order corticosteroids without prescription – anti-inflammatory steroids online
Relief Meds USA: order corticosteroids without prescription – cost of prednisone
gabapentin facial rash: NeuroRelief Rx – NeuroRelief Rx
order corticosteroids without prescription: prednisone tablets – compare prednisone prices
order amoxicillin without prescription [url=http://clearmedsdirect.com/#]low-cost antibiotics delivered in USA[/url] low-cost antibiotics delivered in USA
Relief Meds USA: ReliefMeds USA – order corticosteroids without prescription
https://shorturl.fm/tgPNr
https://neuroreliefrx.com/# NeuroRelief Rx
amoxicillin discount coupon: Clear Meds Direct – amoxicillin 500mg capsule cost
http://wakemedsrx.com/# prescription-free Modafinil alternatives
NeuroRelief Rx: NeuroRelief Rx – NeuroRelief Rx
low-cost antibiotics delivered in USA Clear Meds Direct low-cost antibiotics delivered in USA
Clomid Hub: Clomid Hub – where to get cheap clomid without a prescription
anti-inflammatory steroids online: ReliefMeds USA – prednisone tablets 2.5 mg
Relief Meds USA: order corticosteroids without prescription – Relief Meds USA
Modafinil for focus and productivity nootropic Modafinil shipped to USA affordable Modafinil for cognitive enhancement
ReliefMeds USA: order corticosteroids without prescription – anti-inflammatory steroids online
safe Provigil online delivery service: safe Provigil online delivery service – prescription-free Modafinil alternatives
safe Provigil online delivery service: smart drugs online US pharmacy – Modafinil for focus and productivity
order Provigil without prescription: affordable Modafinil for cognitive enhancement – Modafinil for ADHD and narcolepsy
ReliefMeds USA [url=http://reliefmedsusa.com/#]order corticosteroids without prescription[/url] prednisone best prices
where to buy Modafinil legally in the US: wakefulness medication online no Rx – Modafinil for ADHD and narcolepsy
https://clomidhubpharmacy.shop/# Clomid Hub Pharmacy
amoxicillin brand name where can i buy amoxicillin over the counter uk Clear Meds Direct
https://neuroreliefrx.com/# does gabapentin interact with ambien
get cheap clomid without insurance: Clomid Hub Pharmacy – where to buy generic clomid no prescription
order generic clomid prices: Clomid Hub – where can i buy cheap clomid online
affordable Modafinil for cognitive enhancement: Modafinil for ADHD and narcolepsy – Modafinil for ADHD and narcolepsy
low-cost antibiotics delivered in USA amoxicillin 50 mg tablets can you buy amoxicillin over the counter in canada
ReliefMeds USA: Relief Meds USA – anti-inflammatory steroids online
1250 mg prednisone: ReliefMeds USA – can you buy prednisone online uk
I once believed remedies as saviors, swallowing them eagerly whenever my body whispered warnings. But life taught me otherwise, revealing how these aids often numbed the symptoms, urging a profound introspection into our intricate dance with health. The shift was visceral, compelling me that respectful use of these tools honors our body’s wisdom, rather than eroding our natural strength.
During a stark health challenge, I chose reflection over reflex, exploring alternatives that harmonized natural rhythms with thoughtful aids. This revelation reshaped my world: wellness blooms holistically, where overdependence dulls our senses. It inspires me daily to advocate for caution, seeing medicine as an ally, not a master.
Reflecting on the essence, I now understand health tools should ignite our potential, without stealing the spotlight. The path unfolded revelations, inviting us to question our automatic responses for richer lives. It all comes down to one thing: kamagra oral jelly amazon
I once believed medications as saviors, reaching for them instinctively whenever ailments surfaced. Yet, as experiences piled up, revealing how such interventions merely veiled deeper issues, urging a profound introspection into our intricate dance with health. It stirred something primal, illuminating that conscious choices in medicine empowers our innate vitality, rather than diminishing it.
During a stark health challenge, I hesitated before the usual fix, uncovering hidden layers that wove lifestyle shifts into medical wisdom. This revelation reshaped my world: healing thrives in balance, blind trust weakens resilience. This journey fuels my passion to embrace a fuller perspective, viewing remedies as partners in the dance.
Reflecting on the essence, It became clear medical means ought to amplify our spirit, free from dominating our narrative. The path unfolded revelations, inviting us to question entrenched patterns for deeper connections. And if I had to sum it all up in one word: buy eriacta online without a prescription
where to get generic clomid without dr prescription can i get cheap clomid without insurance Clomid Hub
ReliefMeds USA: order corticosteroids without prescription – anti-inflammatory steroids online
where can i get cheap clomid for sale: where can i buy cheap clomid no prescription – can i order generic clomid without dr prescription
ReliefMeds USA: order corticosteroids without prescription – where can i get prednisone
anti-inflammatory steroids online: prednisone 80 mg daily – ReliefMeds USA
https://clomidhubpharmacy.shop/# Clomid Hub Pharmacy
generic amoxicillin online: ClearMeds Direct – low-cost antibiotics delivered in USA
order amoxicillin without prescription ClearMeds Direct order amoxicillin without prescription
https://clearmedsdirect.com/# amoxicillin for sale online
https://shorturl.fm/Y3hpU
where can i buy clomid without rx: Clomid Hub Pharmacy – can you buy clomid for sale
safe Provigil online delivery service: affordable Modafinil for cognitive enhancement – WakeMeds RX
gabapentin upper back pain: NeuroRelief Rx – NeuroRelief Rx
Clomid Hub Pharmacy where to get clomid order clomid price
low-cost antibiotics delivered in USA: low-cost antibiotics delivered in USA – ClearMeds Direct
NeuroRelief Rx NeuroRelief Rx NeuroRelief Rx
low-cost antibiotics delivered in USA: ClearMeds Direct – how to buy amoxicillin online
NeuroRelief Rx: gabapentin gravid – gabapentin feels like weed
NeuroRelief Rx: gabapentin and skin problems – how to get gabapentin
buy amoxicillin 250mg: order amoxicillin without prescription – antibiotic treatment online no Rx
where can i buy cheap clomid without a prescription Clomid Hub Pharmacy Clomid Hub
wakefulness medication online no Rx buy Modafinil online USA prescription-free Modafinil alternatives
ReliefMeds USA: Relief Meds USA – anti-inflammatory steroids online
https://wakemedsrx.shop/# Wake Meds RX
antibiotic treatment online no Rx: cost of amoxicillin prescription – Clear Meds Direct
low-cost antibiotics delivered in USA [url=https://clearmedsdirect.shop/#]antibiotic treatment online no Rx[/url] order amoxicillin without prescription
ReliefMeds USA: ReliefMeds USA – anti-inflammatory steroids online
buy Modafinil online USA affordable Modafinil for cognitive enhancement prescription-free Modafinil alternatives
can i buy prednisone online in uk: Relief Meds USA – ReliefMeds USA
order amoxicillin without prescription: Clear Meds Direct – order amoxicillin no prescription
ReliefMeds USA: how much is prednisone 10mg – buy prednisone 5mg canada
NeuroRelief Rx: NeuroRelief Rx – NeuroRelief Rx
https://shorturl.fm/bxbCN
Clomid Hub: can you get clomid without dr prescription – how to buy clomid without dr prescription
ReliefMeds USA prednisone 5 50mg tablet price ReliefMeds USA
anti-inflammatory steroids online: ReliefMeds USA – order corticosteroids without prescription
can i order prednisone ReliefMeds USA Relief Meds USA
prednisone sale: Relief Meds USA – can i order prednisone
Татуировки — это уникальное искусство , где каждая линия несёт личную историю и отражает характер человека.
Для сотен людей тату — вечный символ , который вдохновляет о преодолённых трудностях и становится частью пути .
Процесс создания — это ритуал доверия между художником и клиентом , где тело становится полотном эмоций.
источники питания тату
Разные направления, от минималистичных узоров до традиционных орнаментов , помогают передать любую идею в гармоничном исполнении.
Эстетика нательного искусства в способности расти вместе с хозяином , превращая воспоминания в незабываемый визуальный язык .
Выбирая узор , люди показывают своё «я» через формы, создавая личное произведение, которое наполняет уверенностью каждый день.
Татуировки — это форму самовыражения, где каждая линия несёт глубокий смысл и подчеркивает индивидуальность человека.
Для сотен людей тату — вечный символ , который вдохновляет о преодолённых трудностях и дополняет жизненный опыт.
Процесс создания — это ритуал доверия между мастером и клиентом , где кожа превращается полотном эмоций.
тату аксессуары
Современные стили , от минималистичных узоров до традиционных орнаментов , позволяют воплотить самую смелую фантазию в изысканной форме .
Красота тату в способности расти вместе с хозяином , превращая эмоции в живой символ внутреннего мира.
Подбирая эскиз, люди показывают своё «я» через формы, создавая неповторимый шедевр , которое радует глаз каждый день.
gabapentin population pharmacokinetics: NeuroRelief Rx – can u drink on gabapentin
https://reliefmedsusa.com/# order corticosteroids without prescription
amoxicillin without a prescription: order amoxicillin without prescription – order amoxicillin without prescription
generic amoxicillin cost: buy amoxil – amoxicillin 500mg prescription
prescription-free Modafinil alternatives: affordable Modafinil for cognitive enhancement – Modafinil for focus and productivity
http://neuroreliefrx.com/# how many times a day can you take gabapentin
order amoxicillin without prescription amoxicillin 500mg buy online canada amoxicillin 500 mg online
https://shorturl.fm/2Esqi
https://shorturl.fm/o0qeb
ReliefMeds USA: anti-inflammatory steroids online – order corticosteroids without prescription
ReliefMeds USA ReliefMeds USA order corticosteroids without prescription
prednisone canada pharmacy: ReliefMeds USA – Relief Meds USA
low-cost antibiotics delivered in USA: can you buy amoxicillin uk – order amoxicillin without prescription
where can i buy clomid: clomid without a prescription – can i purchase generic clomid pills
NeuroRelief Rx: NeuroRelief Rx – gabapentin and the contraceptive pill
prescription-free Modafinil alternatives wakefulness medication online no Rx where to buy Modafinil legally in the US
https://shorturl.fm/UbNjd
prednisone 10mg cost: anti-inflammatory steroids online – Relief Meds USA
how to buy clomid without rx [url=https://clomidhubpharmacy.shop/#]Clomid Hub Pharmacy[/url] Clomid Hub Pharmacy
https://shorturl.fm/02pzc
anti-inflammatory steroids online: Relief Meds USA – prednisone no rx
NeuroRelief Rx: NeuroRelief Rx – NeuroRelief Rx
prescription-free Modafinil alternatives: where to buy Modafinil legally in the US – WakeMeds RX
https://shorturl.fm/XRx8O
https://shorturl.fm/AV2X9
prednisone 20 mg tablet price: prednisone 50 mg price – ReliefMeds USA
http://neuroreliefrx.com/# gabapentin effect time
where can you buy amoxicillin over the counter: order amoxicillin without prescription – antibiotic treatment online no Rx
NeuroRelief Rx can i take gabapentin and effexor together NeuroRelief Rx
http://reliefmedsusa.com/# anti-inflammatory steroids online
https://shorturl.fm/5ujnf
https://shorturl.fm/UXJw4
Relief Meds USA ReliefMeds USA prednisone in india
prednisone price: Relief Meds USA – prednisone 0.5 mg
where to buy prednisone uk: Relief Meds USA – how can i get prednisone
can i order cheap clomid: Clomid Hub Pharmacy – how can i get generic clomid without prescription
prednisone 50: prednisone online australia – order corticosteroids without prescription
ClearMeds Direct: Clear Meds Direct – amoxicillin 500mg pill
generic amoxil 500 mg: Clear Meds Direct – buy amoxicillin without prescription
срочные онлайн займы на карту проверок срочные онлайн займы на карту проверок .
prednisone steroids Relief Meds USA india buy prednisone online
buy Modafinil online USA Wake Meds RX safe Provigil online delivery service
привезти автомобиль из южной кореи привезти автомобиль из южной кореи .
prednisone: ReliefMeds USA – Relief Meds USA
where to buy Modafinil legally in the US: Wake Meds RX – WakeMedsRX
anti-inflammatory steroids online: Relief Meds USA – anti-inflammatory steroids online
canadian pharmacy antibiotics: canadadrugpharmacy com – buy canadian drugs
buy from mexico pharmacy: buy cheap meds from a mexican pharmacy – MexiCare Rx Hub
CanadRx Nexus: onlinepharmaciescanada com – CanadRx Nexus
http://indigenixpharm.com/# indian pharmacy online
CanadRx Nexus canadian pharmacy 1 internet online drugstore CanadRx Nexus
canadian pharmacy near me CanadRx Nexus canadian pharmacy meds
http://indigenixpharm.com/# IndiGenix Pharmacy
MexiCare Rx Hub: MexiCare Rx Hub – order from mexican pharmacy online
canadian pharmacies: CanadRx Nexus – global pharmacy canada
CanadRx Nexus: reliable canadian pharmacy – CanadRx Nexus
cheapest online pharmacy india: Online medicine home delivery – cheapest online pharmacy india
IndiGenix Pharmacy: Online medicine home delivery – IndiGenix Pharmacy
best canadian pharmacy to buy from CanadRx Nexus pharmacy in canada
top 10 online pharmacy in india: IndiGenix Pharmacy – cheapest online pharmacy india
indian pharmacy paypal IndiGenix Pharmacy IndiGenix Pharmacy
indian pharmacy: indian pharmacy online – indian pharmacies safe
CanadRx Nexus: northwest canadian pharmacy – CanadRx Nexus
indian pharmacy paypal: IndiGenix Pharmacy – IndiGenix Pharmacy
CanadRx Nexus: CanadRx Nexus – CanadRx Nexus
https://canadrxnexus.com/# canadian pharmacy 24h com safe
IndiGenix Pharmacy IndiGenix Pharmacy IndiGenix Pharmacy
pharmacy website india: india pharmacy – india online pharmacy
https://indigenixpharm.shop/# IndiGenix Pharmacy
MexiCare Rx Hub MexiCare Rx Hub accutane mexico buy online
CanadRx Nexus: canadapharmacyonline legit – canadian pharmacy mall
canadian drugs pharmacy: CanadRx Nexus – CanadRx Nexus
CanadRx Nexus: CanadRx Nexus – canadian drug pharmacy
canadapharmacyonline com: canadian online drugstore – CanadRx Nexus
northwest canadian pharmacy: canadian online drugstore – canadian pharmacy india
india online pharmacy [url=https://indigenixpharm.shop/#]IndiGenix Pharmacy[/url] online pharmacy india
mexican mail order pharmacies: MexiCare Rx Hub – MexiCare Rx Hub
CanadRx Nexus [url=https://canadrxnexus.shop/#]CanadRx Nexus[/url] pet meds without vet prescription canada
IndiGenix Pharmacy: indian pharmacy – indianpharmacy com
MexiCare Rx Hub: mexican pharmacy for americans – MexiCare Rx Hub
canadian pharmacy ltd: pharmacies in canada that ship to the us – CanadRx Nexus
canadian pharmacy price checker: CanadRx Nexus – CanadRx Nexus
buying from online mexican pharmacy: buying prescription drugs in mexico online – best online pharmacies in mexico
https://canadrxnexus.com/# best canadian online pharmacy
https://shorturl.fm/8xvj3
MexiCare Rx Hub MexiCare Rx Hub MexiCare Rx Hub
https://shorturl.fm/OKbkq
best online pharmacy india: india pharmacy – IndiGenix Pharmacy
https://canadrxnexus.com/# CanadRx Nexus
MexiCare Rx Hub MexiCare Rx Hub finasteride mexico pharmacy
MexiCare Rx Hub: finasteride mexico pharmacy – MexiCare Rx Hub
IndiGenix Pharmacy: IndiGenix Pharmacy – IndiGenix Pharmacy
IndiGenix Pharmacy: IndiGenix Pharmacy – Online medicine order
adderall canadian pharmacy: pharmacy in canada – best rated canadian pharmacy
https://shorturl.fm/ZOujd
CanadRx Nexus cheap canadian pharmacy online canadian pharmacy victoza
IndiGenix Pharmacy: IndiGenix Pharmacy – indian pharmacy
CanadRx Nexus canada pharmacy world CanadRx Nexus
[url=https://vc.ru/seo/932183-poisk-zabroshennyh-saitov-dlya-ispolzovaniya-v-setke-proverennye-sposoby]Поиск дропов[/url] — это основа при построении качественной приватной сети сайтов. Навык подбора хороших дроп-доменов позволяет усилить продвигаемые проекты и избежать фильтров. Чтобы получить желаемый эффект, стоит совмещать разные подходы. Начать стоит с expired-доменов, которые можно отслеживать через платформы вроде ExpiredDomains.net. Ищите домены с трастовыми ссылками, стабильной историей и без спама. Сервисы позволяют удобно отсортировать дропы по SEO-показателям, возрасту и другим характеристикам. Вручную можно находить интересные домены, анализируя упоминания и ссылочные профили. Можно находить старые сайты через веб-архив, затем смотреть, освободились ли домены. Зарегистрировать такой домен можно сразу после освобождения или заранее через аукционы. Бэкордеры — ещё один способ не упустить ценные дропы. Среди популярных сервисов: SnapNames, Dynadot Backorder, Name.com. Они увеличивают шансы на получение нужного домена с хорошей историей. Обязательно проверяйте домены через Wayback Machine. Так можно убедиться, что домен использовался легально и подходил под вашу нишу. Анализ ссылок поможет не взять домен с плохой репутацией. Поиск дроп-доменов требует внимания и анализа, но даёт отличные результаты. Максимальная эффективность достигается при использовании разных стратегий. Со временем вы научитесь быстро определять перспективные домены и отсеивать мусор.
https://vc.ru/seo/932183-poisk-zabroshennyh-saitov-dlya-ispolzovaniya-v-setke-proverennye-sposoby
CanadRx Nexus: pet meds without vet prescription canada – canadian pharmacies compare
amoxicillin mexico online pharmacy: MexiCare Rx Hub – accutane mexico buy online
IndiGenix Pharmacy: cheapest online pharmacy india – IndiGenix Pharmacy
IndiGenix Pharmacy: india pharmacy – п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india
canadian pharmacy online: ordering drugs from canada – CanadRx Nexus
real mexican pharmacy USA shipping [url=https://mexicarerxhub.com/#]buy from mexico pharmacy[/url] MexiCare Rx Hub
http://canadrxnexus.com/# CanadRx Nexus
legit mexican pharmacy without prescription order from mexican pharmacy online MexiCare Rx Hub
MexiCare Rx Hub: MexiCare Rx Hub – buying prescription drugs in mexico online
isotretinoin from mexico: buy modafinil from mexico no rx – MexiCare Rx Hub
indian pharmacy paypal: top online pharmacy india – indian pharmacies safe
http://canadrxnexus.com/# CanadRx Nexus
order azithromycin mexico: buy propecia mexico – MexiCare Rx Hub
cheapest online pharmacy india [url=https://indigenixpharm.shop/#]IndiGenix Pharmacy[/url] IndiGenix Pharmacy
zithromax mexican pharmacy: MexiCare Rx Hub – gabapentin mexican pharmacy
MexiCare Rx Hub: medication from mexico pharmacy – mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
CanadRx Nexus is canadian pharmacy legit canadadrugpharmacy com
CanadRx Nexus: CanadRx Nexus – CanadRx Nexus
CanadRx Nexus: canadian compounding pharmacy – canadian pharmacy no rx needed
MexiCare Rx Hub: online mexico pharmacy USA – MexiCare Rx Hub
IndiGenix Pharmacy: п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india – top 10 pharmacies in india
IndiGenix Pharmacy IndiGenix Pharmacy IndiGenix Pharmacy
top 10 pharmacies in india: cheapest online pharmacy india – top 10 pharmacies in india
medication from mexico pharmacy: mexican drugstore online – MexiCare Rx Hub
canadian pharmacy sarasota best canadian pharmacy CanadRx Nexus
IndiGenix Pharmacy: IndiGenix Pharmacy – IndiGenix Pharmacy
best online pharmacy india: IndiGenix Pharmacy – IndiGenix Pharmacy
https://canadrxnexus.com/# trusted canadian pharmacy
https://shorturl.fm/ytla5
https://mexicarerxhub.com/# mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs
BonBon Blast – Sugar Rush jest uruchamiany w następujących systemach operacyjnych: iOS. Jak grać w Pragmatic Play’s Sugar Rush 1000 Komentarz będzie widoczny dopiero po wcześniejszym zweryfikowaniu go przez naszych pracowników. 3. Pozostaw ubranie w zamrażarce na kilka godzin, wyjmij je i wytrzep ponownie. Student – Always Learning ✌️ Sugar Rush DROPS 4-17 Użytkownicy BonBon Blast – Sugar Rush dał pewien oszacowanie od 5 z 5 gwiazdek. Finance Director Member of the Management Board Najnowsza wersja BonBon Blast – Sugar Rush jest 1.1.0, wydany na 15.12.2023. Początkowo był to dodane do naszej bazy na 15.12.2023. Sugar Rush DROPS 4-17 RTP w Sugar Rush wynosi ponadprzeciętne 96,50% i charakteryzuje się modelem gry o wysokiej zmienności. Dzięki temu możesz spodziewać się krótszych wygranych, ale za to większych.
http://boyon-sakura.net/wiki/index.php?enconnocour1980
Kulikowski, K., & Orzechowski, J. (2019). Working memory and fluid intelligence as predictors of work engagement : testing preliminary models. Applied Cognitive Psychology, 33(4), 596–616. doi.org 10.1002 acp.3500 Sobol-Kwapińska, M., Płotek, W., Bąbel, P., Cybulski, M., Kluzik, A., Krystianc, J., & Mandecki, M. (2017). Time perspective as a predictor of acute postsurgical pain and coping with pain following abdominal surgery. European Journal of Pain, 21(4), 635–644. doi.org 10.1002 ejp.967 Sobol-Kwapińska, M., Płotek, W., Bąbel, P., Cybulski, M., Kluzik, A., Krystianc, J., & Mandecki, M. (2017). Time perspective as a predictor of acute postsurgical pain and coping with pain following abdominal surgery. European Journal of Pain, 21(4), 635–644. doi.org 10.1002 ejp.967
IndiGenix Pharmacy: Online medicine order – indianpharmacy com
Online medicine order IndiGenix Pharmacy IndiGenix Pharmacy
IndiGenix Pharmacy: india pharmacy mail order – IndiGenix Pharmacy
legit canadian pharmacy online: canadian 24 hour pharmacy – CanadRx Nexus
canadian valley pharmacy canadapharmacyonline canadian pharmacy tampa
https://shorturl.fm/vq2Y5
cheapest online pharmacy india: pharmacy website india – indian pharmacy
CanadRx Nexus: CanadRx Nexus – CanadRx Nexus
canadian mail order pharmacy: canadian pharmacy india – canadian pharmacy
https://shorturl.fm/uX4NX
best india pharmacy IndiGenix Pharmacy online pharmacy india
northwest canadian pharmacy: trustworthy canadian pharmacy – CanadRx Nexus
cheap mexican pharmacy: MexiCare Rx Hub – MexiCare Rx Hub
https://shorturl.fm/aEYT1
mexico drug stores pharmacies: MexiCare Rx Hub – mexico drug stores pharmacies
buy antibiotics from mexico MexiCare Rx Hub MexiCare Rx Hub
IndiGenix Pharmacy: buy prescription drugs from india – IndiGenix Pharmacy
IndiGenix Pharmacy: indianpharmacy com – IndiGenix Pharmacy
buy drugs from canada: legal to buy prescription drugs from canada – CanadRx Nexus
https://indigenixpharm.shop/# IndiGenix Pharmacy
CanadRx Nexus CanadRx Nexus CanadRx Nexus
buy medicines online in india: IndiGenix Pharmacy – Online medicine home delivery
https://canadrxnexus.com/# CanadRx Nexus
MexiCare Rx Hub: MexiCare Rx Hub – MexiCare Rx Hub
legitimate canadian mail order pharmacy CanadRx Nexus CanadRx Nexus
https://shorturl.fm/m7QGX
CanadRx Nexus: reputable canadian online pharmacies – CanadRx Nexus
online pharmacy india: indian pharmacy online – IndiGenix Pharmacy
CanadRx Nexus: CanadRx Nexus – buying drugs from canada
https://shorturl.fm/2IYjP
CanadRx Nexus canada online pharmacy canadian pharmacy king reviews
https://shorturl.fm/jHmYj
online canadian pharmacy reviews: canada discount pharmacy – reliable canadian online pharmacy
IverCare Pharmacy: IverCare Pharmacy – IverCare Pharmacy
AsthmaFree Pharmacy ventolin 50 mcg ventolin tablets australia
AsthmaFree Pharmacy: AsthmaFree Pharmacy – switching from ozempic to rybelsus
buy ventolin online cheap: AsthmaFree Pharmacy – AsthmaFree Pharmacy
FluidCare Pharmacy: furosemide – lasix 100 mg tablet
https://relaxmedsusa.shop/# muscle relaxants online no Rx
prescription-free muscle relaxants prescription-free muscle relaxants Tizanidine tablets shipped to USA
https://glucosmartrx.com/# AsthmaFree Pharmacy
Tizanidine tablets shipped to USA: Tizanidine tablets shipped to USA – Tizanidine 2mg 4mg tablets for sale
FluidCare Pharmacy: lasix 100mg – FluidCare Pharmacy
https://shorturl.fm/htPiT
https://shorturl.fm/iNDDe
trusted pharmacy Zanaflex USA: Tizanidine 2mg 4mg tablets for sale – relief from muscle spasms online
RelaxMedsUSA: relief from muscle spasms online – muscle relaxants online no Rx
IverCare Pharmacy can ivermectin be given orally IverCare Pharmacy
AsthmaFree Pharmacy: AsthmaFree Pharmacy – side effects of rybelsus 14 mg
AsthmaFree Pharmacy: ventolin for sale – ventolin nebulizer
FluidCare Pharmacy lasix furosemide 40 mg FluidCare Pharmacy
how to get rybelsus cheap: AsthmaFree Pharmacy – rybelsus who makes it
AsthmaFree Pharmacy: AsthmaFree Pharmacy – AsthmaFree Pharmacy
https://asthmafreepharmacy.shop/# ventolin inhaler for sale
FluidCare Pharmacy FluidCare Pharmacy FluidCare Pharmacy
оформить кредитную карту онлайн kreditnye-karty-kg-1.ru .
IverCare Pharmacy: ivermectin amazon – IverCare Pharmacy
https://ivercarepharmacy.shop/# IverCare Pharmacy
AsthmaFree Pharmacy AsthmaFree Pharmacy AsthmaFree Pharmacy
relief from muscle spasms online: trusted pharmacy Zanaflex USA – RelaxMeds USA
AsthmaFree Pharmacy: rybelsus novo nordisk – AsthmaFree Pharmacy
AsthmaFree Pharmacy: ventolin tablets uk – ventolin with out prescription
автокредит с первоначальным взносом автокредит с первоначальным взносом .
IverCare Pharmacy pig wormer ivermectin IverCare Pharmacy
https://shorturl.fm/rLzAs
IverCare Pharmacy: IverCare Pharmacy – ivermectin where to purchase
IverCare Pharmacy: IverCare Pharmacy – ivermectin spot on for rabbits
AsthmaFree Pharmacy: AsthmaFree Pharmacy – cheapest ventolin online uk
ventolin otc buy ventolin pharmacy online ventolin
https://shorturl.fm/rw5X4
https://shorturl.fm/3SGJ2
furosemide 40mg: FluidCare Pharmacy – furosemide 40 mg
Holgura mecanica
Dispositivos de calibracion: clave para el operacion uniforme y eficiente de las maquinarias.
En el campo de la avances actual, donde la eficiencia y la fiabilidad del equipo son de gran relevancia, los sistemas de balanceo juegan un papel crucial. Estos aparatos dedicados estan desarrollados para ajustar y fijar partes moviles, ya sea en maquinaria manufacturera, medios de transporte de movilidad o incluso en equipos domesticos.
Para los profesionales en reparacion de equipos y los especialistas, trabajar con sistemas de ajuste es importante para proteger el desempeno estable y seguro de cualquier sistema dinamico. Gracias a estas soluciones tecnologicas modernas, es posible minimizar considerablemente las vibraciones, el zumbido y la esfuerzo sobre los rodamientos, aumentando la tiempo de servicio de piezas caros.
Asimismo significativo es el tarea que juegan los sistemas de ajuste en la servicio al usuario. El ayuda tecnico y el soporte permanente empleando estos aparatos posibilitan proporcionar servicios de excelente excelencia, elevando la contento de los consumidores.
Para los titulares de proyectos, la financiamiento en equipos de balanceo y sensores puede ser importante para aumentar la rendimiento y eficiencia de sus dispositivos. Esto es sobre todo relevante para los emprendedores que dirigen reducidas y intermedias empresas, donde cada elemento vale.
Asimismo, los equipos de ajuste tienen una vasta utilizacion en el campo de la prevencion y el monitoreo de nivel. Permiten detectar probables defectos, evitando mantenimientos elevadas y danos a los dispositivos. Incluso, los indicadores obtenidos de estos dispositivos pueden aplicarse para maximizar procedimientos y aumentar la visibilidad en plataformas de exploracion.
Las sectores de utilizacion de los sistemas de ajuste cubren variadas sectores, desde la manufactura de bicicletas hasta el supervision de la naturaleza. No influye si se considera de extensas producciones manufactureras o pequenos espacios caseros, los sistemas de balanceo son necesarios para proteger un desempeno optimo y libre de interrupciones.
lasix furosemide FluidCare Pharmacy FluidCare Pharmacy
Tizanidine 2mg 4mg tablets for sale: Tizanidine tablets shipped to USA – Zanaflex medication fast delivery
Tizanidine 2mg 4mg tablets for sale: cheap muscle relaxer online USA – prescription-free muscle relaxants
http://fluidcarepharmacy.com/# FluidCare Pharmacy
ventolin otc canada [url=https://asthmafreepharmacy.shop/#]buy ventolin[/url] AsthmaFree Pharmacy
muscle relaxants online no Rx: prescription-free muscle relaxants – Zanaflex medication fast delivery
lasix generic name: lasix dosage – FluidCare Pharmacy
affordable Zanaflex online pharmacy: affordable Zanaflex online pharmacy – affordable Zanaflex online pharmacy
AsthmaFree Pharmacy semaglutide buy online how to give semaglutide injection in thigh
IverCare Pharmacy: ivermectin paste for humans – IverCare Pharmacy
rybelsus recall AsthmaFree Pharmacy AsthmaFree Pharmacy
ivermectin pinworms: IverCare Pharmacy – cheap stromectol
ivermectin livestock IverCare Pharmacy IverCare Pharmacy
lasix medication: furosemide 40 mg – lasix 40 mg
https://shorturl.fm/3851b
heartworm prevention without ivermectin: IverCare Pharmacy – IverCare Pharmacy
http://ivercarepharmacy.com/# ivermectin antiviral
IverCare Pharmacy ivermectin for mites IverCare Pharmacy
buy cheap ventolin: ventolin drug – ventolin generic cost
lasix 100 mg tablet: lasix pills – lasix dosage
IverCare Pharmacy IverCare Pharmacy IverCare Pharmacy
AsthmaFree Pharmacy: ventolin cost in canada – how much is ventolin in canada
lasix 40 mg: FluidCare Pharmacy – furosemida
adderall and semaglutide AsthmaFree Pharmacy AsthmaFree Pharmacy
http://asthmafreepharmacy.com/# buy ventolin nz
IverCare Pharmacy: ivermectin 5 mg price – ivermectin lotion 0.5
microdosing semaglutide AsthmaFree Pharmacy semaglutide weight loss side effects
AsthmaFree Pharmacy: AsthmaFree Pharmacy – AsthmaFree Pharmacy
AsthmaFree Pharmacy: AsthmaFree Pharmacy – semaglutide dose for weight loss
lasix 20 mg lasix 100 mg tablet lasix medication
http://ivercarepharmacy.com/# IverCare Pharmacy
AsthmaFree Pharmacy: how to get rybelsus for weight loss – semaglutide compounded
rijbewijs kopen, rijbewijs b kopen, vals rijbewijs kopen, rijbewijs b kopen in belgie, rijbewijs kopen prijs, rijbewijs kopen legaal, rijbewijs kopen 247 ervaringen, rijbewijs kopen online, rijbewijs kopen belgie, nep rijbewijs, motorrijbewijs kopen, kan je een rijbewijs kopen, koop een rijbewijs, motor rijbewijs kopen, rijbewijs kopen betrouwbaar, neppe rijbewijs kopen, auto zonder rijbewijs kopen belgie, rijbewijs koop, rijbewijs kopen nederland, auto zonder rijbewijs kopen, rijbewijs kopen belgië, rijbewijs kopen belgie, rijbewijs kopen in nederland, rijbewijs b belgie, rijbewijs kopen met registratie.99uu9juj Belatra Games – 3 Pedir un juego¿No encuentras tu juego preferido? Avísanos en el foro. 👉 ¡HAZ CLIC AQUÍ para REGISTRARTE y conseguir tu BONO de hasta 100€ + 50 GIROS GRATIS!
https://sumiccouldho1974.raidersfanteamshop.com/jackpotcity-contacto-chile
Big Bass Amazon Xtreme es lo último de la saga Big Bass Bonanza que transporta a los jugadores a una aventura de pesca en el corazón de la selva amazónica. Con una mecánica de juego mejorada, esta versión ofrece características únicas como símbolos de dinero y la posibilidad de activar giros gratis con símbolos especiales. Estadísticas deportivas En Big Bass Bonanza Megaways nos vamos de pesca (por así decirlo), con la compañía de los símbolos más típicos que te puedas imaginar: el pescador, perfectamente caracterizado con su barba y gorro, las cañas, los anzuelos y los peces saltando. Los gráficos del juego son nítidos, las animaciones son fluidas y la música también suma puntos y hace que nos relajemos al jugar. Bass Hold & Spinner Megaways de Pragmatic Play. Esta tragaperras se inspira en la pesca de lubinas, un tema que últimamente viene siendo cada vez más aclamado. Este juego de casino online combina elementos interesantes en comparación con otroas máquina tragaperras en línea.
IverCare Pharmacy: ivermectin and covid – IverCare Pharmacy
40 units of semaglutide is how many ml oral semaglutide side effects oral semaglutide (rybelsus)
AsthmaFree Pharmacy: how quickly does semaglutide work – AsthmaFree Pharmacy
ivermectin goodrx IverCare Pharmacy IverCare Pharmacy
buy ivermectin online: how much ivermectin to give a dog with sarcoptic mange – IverCare Pharmacy
IverCare Pharmacy: how long after taking ivermectin can you drink alcohol – IverCare Pharmacy
IverCare Pharmacy: IverCare Pharmacy – how much ivermectin to give a dog
IverCare Pharmacy ivermectin amazon ivermectin 200 mcg
https://asthmafreepharmacy.shop/# can you buy ventolin over the counter in australia
order Tizanidine without prescription: Tizanidine tablets shipped to USA – prescription-free muscle relaxants
where to buy ventolin ventolin online uk ventolin price in india
https://glucosmartrx.com/# semaglutide refrigeration
robert malone ivermectin: IverCare Pharmacy – ivermectin 10 ml
buy ventolin without prescription: ventolin uk pharmacy – AsthmaFree Pharmacy
ivermectin fleas: stromectol tablets – ivermectin tablet price
W dzisiejszych czasach prawie wszystko można osiągnąć za pomocą smartfona, dzięki czemu twoja ręka ma wartość 23. Ramzes Book to bardzo łatwy slot, jak ubiegać się o bonusy i promocje dla sugar rush a uzyskanie bonusu powitalnego było proste. Bonusy dla stałych klientów automatów mogą przybierać różne formy, jak również system operacyjny Android. Czas spędzony przy Sugar Rush mija niezwykle szybko – a to za sprawą świetnej (i słodkiej!) grafiki, symbolom specjalnym, opcji zakupu bonusu czy free spinom. Tych ostatnich możemy wygrać tutaj aż 30! Jak przystało na gry tego uznanego dostawcy, RTP należy do wysokich zaś maksymalna wygrana może wynieść nawet 2 000 000 złotych.
https://www.zonotrikia.com.ar/2025/08/04/jak-zdobyc-50-darmowych-spinow-na-starburst-w-verde-casino-bez-wplaty/
Czy maszyna hazardowa Sugar Rush zawiera funkcję Jackpota? Sloty i gry od Pragmatic Play słyną z tego, że są wręcz naszpikowane funkcjami bonusowymi. Deweloper nie tylko wdraża znane bonusy i promocje do oferty automatów, ale współpracuje też z kasynami w kierunku organizacji turniejów i loterii między kasynowych. Dowiedz się więcej o promocjach i bonusach kasyn online dostępnych w grach tej firmy. Szczęście z PL Few Keys w kasynie Wszystkie wypłaty w kasynie mają 24-godzinny okres oczekiwania i są przetwarzane na konta e-portfela w ciągu 24 godzin po zakończeniu okresu oczekiwania, istnieje ryzyko. Symbolem bonusowym jest koło bonusowe, że nie ma nikogo. Zagraj w archer online ich agresywny styl gry zyskał szacunek najlepszych drużyn w regionach, numer międzynarodowy istnieje dla wszystkich innych graczy.
ivermectin river blindness ivermectin side effects horses ivermectin horse wormer paste
FluidCare Pharmacy furosemide 100 mg FluidCare Pharmacy
IverCare Pharmacy: IverCare Pharmacy – cost for ivermectin 3mg
can you buy ventolin over the counter: can you buy ventolin over the counter in uk – ventolin hfa
IverCare Pharmacy: IverCare Pharmacy – ivermectin 80 mg
januvia vs rybelsus constipation from semaglutide does semaglutide lower blood sugar
[url=https://7sharov.ru]Доставка шариков москва[/url] — это быстрый способ порадовать близких в любое время. Доступна доставка ярких воздушных шаров в пределах Москвы через сайт. Композиции создаются под заказ, учитываются все пожелания. Будь то день рождения, свадьба или корпоратив — мы сделаем всё красиво. Оформление из воздушных шаров не сдуваются долго, доставляются по времени, указанному клиентом. Цифры, поздравления, оригинальные формы — всё на выбор. Наши курьеры аккуратны и пунктуальны. Заказ принимается онлайн круглосуточно. Наши менеджеры готовы помочь с оформлением и проконсультировать. Доставляем шары в будни, выходные и праздничные дни. Используем только качественные материалы — шары не лопаются и не тускнеют. Периодически проводим акции и распродажи. Работаем с агентствами, организаторами, корпоративными клиентами. Не откладывайте — закажите шарики с доставкой уже сегодня.
https://7sharov.ru
furosemide FluidCare Pharmacy furosemida
https://ivercarepharmacy.com/# how much ivermectin to give a dog for worms
order Tizanidine without prescription: RelaxMedsUSA – Tizanidine tablets shipped to USA
Zanaflex medication fast delivery: muscle relaxants online no Rx – order Tizanidine without prescription
furosemida: FluidCare Pharmacy – FluidCare Pharmacy
RelaxMeds USA RelaxMedsUSA RelaxMeds USA
https://relaxmedsusa.com/# muscle relaxants online no Rx
ventolin price in usa cheap ventolin inhalers AsthmaFree Pharmacy
rybelsus 50mg: AsthmaFree Pharmacy – groupon semaglutide
semaglutide covered by insurance: AsthmaFree Pharmacy – rybelsus use for
FluidCare Pharmacy: lasix 40 mg – buy furosemide online
cheap muscle relaxer online USA trusted pharmacy Zanaflex USA relief from muscle spasms online
AsthmaFree Pharmacy: AsthmaFree Pharmacy – ventolin script
Explore an abundance of engaging and valuable materials on this site .
From detailed tutorials to quick tips , you’ll find for everyone .
Enhance your knowledge with curated content designed to inspire while also entertain visitors.
Here provides a user-friendly experience ensuring you can access tools you need .
Become part of a growing community and appreciate trusted insights consistently.
Start exploring immediately and unlock the full potential these resources has to offer .
https://xbmc.us
We only accept payment methods that are fast, safe and secure. Not only does this mean your sensitive information is safe, but it also means when you make a withdrawal we can put it into your account in a matter of hours. Yes, you read that right, hours! You can find the best free online casinos here at Casino.org. Have a look at our shortlist of recommended casinos at the top of this page to get started. You will find casinos with excellent bonuses, ongoing rewards and massive selection of games. Basic Game Info Every gambler aims to hit a big win and this slot can potentially award them. You will hit these wins when you play this slot patiently. The slot bonus rounds are more promising compared to the base game. Thus, you must play until you trigger these rounds. This slot comes with high volatility so it can be quite unfriendly to your bankroll. Therefore, you should set your bets tactfully to play several times and optimize your chances of activating the bonuses and hitting the massive wins.
https://viticusgroup.info/we-verified-the-chicken-road-claims-heres-the-source/
Play buffalo king megaways to name a few, the casino will offer you a small amount of bonus funds just for signing up. Players who wish or need to take a rest from the video games, giving a maximum of 117,649 paylines when each is fully expanded you need to land identical symbols ANYWHERE on adjacent reels from left to right to create a payline. The Buffalo King Megaways slot review has shown that it is a remarkable slot game that successfully builds upon the legacy of its predecessor. Whether you are a fan of the original Buffalo King or simply seeking a unique Megaways adventure, Buffalo King Megaways is sure to captivate and thrill. Embark on this majestic journey and uncover the hidden treasures that await amidst the untamed wilderness of North America. Some games will offer a no-deposit bonus offering coins or credits, but remember, free slots are just for fun. So, whilst you may miss the thrill of a real money prize or big cash bonuses, you will however benefit from the fact that you can’t lose real money either.
https://pinwinaz.pro/# Pinco casino mobil t?tbiq
jilwin: Jiliko – Jiliko app
jollibet app: jollibet app – Online betting Philippines
Beta138: Promo slot gacor hari ini – Withdraw cepat Beta138
Bandar togel resmi Indonesia: Link alternatif Abutogel – Situs togel online terpercaya
Abutogel Jackpot togel hari ini Link alternatif Abutogel
Yuks?k RTP slotlar: Onlayn kazino Az?rbaycan – Pinco r?smi sayt
Bandar togel resmi Indonesia: Link alternatif Abutogel – Abutogel login
Live casino Mandiribet: Mandiribet login – Situs judi resmi berlisensi
Live casino Indonesia Bandar bola resmi Bonus new member 100% Beta138
https://betawinindo.top/# Beta138
Yuks?k RTP slotlar: Onlayn rulet v? blackjack – Pinco kazino
Swerte99 casino: Swerte99 slots – Swerte99 login
Jiliko slots: maglaro ng Jiliko online sa Pilipinas – Jiliko login
Swerte99 online gaming Pilipinas: Swerte99 bonus – Swerte99 app
Jiliko bonus Jiliko login maglaro ng Jiliko online sa Pilipinas
maglaro ng Jiliko online sa Pilipinas: jilwin – Jiliko casino
https://1winphili.company/# Online gambling platform Jollibet
Link alternatif Abutogel: Jackpot togel hari ini – Situs togel online terpercaya
Swerte99 bonus: Swerte99 – Swerte99 login
Jiliko casino: Jiliko – maglaro ng Jiliko online sa Pilipinas
Live casino Indonesia: Withdraw cepat Beta138 – Slot gacor Beta138
Swerte99 casino: Swerte99 casino – Swerte99 casino
Link alternatif Abutogel: Link alternatif Abutogel – Situs togel online terpercaya
Jiliko casino walang deposit bonus para sa Pinoy Jiliko app Jiliko login
Link alternatif Abutogel: Abutogel login – Abutogel
Napoleon Vs Rabbits Bonusfunctie Het beste Sugar Rush casino van Nederland is One Casino. Zij geven nieuwe spelers namelijk een 10 euro no deposit bonus. Met dit gratis speelgeld kun je alles in het casino proberen, dus ook Sugar Rush! Met deze bonus loop je geen risico, maar maak je wel kans op het winnen van echt geld! Op ons platform kun je, naast Sugar Rush 1000 spelen, ook genieten van de traditionele versie en Sugar Rush Xmas wanneer de feestdagen naderen! Mini Roulette Innovative Slot Design You can choose to enable or disable some or all of these cookies but disabling some of them may affect your browsing experience. Pragmatic Play is het brein achter deze gokkast en dus moet elk Sugar Rush Casino een samenwerking hebben met Pragmatic Play. Gelukkig bieden de meeste Nederlandse online casino’s de spellen aan van Pragmatic Play, omdat ze simpelweg een van de grootste en meest populaire spel providers zijn. Naast Sweet Bonanza, Sugar Rush en Fruit Party heeft Pragmatic Play ook toppers als Big Bass Bonanza en Gates of Olympus uitgebracht. Online casino’s kunnen dus gewoon niet om Pragmatic Play heen! Hieronder vind je de beste Sugar Rush casino’s!
https://astraonline.com.br/sugar-rush-casino-analyse-rtp-consistentie-en-winstructuur/
Brievenbus €3,50 Als je investeert in nieuwe premiumtechnologie, verdien je ook hoge prestaties. Xbox One X Enhanced-games presteren beter, hebben snellere laadtijden en kunnen een hogere resolutie hebben. Beauty and the Beast (1994) #8 Het is winter in het Oude Westen. De charismatische gokker John McCabe rijdt door het regenachtige, indrukwekkende berglandschap van Washington in 1902, begeleid door Leonard Cohens “The Stranger Song”. Hij houdt halt in een klein mijnstadje in opbouw en groeit al snel uit tot een van de notabelen ter plaatse. McCabe richt een bordeel op dat gerund wordt door de geslepen Mrs. Miller, en baat zelf een gokhal uit. McCabe en Mrs. Miller worden succesvolle zakenpartners en groeien ook op persoonlijk vlak dichter naar elkaar toe. Wanneer McCabe het uitkoopaanbod van een groot mijnbedrijf afslaat, heeft dat niet enkel gevolgen voor zijn eigen veiligheid, maar ook voor die van Mrs. Miller en de rest van het stadje.
Bandar bola resmi: Beta138 – Promo slot gacor hari ini
Situs togel online terpercaya Jackpot togel hari ini Jackpot togel hari ini
GK88: Trò choi n? hu GK88 – Ðang ký GK88
https://abutowin.icu/# Jackpot togel hari ini
Jiliko login: jilwin – Jiliko casino
Etibarl? onlayn kazino Az?rbaycanda: Pinco r?smi sayt – Uduslar? tez c?xar Pinco il?
https://shorturl.fm/BlN5v
Onlayn kazino Az?rbaycan Pinco casino mobil t?tbiq Pinco casino mobil t?tbiq
Rut ti?n nhanh GK88: GK88 – Khuy?n mai GK88
Link alternatif Mandiribet: Slot jackpot terbesar Indonesia – Mandiribet
Online casino Jollibet Philippines: 1winphili – Jollibet online sabong
https://pinwinaz.pro/# Pinco casino mobil t?tbiq
Swerte99 Swerte99 casino Swerte99 online gaming Pilipinas
Bandar togel resmi Indonesia: Link alternatif Abutogel – Bandar togel resmi Indonesia
Jiliko slots: Jiliko casino walang deposit bonus para sa Pinoy – maglaro ng Jiliko online sa Pilipinas
Live casino Mandiribet: Live casino Mandiribet – Mandiribet login
Slot game d?i thu?ng Slot game d?i thu?ng Ca cu?c tr?c tuy?n GK88
Login Beta138: Situs judi resmi berlisensi – Live casino Indonesia
https://shorturl.fm/8UCNn
Situs togel online terpercaya: Abutogel login – Jackpot togel hari ini
Situs togel online terpercaya: Link alternatif Abutogel – Jackpot togel hari ini
https://1winphili.company/# Jollibet online sabong
Situs togel online terpercaya: Situs togel online terpercaya – Situs togel online terpercaya
Mandiribet login Judi online deposit pulsa Judi online deposit pulsa
Link vao GK88 m?i nh?t: GK88 – Khuy?n mai GK88
Swerte99: Swerte99 online gaming Pilipinas – Swerte99 app
https://shorturl.fm/t3t9K
Promo slot gacor hari ini Link alternatif Beta138 Link alternatif Beta138
Pinco kazino: Pinco il? real pul qazan – Onlayn rulet v? blackjack
Les modèles Garmin proposent des fonctionnalités innovantes au quotidien.
Dotées de capteurs optiques ainsi que de moniteur cardiaque , ces montres s’ajustent à tous objectifs .
La durée atteint jusqu’à 14 jours selon le modèle, idéale pour activités intenses .
garantie constructeur Garmin
Les fonctions santé analysent le sommeil ainsi que le stress , offrant complet .
Faciles à utiliser , ces montres s’intègrent facilement dans votre vie, via un design intelligente .
Opter pour Garmin signifie bénéficier de un partenaire fiable afin d’optimiser votre quotidien.
Swerte99 online gaming Pilipinas: Swerte99 bonus – Swerte99 app
https://betawinindo.top/# Live casino Indonesia
Pinco il? real pul qazan: Pinco r?smi sayt – Onlayn rulet v? blackjack
jilwin: Jiliko login – Jiliko casino
1winphili: jollibet – Online gambling platform Jollibet
Jiliko casino walang deposit bonus para sa Pinoy: jilwin – maglaro ng Jiliko online sa Pilipinas
Pinco r?smi sayt Onlayn rulet v? blackjack Kazino bonuslar? 2025 Az?rbaycan
Yuks?k RTP slotlar: Etibarl? onlayn kazino Az?rbaycanda – Pinco kazino
https://jilwin.pro/# Jiliko casino walang deposit bonus para sa Pinoy
Situs judi online terpercaya Indonesia: Situs judi online terpercaya Indonesia – Live casino Mandiribet
Nhà cái uy tín Vi?t Nam: Nhà cái uy tín Vi?t Nam – Khuy?n mãi GK88
1winphili Jollibet online sabong Online gambling platform Jollibet
Link vào GK88 m?i nh?t: Trò choi n? hu GK88 – Khuy?n mãi GK88
Beta138: Situs judi resmi berlisensi – Live casino Indonesia
Rut ti?n nhanh GK88: Casino online GK88 – Casino online GK88
Jiliko login: Jiliko casino walang deposit bonus para sa Pinoy – Jiliko app
Canl? krupyerl? oyunlar Pinco casino mobil t?tbiq Onlayn rulet v? blackjack
Jiliko casino walang deposit bonus para sa Pinoy: Jiliko slots – maglaro ng Jiliko online sa Pilipinas
Onlayn kazino Az?rbaycan: Yuks?k RTP slotlar – Pinco r?smi sayt
jollibet: Online betting Philippines – jollibet casino
Tro choi n? hu GK88: Rut ti?n nhanh GK88 – Ca cu?c tr?c tuy?n GK88
Yeni az?rbaycan kazino sayt?: Onlayn rulet v? blackjack – Onlayn kazino Az?rbaycan
Jackpot togel hari ini Abutogel login Bandar togel resmi Indonesia
Canli krupyerl? oyunlar: Kazino bonuslari 2025 Az?rbaycan – Yüks?k RTP slotlar
https://jilwin.pro/# Jiliko login
Jiliko bonus: Jiliko bonus – Jiliko casino
мастер по ремонту швейных машин ремонт швейных машин в москве
Etibarli onlayn kazino Az?rbaycanda: Uduslari tez çixar Pinco il? – Onlayn rulet v? blackjack
Situs togel online terpercaya Jackpot togel hari ini Situs togel online terpercaya
Etibarl? onlayn kazino Az?rbaycanda: Onlayn kazino Az?rbaycan – Kazino bonuslar? 2025 Az?rbaycan
Pinco kazino: Uduslar? tez c?xar Pinco il? – Kazino bonuslar? 2025 Az?rbaycan
Canl? krupyerl? oyunlar: Canl? krupyerl? oyunlar – Canl? krupyerl? oyunlar
ремонт кофемашин саеко ремонт капсульных кофемашин
Mexican Pharmacy Hub buy cialis from mexico buy viagra from mexican pharmacy
https://medidirectusa.com/# my 24 hour pharmacy online
order azithromycin mexico: modafinil mexico online – accutane mexico buy online
Indian Meds One: Indian Meds One – Indian Meds One
online shopping pharmacy india: Indian Meds One – Indian Meds One
Indian Meds One: Indian Meds One – Indian Meds One
pharmacy website india: Indian Meds One – Indian Meds One
india online pharmacy Indian Meds One top online pharmacy india
https://shorturl.fm/OowPU
https://mexicanpharmacyhub.shop/# mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
top 10 pharmacies in india: Indian Meds One – online pharmacy india
MediDirect USA: Glucophage – MediDirect USA
top 10 online pharmacy in india: india online pharmacy – reputable indian online pharmacy
people’s pharmacy wellbutrin xl MediDirect USA central rx pharmacy
Mexican Pharmacy Hub: Mexican Pharmacy Hub – best mexican online pharmacies
indianpharmacy com: Indian Meds One – india pharmacy
indian pharmacy online: online shopping pharmacy india – indian pharmacy online
https://indianmedsone.shop/# Indian Meds One
remedies rx pharmacy MediDirect USA MediDirect USA
best india pharmacy: indian pharmacy online – Indian Meds One
reputable indian online pharmacy: Indian Meds One – Indian Meds One
Indian Meds One: mail order pharmacy india – indian pharmacy paypal
Indian Meds One Indian Meds One india pharmacy mail order
http://medidirectusa.com/# Paxil
Online medicine home delivery: п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india – Indian Meds One
watson pharmacy viagra: lamisil online pharmacy – MediDirect USA
indian pharmacy: top online pharmacy india – Indian Meds One
medication from mexico pharmacy: Mexican Pharmacy Hub – best mexican online pharmacies
MediDirect USA tamoxifen pharmacy MediDirect USA
Botox price Marbella http://www.cosmetology-in-marbella.com .
buying from online mexican pharmacy: mexican rx online – Mexican Pharmacy Hub
https://mexicanpharmacyhub.com/# best online pharmacies in mexico
safe place to buy semaglutide online mexico: cheap cialis mexico – isotretinoin from mexico
giant food store pharmacy: MediDirect USA – permethrin cream pharmacy
Indian Meds One cheapest online pharmacy india indian pharmacy
Indian Meds One: top 10 online pharmacy in india – india pharmacy mail order
MediDirect USA: coop pharmacy store locator – MediDirect USA
лучшая клиника косметологии лучшая клиника косметологии .
Online medicine home delivery: Indian Meds One – best india pharmacy
avandia specialty pharmacy: valtrex mexico pharmacy – Desyrel
cheap mexican pharmacy rybelsus from mexican pharmacy buy from mexico pharmacy
legit mexican pharmacy for hair loss pills: Mexican Pharmacy Hub – order kamagra from mexican pharmacy
Indian Meds One: Indian Meds One – Indian Meds One
http://mexicanpharmacyhub.com/# Mexican Pharmacy Hub
Indian Meds One: reputable indian online pharmacy – Online medicine order
buy medicines online in india: online pharmacy india – Indian Meds One
Mexican Pharmacy Hub Mexican Pharmacy Hub legit mexican pharmacy for hair loss pills
Indian Meds One: Indian Meds One – indianpharmacy com
buy viagra from mexican pharmacy: Mexican Pharmacy Hub – Mexican Pharmacy Hub
top online pharmacy india: Indian Meds One – cheapest online pharmacy india
https://medidirectusa.com/# no prescription pharmacy
Indian Meds One india pharmacy mail order Indian Meds One
Mexican Pharmacy Hub: trusted mexico pharmacy with US shipping – Mexican Pharmacy Hub
indian pharmacies safe: indian pharmacies safe – Indian Meds One
india pharmacy mail order: Indian Meds One – indian pharmacy paypal
MediDirect USA: pill pharmacy – MediDirect USA
viagra certified pharmacy online global rx pharmacy irvine MediDirect USA
Indian Meds One: buy medicines online in india – best online pharmacy india
[url=https://japan-medical-training.ru/]Лиофильная сушка[/url] — это передовая технология, обеспечивающая деликатное удаление влаги путём их замораживания и последующего сублимационного испарения. Процесс лиофильной сушки позволяет сохранить структуру, состав и активность вещества, что критично в фармацевтике, биотехнологиях и пищевой промышленности. Лабораторные лиофильные аппараты дают возможность тонкой настройки температуры и давления, что снижает риски потери ценных свойств. Небольшие модели лиофильных сушилок подходят для научных задач, удобная для ежедневного применения при ограниченном пространстве. Лиофилизация актуальна при создании вакцин, консервировании микроорганизмов и ферментов. Лиофилизация продлевает стабильность и пригодность продуктов в сложных условиях. Высушенные образцы можно легко восстанавливать водой без потери качества. Кроме того, современные модели лиофильных сушилок оснащаются сенсорными дисплеями, USB-интерфейсами и системами защиты. На рынке представлены устройства как для научных исследований, так и для производственных нужд. Ключ к успеху — точная настройка времени заморозки, температуры и уровня вакуума. Технология широко внедрена в научных учреждениях и лабораториях по всему миру. Покупка лиофильного оборудования — это вклад в эффективность лабораторных процессов.
https://japan-medical-training.ru/
https://mexicanpharmacyhub.com/# mexican mail order pharmacies
Mexican Pharmacy Hub: Mexican Pharmacy Hub – Mexican Pharmacy Hub
Indian Meds One: Indian Meds One – Indian Meds One
Indian Meds One world pharmacy india Indian Meds One
Увеличьте свою аудиторию с помощью лайки youtube!
Количество подписчиков в Телеграме играет ключевую роль в развитии вашего канала. Знание стратегий привлечения и удержания подписчиков может значительно повысить эффективность вашего канала.
Создание привлекательного контента — это первоначальный этап на пути к росту числа подписчиков. Люди не будут подписываться на канал, если не найдут там ничего полезного или интересного.
Другим способом увеличения числа подписчиков является проведение активной рекламной кампании. Использование социальных сетей для рекламы канала может значительно ускорить прирост подписчиков.
Регулярное взаимодействие с вашей аудиторией способствует не только ее удержанию, но и привлечению новых подписчиков. Задавайте вопросы и проводите опросы для улучшения понимания потребностей вашей аудитории.
Indian Meds One: indianpharmacy com – best online pharmacy india
Indian Meds One: Indian Meds One – Indian Meds One
Mexican Pharmacy Hub: modafinil mexico online – amoxicillin mexico online pharmacy
MediDirect USA MediDirect USA abilify india pharmacy
Allegra: thailand pharmacy ambien – online pharmacy flovent
MediDirect USA: MediDirect USA – MediDirect USA
https://shorturl.fm/ZiwL6
buy prescription drugs from india: mail order pharmacy india – Indian Meds One
MediDirect USA: best no prescription pharmacy – discount pharmacy viagra
roman online pharmacy reviews MediDirect USA viagra best online pharmacy
buy viagra us pharmacy: viagra pharmacy prices – which pharmacy has the best price on viagra
п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india: mail order pharmacy india – Indian Meds One
MediDirect USA clozapine registered pharmacy MediDirect USA
buy viagra from mexican pharmacy: Mexican Pharmacy Hub – Mexican Pharmacy Hub
Mexican Pharmacy Hub: best online pharmacies in mexico – Mexican Pharmacy Hub
https://medidirectusa.com/# publix pharmacy online
Нужен вентилируемый фасад: алюминиевая подсистема для вентилируемых фасадов
Нужны пластиковые окна: заказать пластиковые окна
Indian Meds One: cheapest online pharmacy india – Indian Meds One
MediDirect USA: spironolactone in house pharmacy – rx reliable pharmacy
top 10 online pharmacy in india: Indian Meds One – Indian Meds One
generic viagra canadian pharmacy: SildenaPeak – SildenaPeak
truth behind generic cialis Tadalify snorting cialis
Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging: Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men – KamaMeds
https://tadalify.shop/# Tadalify
Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped: Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect – Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men
Tadalify: Tadalify – buy cialis online from canada
Kamagra reviews from US customers: Kamagra reviews from US customers – Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped
Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men Online sources for Kamagra in the United States Online sources for Kamagra in the United States
Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect: KamaMeds – Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men
http://kamameds.com/# Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives
how well does cialis work: Tadalify – Tadalify
Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect ED treatment without doctor visits
Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men: Men’s sexual health solutions online – Kamagra reviews from US customers
ny delivery delivery nyc
Kamagra reviews from US customers: Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives – Online sources for Kamagra in the United States
Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect [url=http://kamameds.com/#]Men’s sexual health solutions online[/url] Kamagra reviews from US customers
https://shorturl.fm/Ze3bM
Kamagra oral jelly USA availability: Kamagra reviews from US customers – Online sources for Kamagra in the United States
Tadalify: Tadalify – Tadalify
nyc freight new york freight
Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging: Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging – Men’s sexual health solutions online
Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men Men’s sexual health solutions online Men’s sexual health solutions online
Kamagra reviews from US customers: KamaMeds – ED treatment without doctor visits
Tadalify when will cialis become generic cheap cialis generic online
Tadalify: Tadalify – Tadalify
Safe access to generic ED medication: Men’s sexual health solutions online – Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped
canadian pharmacy cialis brand: Tadalify – cialis a domicilio new jersey
buy cialis united states: cialis generic for sale – where to get generic cialis without prescription
http://tadalify.com/# Tadalify
what does cialis treat: Tadalify – cialis 30 mg dose
Online sources for Kamagra in the United States: ED treatment without doctor visits – Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped
tadalafil liquid review shelf life of liquid tadalafil Tadalify
Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives: Men’s sexual health solutions online – Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped
Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging: Online sources for Kamagra in the United States – ED treatment without doctor visits
active ingredient in cialis: cialis free trial offer – does medicare cover cialis
SildenaPeak viagra 100 price SildenaPeak
http://sildenapeak.com/# SildenaPeak
Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging: Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men – Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging
cialis and blood pressure: Tadalify – tadalafil (exilar-sava healthcare) version of cialis] (rx) lowest price
Men’s sexual health solutions online: Kamagra reviews from US customers – Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men
purchase cialis on line cialis for sale brand Tadalify
maxim peptide tadalafil citrate: cialis prescription online – Tadalify
KamaMeds: Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives – ED treatment without doctor visits
https://tadalify.com/# Tadalify
cialis prices: cialis medicine – Tadalify
SildenaPeak: order viagra online no prescription – can i buy over the counter viagra
buy viagra in us online how much is female viagra pill viagra gel in india
cialis for daily use side effects: Tadalify – cialis dapoxetine europe
https://shorturl.fm/f6Cot
Online sources for Kamagra in the United States: Online sources for Kamagra in the United States – Safe access to generic ED medication
cheap sildenafil 100mg: buy viagra online new zealand – SildenaPeak
Tadalify Tadalify Tadalify
SildenaPeak: how to buy viagra over the counter – viagra south africa
https://kamameds.shop/# Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging
Качественные шины — это залог безопасности на дороге, обеспечивающая надёжное торможение даже в сложных погодных условиях .
Подходящие по сезону шины минимизируют риск заносов во время дождя , поддерживая вашу безопасность .
Выбор износостойкой резины сокращают расходы на топливо благодаря низкому сопротивлению .
Плавность хода обеспечивается качества протектора , вместе с прочностью каркаса .
Своевременная смена сезонки снижает риск аварийных ситуаций, сохраняя безопасность пассажиров.
Не экономьте на шинах — это напрямую влияет сохранность жизни даже в экстренных случаях.
http://strahove.evropea.com/index.php?topic=300.new#new
Качественные шины — это залог безопасности на дороге, гарантирующая стабильное сцепление даже в сложных погодных условиях .
Правильно подобранные покрышки снижают вероятность заносов в условиях гололёда, сохраняя вашу безопасность .
Покупка проверенных покрышек экономят средства на обслуживание за счёт оптимального качения .
Точный отклик руля определяется состояния резины , а также составом резиновой смеси .
Регулярная замена изношенной резины защищает от повреждения дисков , сохраняя безопасность пассажиров.
Не экономьте на шинах — это определяет сохранность жизни даже в экстренных случаях.
http://zhensizhuan.xclub.tw/viewthread.php?tid=187645&extra=
Tadalify: cialis definition – Tadalify
SildenaPeak: buy viagra online – viagra 150 mg online
buy cipla tadalafil cialis buy Tadalify
shipping new york ny delivery
SildenaPeak: cheap generic viagra 150 mg – SildenaPeak
Tadalify: purchase cialis online cheap – cheap generic cialis canada
viagra prescription australia: SildenaPeak – female viagra buy online in india
SildenaPeak: SildenaPeak – SildenaPeak
https://sildenapeak.shop/# SildenaPeak
Tadalify: Tadalify – cialis side effects
delivery new york shipping in nyc
sildenafil canada prescription: SildenaPeak – SildenaPeak
delivery nyc https://delivery-new-york.com/
SildenaPeak SildenaPeak generic sildenafil prescription
Kamagra reviews from US customers: Men’s sexual health solutions online – Men’s sexual health solutions online
how can i get viagra in canada: canadian pharmacy viagra paypal – where can i buy cheap viagra online
https://sildenapeak.shop/# SildenaPeak
SildenaPeak: order viagra online pharmacy – buy real viagra canada
cialis professional 20 lowest price: tadalafil dose for erectile dysfunction – Tadalify
Kamagra reviews from US customers Kamagra reviews from US customers KamaMeds
sildenafil capsules in india: SildenaPeak – SildenaPeak
Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging: Men’s sexual health solutions online – Safe access to generic ED medication
Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect: Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging – ED treatment without doctor visits
Tadalify difference between tadalafil and sildenafil cialis for sale online
purchase viagra online in usa: SildenaPeak – can you buy viagra over the counter
http://kamameds.com/# Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men
cialis generics: Tadalify – cialis for sale over the counter
buy generic cialis: Tadalify – Tadalify
Kamagra reviews from US customers Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging
Tadalify: original cialis online – cialis dose
Tadalify: buy cialis canadian – Tadalify
https://shorturl.fm/3uvLP
http://sildenapeak.com/# SildenaPeak
how to buy viagra online usa: sildenafil generic discount – where can i buy viagra otc
viagra no prescription canada how to buy generic viagra SildenaPeak
SildenaPeak: best generic viagra – generic viagra online
generic viagra online pharmacy india: sildenafil 50 mg buy online – SildenaPeak
KamaMeds: Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped – Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging
A friend of mine advised this site. And yes. it has some useful pieces of info and I enjoyed scaning it. Therefore i would love to drop you a quick note to express my thank. Take care
Whenever a winning symbol explodes, its spot is marked on the grid. If another blasts upon that spot for a second time, a multiplier is added, starting from x2 and doubling up to x1,024 with each instance. The resulting multiplier is added to all winning combinations that are formed on top of it. Diabetes Scotland is proud to be able to congratulate Team Sugar Rush from Inverness, who are celebrating their fourth year of fundraising success. Basic Game Info Verification can help ensure real people are writing the reviews you read on Trustpilot. Join us for the eighth annual Sugar Rush 5k race, 1-mile fun run, and 1-mile walk! Together we can make a difference in our community. By visiting our site and or purchasing something from us, you engage in our “Service” and agree to be bound by the following terms and conditions (“Terms of Service”, “Terms”), including those additional terms and conditions and policies referenced herein and or available by hyperlink. These Terms of Service apply to all users of the site, including without limitation users who are browsers, vendors, customers, merchants, and or contributors of content.
https://nyvapeplus.com/online-casino-game-colour-trading-by-tadagaming-a-review-and-withdrawal-guide-for-pakistani-players/
You know what you want to achieve… but how can you get there? With dozens of educational resources, guides, quizzes, and customizable templates at your fingertips, you’re sure to connect the financial dots in planning, implementing, and reaching success. The gift code system used by the platform provides extra chances to earn money and keeps users active by giving gifts and surprises regularly. These codes have possibilities of opening up various rewards such as bonus credits, free plays and even special modes of exclusive gaming that users using OK Win Color will definitely find interesting to employ and explore on a daily basis. Color trading is a type of online trading where users predict the outcome of a pattern based on color, frequently in an approach similar to a game. It works similarly to a game of guessing in which traders select a color (for example, red, green, or blue) and profit if their prediction is accurate. Users of these platforms bet based on their analysis or luck, and algorithms are used to decide color outcomes.
Tadalify cialis daily side effects purchasing cialis
SildenaPeak: viagra for sale uk – SildenaPeak
GMO Gaika Reputation – Pros, Cons, and the Truth About Withdrawal Refusals
GMO Gaika is widely used by both beginners and experienced FX traders. Its popularity stems from easy-to-use trading tools, stable spreads, and a high level of trust due to its operation by a major Japanese company. Many users feel secure thanks to this strong domestic backing.
On the other hand, there are some online rumors about “withdrawal refusals,” but in most cases, these are due to violations of terms or incomplete identity verification. GMO Gaika’s transparent response to such issues suggests that serious problems are not a frequent occurrence.
You can find more detailed insights into the pros and cons of GMO Gaika, as well as real user experiences, on the trusted investment site naughty-cao.jp. If you’re considering opening an account, it’s a good idea to review this information beforehand.
https://tadalify.shop/# Tadalify
SildenaPeak: viagra australia buy – SildenaPeak
I encountered your site after doing a search for new contesting using Google, and decided to stick around and read more of your articles. Thanks for posting, I have your site bookmarked now.
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
Выяснить больше – https://quick-vyvod-iz-zapoya-1.ru/
https://shorturl.fm/tNOhR
Обучение английского с малого возраста крайне важно.
На этом этапе способности ребёнка легко воспринимает новые знания.
Первые шаги с иностранной речью формирует память.
К тому же, ребёнку становится проще изучать другие языки в будущем.
Практика английского даёт многочисленные перспективы в учёбе и жизни.
Таким образом, освоение с детства английского ведёт к высоким результатам.
http://forum.zplatformu.com/index.php?topic=413976.new#new
Kamagra oral jelly USA availability ED treatment without doctor visits Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped
SildenaPeak: best viagra tablets india – SildenaPeak
Enjoyed studying this, very good stuff, thanks.
cialis recreational use: Tadalify – Tadalify
sildenafil uk otc: order viagra australia – cheap generic viagra online
Tadalify: Tadalify – order cialis canada
SildenaPeak: SildenaPeak – viagra cheapest prices
http://tadalify.com/# is tadalafil the same as cialis
KamaMeds Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives
https://shorturl.fm/FlMLD
viagra tablets in india online purchase: SildenaPeak – SildenaPeak
Hi, possibly i’m being a little off topic here, but I was browsing your site and it looks stimulating. I’m writing a blog and trying to make it look neat, but everytime I touch it I mess something up. Did you design the blog yourself?
price of viagra 100mg uk: SildenaPeak – SildenaPeak
Tadalify: cialis 5mg best price – cialis canada sale
Tadalify Tadalify Tadalify
ED treatment without doctor visits: Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives – Men’s sexual health solutions online
Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men: Kamagra reviews from US customers – Safe access to generic ED medication
https://kamameds.shop/# Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped
Tadalify: Tadalify – cialis daily dosage
is tadalafil from india safe cialis 5mg price walmart cialis prices at walmart
Этот информативный текст выделяется своими захватывающими аспектами, которые делают сложные темы доступными и понятными. Мы стремимся предложить читателям глубину знаний вместе с разнообразием интересных фактов. Откройте новые горизонты и развивайте свои способности познавать мир!
Узнать больше – https://quick-vyvod-iz-zapoya-1.ru/
ED treatment without doctor visits: Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging – Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging
Kamagra reviews from US customers: Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives – Safe access to generic ED medication
Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives: Kamagra reviews from US customers – KamaMeds
SildenaPeak: SildenaPeak – SildenaPeak
best time to take cialis Tadalify Tadalify
I think other website proprietors should take this web site as an model, very clean and great user pleasant style and design .
Online sources for Kamagra in the United States: Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging – Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives
http://sildenapeak.com/# SildenaPeak
стоимость оценки ООО оценочная компания
https://shorturl.fm/XiQSc
В этом информативном обзоре собраны самые интересные статистические данные и факты, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тренды. Мы представим вам цифры и графики, которые иллюстрируют, как развиваются различные сферы жизни. Эта информация станет отличной основой для глубокого анализа и принятия обоснованных решений.
Подробнее – https://quick-vyvod-iz-zapoya-1.ru/
Note: If you’re in a state that has not legalized online casinos, you’ll see a list of top sweepstakes social casinos, which are available in most states. All of them have casino-style games you can play for free or to redeem cash prizes. Open an online slot and look for a spot in the corners to click and view information on the game. It might be a lowercase “i” (information), a question mark, or three horizontal lines. That information will tell you what the symbols mean, the payline structure, how to adjust your bets and the game’s RTP percentage. Your application has been sent successfully. We will talk to you soon. Many of these sweepstakes casinos (also known as social casinos) provide popular casino games, including free slot games, table games and live dealer games. In Almighty Buffalo Megaways, the symbols reflect the game’s Wild West theme, featuring various wildlife and traditional slot icons. The buffalo symbol offers the highest payout (up to 50x your bet), followed by the bear (5x), wolf (2.5x), and moose (2x).
https://creativehand.co.in/inside-the-1x-game-version-of-bgamings-plinko/
UFC also recently lost one of its other big stars, understand the rules of the game. Blueprint Gaming have taken the Megaways mechanic and taken it to town thanks to their great talent in design and panache for innovation, set a budget. Mobile players can have a fully interactive live table from a real casino webcast to their device, if you’re looking for unusually profitable slot machines. Can i win real money on casino apps the platform is optimized for mobile devices, we can say that WooCasino is an excellent guide to the world of quality gambling. The Money Men Megaways Slots are massively popular. You spin the reels and hope to land on a winning combination. There are several tips and tricks to improve how you bet on slot games, whether you’re playing for free or real money with no deposit free spins. Our top tip is to think about paylines. Take the time to research each game’s paylines before you play to know which ones give you the biggest chance to win. At Casino.org we’ve got hundreds of free online slot machines for you to enjoy
generic tadalafil in us: Tadalify – order generic cialis online
Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men Men’s sexual health solutions online
Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped: Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives – Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped
tadalafil prescribing information: cialis payment with paypal – cost of cialis for daily use
Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped: Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped – Kamagra reviews from US customers
Online sources for Kamagra in the United States: Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped – Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging
This is something that will need all of our combined efforts to address.
Kamagra oral jelly USA availability: Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect – Online sources for Kamagra in the United States
https://shorturl.fm/UQUpT
https://tadalify.shop/# tadalafil 20mg (generic equivalent to cialis)
cialis bodybuilding vidalista 20 tadalafil tablets cialis price comparison no prescription
Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives: Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped – Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives
is tadalafil as effective as cialis: cheap cialis free shipping – tadalafil 40 mg india
Tadalify: Tadalify – generic cialis tadalafil 20mg india
оценка малого бизнеса https://ocenochnaya-kompaniya1.ru
SildenaPeak: where can you get viagra – cheap sildenafil canada
Tadalify: Tadalify – Tadalify
https://shorturl.fm/h3AKA
KamaMeds Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect
клиника эстетической медицины и косметологии клиника эстетической медицины и косметологии .
медицинский косметолог медицинский косметолог .
KamaMeds: ED treatment without doctor visits – KamaMeds
https://sildenapeak.com/# SildenaPeak
оценка цены выкупа акций сайт оценочной компании
cheap generic viagra 100mg canada: 12.5 mg viagra – SildenaPeak
Safe access to generic ED medication KamaMeds Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men
[url=https://vipusknick.ru/]Канцелярские товары для дома и офиса[/url] — это важная часть ежедневной жизни, которая помогает поддерживать порядок и повышает эффективность. Регулярное использование канцелярских принадлежностей облегчает процесс работы и учебы. Современные производители предлагают широкий ассортимент: от простых карандашей и ручек до специализированных аксессуаров. Для офиса особенно востребованы папки, скоросшиватели, блокноты, маркеры и наборы бумаги. Канцелярские принадлежности в домашних условиях помогают детям и взрослым. Основное достоинство канцелярии в том, что она подходит для разных сфер жизни. Сегодня все чаще товары для офиса и дома приобретают в онлайн-магазинах. Покупка онлайн позволяет выбирать из десятков вариантов и получать товары прямо домой. Для бизнеса выгодно приобретать канцелярию оптом. Для личного использования канцелярию обычно берут в небольших количествах. Разнообразие производителей и брендов позволяет подобрать канцтовары на любой вкус и кошелек. Хорошая канцелярия отличается прочностью и комфортом. Рекомендуется оценивать качество исполнения и надежность. Использование качественных принадлежностей мотивирует и вдохновляет. Таким образом, канцтовары для дома и офиса остаются незаменимыми помощниками в учебе, бизнесе и быту.
https://vipusknick.ru/
SildenaPeak: buy sildenafil generic canada – SildenaPeak
Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men: Kamagra oral jelly USA availability – Kamagra reviews from US customers
prednisone 20 mg: SteroidCare Pharmacy – SteroidCare Pharmacy
can you buy clomid without prescription: where can i buy generic clomid pill – how can i get clomid tablets
Freight delivery from China is trustworthy and fast.
Our company delivers tailored solutions for enterprises of any capacity.
We take care of all shipping processes to make your operations smooth.
cargo shipping from china air prices
With scheduled shipments, we ensure timely dispatch of your orders.
Clients trust our skilled team and affordable rates.
Choosing us means confidence in every order.
TrustedMeds Direct TrustedMeds Direct amoxicillin 500mg prescription
TrustedMeds Direct: amoxicillin 875 mg tablet – amoxicillin online without prescription
Откройте для себя мир комфорта с автоматическими рулонными шторами с электроприводом, которые идеально подходят для создания уюта в вашем доме.
Рулонные шторы с электроприводом — это удобное и стильное решение для современных интерьеров. Они позволяют не только регулировать уровень света в помещении, но и добавляют уют в ваш дом .
Электрические шторы имеют множество преимуществ. Управление такими шторами с помощью пульта делает их использование комфортным и практичным. В-третьих, рулонные шторы могут быть связаны с другими умными устройствами в вашем доме.
Установить рулонные шторы с электроприводом можно в любом помещении . Вполне естественно, что такие шторы находят свое применение не только в домашних условиях. Однако для установки рулонных штор нужно предусмотреть наличие источника электричества .
Фактор выбора материала и дизайна штор также играет важную роль. Можно найти рулонные шторы в самых разнообразных вариантах, что помогает гармонично вписать их в интерьер. Наконец, стоит заметить, что есть возможность заказать шторы по индивидуальным размерам.
CardioMeds Express: CardioMeds Express – CardioMeds Express
SteroidCare Pharmacy: buy prednisone from canada – SteroidCare Pharmacy
amoxicillin 750 mg price: purchase amoxicillin online – amoxicillin 500mg pill
IverGrove: ivermectin acne – ivermectin discovery
buy amoxicillin online no prescription TrustedMeds Direct amoxicillin 500 mg without a prescription
cheap vps hosting vps hosting
SteroidCare Pharmacy: SteroidCare Pharmacy – 5mg prednisone
CardioMeds Express: lasix – lasix 100mg
TrustedMeds Direct buy amoxicillin 500mg uk TrustedMeds Direct
over the counter prednisone medicine: prednisone 50 mg price – where can i get prednisone
TrustedMeds Direct: TrustedMeds Direct – can we buy amoxcillin 500mg on ebay without prescription
amoxicillin 500 mg purchase without prescription: TrustedMeds Direct – buy amoxicillin online with paypal
http://cardiomedsexpress.com/# CardioMeds Express
amoxicillin 800 mg price: TrustedMeds Direct – TrustedMeds Direct
TrustedMeds Direct: amoxicillin no prescription – TrustedMeds Direct
Здравствуйте!
Долго не спал и думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты в топ и узнал от успещных seo,
энтузиастов ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное лучший прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Линкбилдинг курс ускоряет обучение специалистов. Линкбилдинг Москва предоставляет локальные возможности для продвижения. Линкбилдинг курсы позволяют освоить техники Xrumer. Линкбилдинг план помогает системно создавать ссылки. Линкбилдинг правила обеспечивают соблюдение безопасных методов продвижения.
сео социальные сети, продвижения сайта google, линкбилдинг это что
линкбилдинг стратегии, интернет продвижение сайтов москва, сайт магазина продвижения
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
[url=https://forzacoin.org/]FORZA Coin[/url] represents a new wave of blockchain innovation built on the Binance Smart Chain. The FORZA™ project generates income for holders simply by holding while driving the development of a community-driven NFT marketplace. Compared to typical BSC coins, the system ensures long-term security including long-term liquidity lock to secure the project, built-in anti-bot defense, and deflationary mechanics ensuring scarcity. Holders benefit from passive income through reflections, strengthening loyalty to the project. FORZA’s upcoming NFT ecosystem will serve creators and collectors with next-gen features with low fees and decentralized governance. Through merging passive income with NFT innovation, FORZA Coin delivers an ecosystem built for growth. Community plays a central role, shaping the roadmap. That means members are co-creators of the project, and directly influence the long-term vision. Transparency, security, and rewards make up the philosophy behind the project, setting it apart from the majority of BSC tokens. Whether you are an investor, this token presents passive rewards and strong fundamentals. The roadmap of FORZA Coin is entering its most exciting phase, and being part of it today means future rewards. Join the FORZA Coin community, earn passive income by holding, and see how innovation meets community.
https://forzacoin.org/
Рулонные шторы блэкаут с электроприводом идеально подойдут для создания уюта и контроля освещения в вашем доме.
превосходный выбор для. Эти шторы эффективно блокируют свет, что способствует комфортному сну даже днём.
Важным преимуществом рулонных штор блэкаут с электроприводом считается. Вы можете управлять шторами с помощью пульта дистанционного управления, что упрощает их использование в современном дизайне.
К тому же, рулонные шторы блэкаут легко устанавливаются. Вы можете выбрать различные варианты крепления. Таким образом, вы сможете легко установить шторы на любые окна.
Важно отметить, что электроприводные рулонные шторы блэкаут имеют. Это поможет вам сохранить тепло в холодное время года. Таким образом, рулонные шторы блэкаут с электроприводом – это не только стильный, но и практичный выбор.
Добрый день!
Долго ломал голову как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить CF cituation flow и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
отличных ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное буст прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Программное обеспечение для постинга ускоряет создание ссылок. Ускоренный рост ссылочного профиля виден после первых прогонах. Xrumer: создание ссылочной массы облегчает работу. Линкбилдинг через форумы и блоги помогает получать релевантные ссылки. Повышение авторитетности домена становится возможным с Xrumer.
seo алгоритмы, сайт анализа продвижения сайта, Улучшение ссылочного профиля с Xrumer
Постинг на блогах для SEO, seo и копирайтинг, seo обзор
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
amoxicillin canada price: TrustedMeds Direct – TrustedMeds Direct
TrustedMeds Direct: amoxicillin 500 – TrustedMeds Direct
IverGrove: robert malone ivermectin – scabies ivermectin dosage
TrustedMeds Direct: TrustedMeds Direct – TrustedMeds Direct
[url=https://ansep.ru/]планировщик дел под windows[/url] — это простое решение, которое помогает организовать рабочий день. Благодаря понятному интерфейсу пользователи могут создавать напоминания всего в несколько кликов. Такой софт идеален для фрилансеров, которые стремятся к дисциплине. В отличие от платных программ, такое приложение дает свободу использования без ограничений, сохраняя при этом надежность. Он дает возможность составлять список целей на день, напоминает о событиях, а также фиксирует прогресс. Поддержка синхронизации делает использование еще более гибким, ведь задачи можно переносить между устройствами. Многие отмечают, что планировщик дел под windows free помогает снизить стресс. Программа экономит время и дает ощущение контроля. Для тех, кто ценит минимализм, предлагается удобное управление, а для любителей расширенных функций доступна возможность добавлять заметки. Применение планировщика помогает распределять нагрузку без перегрузок. Таким образом, windows task manager free становится универсальным помощником, который одинаково полезен школьникам, студентам и специалистам. Если вы нуждаетесь в простом решении для планирования, то этот бесплатный планировщик станет вашим верным выбором.
https://ansep.ru/
Рулонные шторы с аккумулятором предоставляют удобство и стиль для любого интерьера, позволяя легко управлять светом и обеспечивая полную свободу от проводов.
В заключение, рулонные шторы с батарейным питанием представляют собой актуальный тренд в оформлении интерьеров.
vps hosting windows vps hosting in europe
prednisone without prescription medication: SteroidCare Pharmacy – SteroidCare Pharmacy
https://steroidcarepharmacy.shop/# prednisone prescription online
Преобразите ваше пространство с помощью автоматических рулонных штор, которые идеально сочетают стиль и современность.
Все больше людей выбирают рулонные шторы с дистанционным управлением для своих домов. Данные изделия соединяют в себе удобство и эстетичность, что делает их идеальным выбором для различных помещений.
Управлять рулонными шторами можно, используя пульт дистанционного управления или специализированное мобильное приложение. Благодаря этому вы сможете легко настраивать уровень света и атмосферу в вашем доме.
Помимо этого, рулонные шторы представлены в множестве дизайнов и цветовых вариантах. Это дает возможность найти идеальный стиль, который будет соответствовать вашему домашнему дизайну.
Важно отметить, что рулонные шторы с дистанционным управлением также удобны в эксплуатации. Эти шторы просто чистятся и не требуют сложного ухода, что делает их подходящими для людей с плотным графиком.
Plinko demo mode offers players a lot of advantages. Most of these were listed by experienced players in their reviews. Our team has highlighted the main pros below: The link will expire in 72 hours. Keunggulannya, akun demo ini tidak hanya tanpa biaya, tapi juga dikenal sangat gacor. Banyak pemain memanfaatkannya untuk menganalisis pola scatter, mengeksplorasi fitur buy spin, ataupun menguji berbagai strategi taruhan. Jika kamu ingin bermain sambil meriset mekanisme game tanpa khawatir kehilangan dana, cukup akses, putar, dan nikmati keseruannya sepenuhnya gratis! The Plinko Demo allows players to engage in multiple rounds without any financial loss, which can be especially beneficial for users aiming to understand the game’s patterns. Platforms also provide interactive settings to customize the game to user preferences, including ball drop speed and board design, which makes for a personalized experience. These options allow players to explore plinko demo mode in a controlled and safe environment.
https://okanguraybulbul.com.tr/jetx-1win-casino-why-players-prefer-it-globally/
If 4 or more scatters land simultaneously, they launch the Buffalo King Megaways Free Spins round. For example, 4, 5, or 6 scatters can trigger 12, 17, and 22 Free Spins, respectively. In addition, landing 4, 5, or 6 scatters can pay out 5x, 20x, or 100x your stake, respectively. RTP stands for Return To Player. The RTP rate is an average calculated by the developer using a large sample of spins over a long period. It is displayed as a percentage and indicates the amount of money taken in by a slot game that is paid back out to players in the long term. The table below outlines the approximate payout potential for symbol combinations in the pragmatic play buffalo megaways, based on standard gameplay settings. These values represent multipliers applied to your current stake and can vary depending on bet size and feature triggers. In the buffalo king untamed megaways demo, these odds work identically, giving players a realistic preview of potential outcomes before playing with real money.
https://shorturl.fm/8fIrc
тележка косметолога кушетка косметологическая с электроприводом
Приобретите что лучше somfy или dooya и насладитесь комфортом и современными технологиями в своем доме.
Электроприводные рулонные шторы представляют собой идеальный способ управления освещением в помещении. Пользователи могут управлять рулонными шторами с электроприводом как через приложение на телефоне, так и с помощью пульта.
Главное достоинство рулонных штор с электроприводом заключается в удобстве использования. С помощью одного нажатия кнопки вы можете регулировать свет и тень в вашем помещении.
Электроприводные шторы могут быть настроены на автоматические режимы работы. Автоматизация позволяет вам выбирать расписание работы штор, что значительно упрощает жизнь.
Умные рулонные шторы легко интегрируются с концепцией “умного дома”, предоставляя новые возможности управления. Таким образом, шторы могут работать в связке с другими устройствами, что делает ваш дом более умным и адаптивным.
vps best hosting vps hosting
how to buy cheap clomid: FertiCare Online – where to get clomid prices
CardioMeds Express: lasix – CardioMeds Express
SteroidCare Pharmacy: best pharmacy prednisone – SteroidCare Pharmacy
stromectol online: ivermectin 4000 mcg – IverGrove
лампа косметолога ширма медицинская мск
furosemide 40mg: CardioMeds Express – CardioMeds Express
amoxicillin 1000 mg capsule: TrustedMeds Direct – TrustedMeds Direct
https://trustedmedsdirect.shop/# amoxicillin buy no prescription
саратов стоимость бетона сколько стоит куб бетона
FertiCare Online: cost clomid no prescription – can you buy clomid without prescription
ordering prednisone: SteroidCare Pharmacy – SteroidCare Pharmacy
SteroidCare Pharmacy: SteroidCare Pharmacy – where to buy prednisone 20mg
ivermectin buy australia: IverGrove – IverGrove
SteroidCare Pharmacy: SteroidCare Pharmacy – SteroidCare Pharmacy
prednisone 10mg SteroidCare Pharmacy buying prednisone
Рулонные шторы блэкаут с электроприводом идеально подойдут для создания уюта и контроля освещения в вашем доме.
поддержания атмосферы в жилом пространстве. Эти шторы эффективно блокируют свет, что дает возможность насладиться темнотой в любое время.
Основное достоинство электроприводных рулонных штор блэкаут заключается в. Управление шторами осуществляется при помощи пульта, что упрощает их использование в современном дизайне.
Кроме того, рулонные шторы с эффектом блэкаут просто монтируются. Вы можете выбрать различные варианты крепления. Такое разнообразие дает возможность подобрать шторы для любых оконных конструкций.
высокую степень теплоизоляции. С их помощью вы сможете поддерживать комфортную температуру в помещении зимой. Таким образом, рулонные шторы блэкаут с электроприводом – это не только стильный, но и практичный выбор.
IverGrove: IverGrove – ivermectin side effects
where buy generic clomid without rx: where buy clomid online – where can i buy generic clomid without dr prescription
order generic clomid without insurance: FertiCare Online – can i get clomid
Здравствуйте!
Долго обмозговывал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить CF cituation flow и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
отличных ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное top прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Прогон по базам форумов помогает охватывать больше ресурсов. Как увеличить показатели домена зависит от качества ссылок. Xrumer для продвижения сайта экономит время специалистов. SEO-прогон для новичков облегчает освоение инструментов. Рассылки с помощью Xrumer ускоряют процесс продвижения.
белое продвижение сайтов, программ продвижение сайта, Как собрать базу для Xrumer
Xrumer и рост Ahrefs DR, seo сайт анализ, агентство продвижения сайтов novelit
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
FertiCare Online: FertiCare Online – FertiCare Online
SteroidCare Pharmacy buy prednisone 10 mg SteroidCare Pharmacy
generic lasix: furosemide 40 mg – lasix tablet
https://shorturl.fm/SggQh
http://steroidcarepharmacy.com/# prednisone 10mg online
купить бетон цена https://beton-saratov64.ru
prednisone 10 prednisone 7.5 mg generic prednisone cost
Эффективные решения контроля трудовых часов способствуют улучшению производительности .
Автоматизация процессов устраняет погрешности при расчёте зарплат .
Менеджерам удобнее анализировать загрузку сотрудников дистанционно .
https://blondeporno.net/finance/the-best-methods-of-working-time-control-in-it-companies/
Сотрудники имеют удобный учёт к своим данным .
Внедрение таких систем заметно оптимизирует кадровые процессы с минимальными усилиями .
Такой подход обеспечивает прозрачность между отделами , сохраняя мотивацию сотрудников.
IverGrove: IverGrove – IverGrove
lasix 40 mg: CardioMeds Express – CardioMeds Express
бетон саратов официальный сайт бетон официальный сайт
IverGrove: IverGrove – is noromectin the same as ivermectin
buying cheap clomid: cheap clomid without prescription – can i buy generic clomid no prescription
http://cardiomedsexpress.com/# CardioMeds Express
where can i buy prednisone online without a prescription: SteroidCare Pharmacy – prednisone for sale online
acquistare farmaci senza ricetta: tadalafil 10mg 20mg disponibile online – Farmacie online sicure
Farmacie on line spedizione gratuita acquisto discreto di medicinali in Italia Farmacie online sicure
top farmacia online: consegna rapida in tutta Italia – farmacie online affidabili
http://farmacidiretti.com/# acquistare farmaci senza ricetta
Farmacia online piГ№ conveniente: farmacia italiana affidabile online – Farmacia online piГ№ conveniente
мониторинг дорожного транспорта мониторинг дорожного транспорта .
купить зеркало от производителя zerkalo-nn-1.ru .
farmacie online affidabili: acquistare cialis generico online – Farmacia online miglior prezzo
farmacie online autorizzate elenco accesso rapido a cialis generico online farmacie online sicure
viagra online spedizione gratuita: sildenafil senza ricetta – le migliori pillole per l’erezione
farmacia online senza ricetta: acquistare kamagra gel online – comprare farmaci online all’estero
https://farmacidiretti.shop/# Farmacia online piГ№ conveniente
farmacia online senza ricetta farmaci generici a prezzi convenienti farmacia online
top farmacia online: FarmaciDiretti – Farmacie online sicure
farmacia online: accesso rapido a cialis generico online – Farmacia online migliore
acquistare farmaci senza ricetta kamagra oral jelly spedizione discreta farmacie online autorizzate elenco
https://shorturl.fm/HgbLi
top farmacia online: tadalafil senza ricetta – acquistare farmaci senza ricetta
farmacia online senza ricetta: accesso rapido a cialis generico online – Farmacia online miglior prezzo
https://farmacidiretti.com/# farmacie online affidabili
alternativa al viagra senza ricetta in farmacia: sildenafil senza ricetta – alternativa al viagra senza ricetta in farmacia
migliori farmacie online 2024 ForzaIntima acquisto farmaci con ricetta
pillole per erezioni fortissime: PotenzaFacile – viagra naturale in farmacia senza ricetta
farmacia online: Pillole Subito – acquisto farmaci con ricetta
https://potenzafacile.com/# gel per erezione in farmacia
Farmacia online migliore: farmacia online cialis Italia – farmacia online
п»їFarmacia online migliore: soluzioni rapide per la potenza maschile – top farmacia online
esiste il viagra generico in farmacia: sildenafil senza ricetta – gel per erezione in farmacia
[url=https://earnforexrebates.com/]Forex Rebates[/url] are a powerful way for traders to get more value from everyday trading. With EarnForexRebates.com you gain access to a trusted rebate system that rewards you on every trade. Unlike complicated promotions, our service is straightforward and easy to use. The system works thanks to our direct cooperation with top-tier Forex companies, which allows us to deliver the best conditions available in the market. Every trade you make can return money back to you, whether you win or lose. EarnForexRebates.com does not interfere with your trading, meaning that you continue trading exactly as you do now, while we help you increase your overall returns. Clients can check our detailed cashback schedule to see exactly how much they will receive for every lot traded. This level of clarity makes it easy for traders to plan their costs. By joining EarnForexRebates.com, traders not only get cash back instantly, but also feel secure knowing they work with a reliable partner. The rebate system is perfect for experienced traders, because it fits seamlessly into existing trading. Many users report that their trading performance feels more rewarding, simply by claiming cashback. With automatic crediting, your rebate arrives without delay. If you are looking for a safe tool to increase returns, EarnForexRebates.com is the solution that combines straightforward service and financial benefits. Sign up today and unlock the cashback potential of your strategy.
https://earnforexrebates.com/
[url=https://earnforexrebates.com/]Forex Rebates[/url] are a powerful way for traders to maximize their earnings from everyday trading. With EarnForexRebates.com you gain access to a reliable rebate system that rewards you on every trade. Unlike time-limited offers, our service is simple and transparent. The system works thanks to our agreements with global brokerage firms, which allows us to deliver the best conditions available in the market. Every trade you make can bring you passive income, whether you win or lose. EarnForexRebates.com does not interfere with your trading, meaning that you continue trading exactly as you do now, while we help you increase your overall returns. Clients can check our detailed cashback schedule to see exactly how much they will receive for every lot traded. This level of detail makes it easy for traders to understand the real value of each deal. By joining EarnForexRebates.com, traders not only receive consistent payments, but also benefit from cooperation with trusted brokers. The rebate system is ideal for beginners, because it requires no extra effort. Many users report that their overall profits have improved, simply by collecting rebates. With automatic crediting, your cashback is always on time. If you are looking for a competitive advantage, EarnForexRebates.com is the right choice that combines straightforward service and financial benefits. Sign up today and unlock the cashback potential of your strategy.
https://earnforexrebates.com/
п»їFarmacia online migliore consegna rapida in tutta Italia migliori farmacie online 2024
farmacie online affidabili: ForzaIntima – comprare farmaci online all’estero
viagra cosa serve PotenzaFacile farmacia senza ricetta recensioni
Преобразите ваше пространство с помощью умных рулонных штор для дома, которые идеально сочетают стиль и современность.
Дистанционно управляемые рулонные шторы приобретают популярность в современных интерьерах. Данные изделия соединяют в себе удобство и эстетичность, что делает их идеальным выбором для различных помещений.
Управлять рулонными шторами можно, используя пульт дистанционного управления или специализированное мобильное приложение. Это позволяет легко регулировать освещение и создавать уютную атмосферу в вашем доме.
Также рулонные шторы доступны в различных стилях и цветовых решениях. Это позволит вам подобрать идеальный вариант, который будет гармонировать с вашим интерьером.
Следует подчеркнуть, что рулонные шторы с дистанционным управлением очень практичны в повседневной жизни. Их просто поддерживать в чистоте, и они не требуют сложного ухода, что идеально подходит для занятых людей.
farmacie online sicure: ordina tadalafil da casa in Italia – Farmacia online miglior prezzo
farmacia online senza ricetta: consegna rapida e riservata kamagra – comprare farmaci online all’estero
https://shorturl.fm/0g6PF
chlorphentermine
Мы гарантируем конфиденциальность всех покупок.
BorderMeds Express prescription drugs mexico pharmacy safe place to buy semaglutide online mexico
https://maplemedsdirect.shop/# MapleMeds Direct
BharatMeds Direct: BharatMeds Direct – BharatMeds Direct
MapleMeds Direct: MapleMeds Direct – MapleMeds Direct
Преобразите ваше пространство с помощью автоматических рулонных штор, которые идеально сочетают стиль и современность.
Все больше людей выбирают рулонные шторы с дистанционным управлением для своих домов. Эти шторы предлагают удобство и стиль, что делает их отличным решением для любого помещения.
Управление рулонными шторами можно производить с помощью пульта или мобильного приложения. Это позволяет легко регулировать освещение и создавать уютную атмосферу в вашем доме.
Также рулонные шторы доступны в различных стилях и цветовых решениях. Таким образом, вы сможете выбрать именно тот вариант, который идеально впишется в ваш интерьер.
Не стоит забывать, что дистанционно управляемые рулонные шторы очень удобны в использовании. Они легко чистятся и не требуют особого ухода, что делает их идеальными для занятых людей.
top 10 pharmacies in india: BharatMeds Direct – BharatMeds Direct
Рулонные шторы с аккумулятором предоставляют удобство и стиль для любого интерьера, позволяя легко управлять светом и обеспечивая полную свободу от проводов.
Аккумуляторные рулонные шторы – это прекрасный выбор для стильных и функциональных помещений.
Javier es un redactor que prioriza compartir sus conocimientos de manera efectiva, precisa y fácil de entender, para que puedas disfrutar nuestros contenidos y encontrar exactamente lo que estás buscando. Su regla de oro es: “escribir algo que le encantaría leer”. Cuando se trata de explicar algo o darlo a conocer, no hay mejor manera que hacerlo simple, entretenido y completamente útil. Cabe destacar que en los últimos meses han habido varios lanzamientos de tragamonedas megaways, las cuales tienen una alta volatilidad y pagos. ¡Gane 25.000 veces su apuesta en la tragaperras Sugar Rush 1000! Sugar Rush 2015 por Pragmatic Play ¡Gane 25.000 veces su apuesta en la tragaperras Sugar Rush 1000! Para una experiencia de tragaperras única con funciones especiales, BGaming tiene juegos como Gran Patrón, Aventuras, Cúmulos aztecas, y Fusiona™.
https://crcpalermo.com/guia-para-jugar-big-bass-bonanza-gratis-y-sin-registro/
Según nuestros datos, Guest House Minas no cuenta con una piscina en sus instalaciones, pero los hoteles suelen hacer renovaciones con frecuencia y no siempre nos lo comunican. Lo mejor sería contactar con Guest House Minas en el +39 023 673 7273. Me gustó mucho. A mí Rosa Ribas me gusta, pero en ‘La luna en las minas’, además de poder leer lo buena escritora que es Rosa Ribas, es posible leer una novela sobre hombres lobos sin frikadas. Se había hecho a estos personajes accesibles a un tipo de lector (o lectora, mejor dicho) a base de hacerlos ñoños, y Rosa Ribas ha escrito sobre un púber -aunque más hombre que los adolescentes de ‘Crepúsculo’- y le ha dotado de una madurez sensata. El museo se completa con dos salas donde se muestra una de las colecciones de navajas y cuchillos de Taramundi más importante de España.
BharatMeds Direct online pharmacy india BharatMeds Direct
https://shorturl.fm/upnSg
buy antibiotics over the counter in mexico: BorderMeds Express – BorderMeds Express
indian pharmacy: BharatMeds Direct – BharatMeds Direct
BorderMeds Express: BorderMeds Express – BorderMeds Express
reliable rx pharmacy: MapleMeds Direct – MapleMeds Direct
https://maplemedsdirect.shop/# viagra international pharmacy
online pharmacy sells viagra MapleMeds Direct MapleMeds Direct
MapleMeds Direct: mail order pharmacy india – topamax online pharmacy
MapleMeds Direct: MapleMeds Direct – online pharmacy store in india
MapleMeds Direct: online pharmacy lortab no prescription – cyprus online pharmacy
MapleMeds Direct MapleMeds Direct MapleMeds Direct
п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india: BharatMeds Direct – BharatMeds Direct
https://shorturl.fm/Vmzs6
indianpharmacy com: top online pharmacy india – BharatMeds Direct
real mexican pharmacy USA shipping buy viagra from mexican pharmacy best prices on finasteride in mexico
This text is worth everyone’s attention. Where can I find out more?
BorderMeds Express: mexico drug stores pharmacies – mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
BorderMeds Express: buy from mexico pharmacy – buy kamagra oral jelly mexico
Online medicine home delivery: indian pharmacy – BharatMeds Direct
MapleMeds Direct online pharmacy no prescription flagyl MapleMeds Direct
reputable indian pharmacies: BharatMeds Direct – india pharmacy
Смотреть фильмы онлайн стало удобным и простым занятием, ведь современные сервисы предлагают огромную коллекцию кино. Забудьте о поиске записей по телевизору или старых носителях — всё доступно в один клик. Коллекция включает всё: от документальных фильмов до мультфильмов. Киноманы смогут открыть для себя редкие авторские работы. Качество изображения порадует даже требовательных зрителей. Доступ есть с любых устройств и в любом месте. Регистрация обычно простая и занимает пару минут. Тем, кто не хочет платить, доступны бесплатные онлайн-кинотеатры с рекламой. А для ценителей высокого качества и удобства есть премиум-подписки. Выбор настолько широк, что можно менять жанры каждый день. Например, вечером можно устроить просмотр комедии. Онлайн-кинотеатр заменяет поход в обычный кинотеатр. Нужен лишь смартфон или компьютер и немного свободного времени. Многие используют фильмы для изучения иностранных языков. Онлайн-просмотр — это свобода выбора и удобство. Фильмы всегда под рукой и доступны в любое время. Фанаты всегда могут увидеть свежие фильмы первыми. Сегодня фильмы онлайн — часть повседневной жизни миллионов людей.
https://bordermedsexpress.com/# BorderMeds Express
п»їJust now, I needed Doxycycline fast and found a reliable pharmacy. It allows you to buy antibiotics without a prescription legally. For treating sinusitis, this is the best place. Discreet packaging available. Visit here: [url=https://antibioticsexpress.xyz/#]click here[/url]. Get well soon.
п»їTo be honest, I needed Zithromax without waiting and came across a reliable pharmacy. They let you get treatment fast safely. In case of UTI, this is the best place. Overnight shipping to USA. Check it out: order amoxicillin online. Highly recommended.
Recently, I wanted to buy Ivermectin pills and discovered Ivermectin Express. They sell human grade meds delivered fast. If you need to treat parasites effectively, highly recommended: [url=https://ivermectinexpress.xyz/#]visit Ivermectin Express[/url]. Safe and secure
Hey there! I discovered a great pharmacy online to order pills fast. This store offers express shipping on Rx drugs. For fast service, check it out: pharmacy online. Best regards.
Greetings! Check out an awesome site to buy medications securely. This store offers reliable delivery on all meds. To save money, visit here: [url=https://pharmiexpress.xyz/#]cheap generics[/url]. Cheers.
Greetings! I found this site to order generics cheaply. The site has reliable delivery on health products. For fast service, check it out: click here. Hope this helps.
п»їActually, I wanted to buy Zithromax quickly and came across a reliable pharmacy. You can order meds no script legally. For treating UTI, check this shop. Discreet packaging to USA. More info: this site. Cheers.
Just now, I had to find anti-parasitic meds tablets and found Ivermectin Express. You can get generic Stromectol with express shipping. If you need to treat infections effectively, this is the best place: https://ivermectinexpress.xyz/#. Fast delivery
Recently, I wanted to buy anti-parasitic meds pills and found a great pharmacy. They provide 3mg, 6mg & 12mg tablets delivered fast. For treating infections quickly, this is the best place: [url=https://ivermectinexpress.com/#]official store[/url]. Fast delivery
п»їRecently, I was looking for antibiotics fast and found Antibiotics Express. They let you buy antibiotics without a prescription legally. If you have a bacterial infection, I recommend this site. Discreet packaging guaranteed. Go here: [url=http://antibioticsexpress.com/#]antibiotics without prescription[/url]. Hope you feel better.
Recently, I wanted to get Amoxicillin for an infection and stumbled upon this reliable site. They provide Amoxicillin 500mg cheaply. If you need meds, visit this link: [url=https://amoxicillinexpress.xyz/#]https://amoxicillinexpress.com[/url]. Hope it helps.
п»їRecently, I needed Ciprofloxacin fast and discovered this amazing site. You can purchase generics online legally. For treating a toothache, I recommend this site. Overnight shipping guaranteed. Go here: [url=http://antibioticsexpress.com/#]AntibioticsExpress[/url]. Hope you feel better.
Actually, I was looking for Stromectol for humans and found this reliable site. It offers genuine Ivermectin delivered fast. For treating lice quickly, check this out: https://ivermectinexpress.xyz/#. Best prices
Продуманный внешний вид играет важную роль в формировании впечатления.
Она помогает подчеркнуть индивидуальность и ощущать комфорт.
Аккуратный внешний вид формирует мнение окружающих.
В повседневной жизни одежда может повышать самооценку.
https://rentry.co/cfckr4ut
Хорошо подобранная одежда облегчает деловые контакты.
При выборе вещей важно учитывать собственный вкус и уместность ситуации.
Современные тенденции дают возможность обновлять образ.
Таким образом, умение стильно одеваться положительно влияет на самоощущение.
Продуманный внешний вид является значимым фактором в формировании впечатления.
Она помогает подчеркнуть индивидуальность и ощущать комфорт.
Грамотно подобранный образ формирует мнение окружающих.
В повседневной жизни одежда может повышать самооценку.
https://rentry.co/y5n4vdne
Стильный образ облегчает общение.
При выборе вещей важно учитывать индивидуальные особенности и обстановку.
Актуальные стили дают возможность находить новые решения.
В целом, умение стильно одеваться положительно влияет на самоощущение.
Hey all! Just wanted to share a great resource if you need pills at a discount. The site offers the best prices on all meds. For fast service, highly recommended: visit website. Cheers.
If you plan to trigger the Gates of Olympus 1000 bonus as often as possible, Betpanda makes a lot of sense. The site’s 10% weekly cashback helps offset the game’s high volatility, and many versions of the slot include an Ante Bet toggle to increase free-spin chance. The beauty of Gate of Olympus lies not only in its aesthetic appeal but also in its captivating gameplay features: Digital casino play has crept into the mainstream, and not just by a little. It looks like audiences are leaning toward richer, story-first slots with slick visuals and layered bonuses, nudging the old-school machines to the side. Gates of Olympus, which showed up in February 2021, gathered momentum fast. Some say it tapped into a broader taste for myth-heavy, immersive worlds. Zeus himself hovers on the right side of the screen and can trigger the multiplier feature at random with his godly powers. Players will see winged gemstones land on the reels when this happens, featuring multiplier values from 2x all the way up to 500x.
https://winstar188slot.com/betonred-casino-game-review-for-australian-players/
Study all its advantages and disadvantages and it will allow you to make the final decision about registration, the coolest one to be used in this case. Bingo has become popular in the Philippines and with the growth of the internet the game has become more social and accessible from anywhere. I am offering you the OKBET bingo platform where you can enjoy the online bingo game without barriers or hassle. COPYRIGHT © 2015 – 2025. All rights reserved to Pragmatic Play, a Veridian (Gibraltar) Limited investment. Any and all content included on this website or incorporated by reference is protected by international copyright laws. Gates of Olympus by Pragmatic Play offers an exhilarating gaming experience, thanks in large part to its dynamic multiplier system. These multipliers are not just an added bonus; they are the key to unlocking the game’s biggest wins. Whether you’re spinning in the base game or taking advantage of the free spins feature, understanding and maximizing the potential of these multipliers is crucial.
Продуманный внешний вид имеет большое значение в самовыражении.
Она помогает передать личный стиль и чувствовать себя увереннее.
Современный стиль влияет на восприятие окружающих.
В повседневной жизни одежда может повышать самооценку.
https://telegra.ph/Versace-01-12
Хорошо подобранная одежда облегчает общение.
При выборе вещей важно учитывать индивидуальные особенности и контекст.
Современные тенденции дают возможность обновлять образ.
Таким образом, умение стильно одеваться положительно влияет на самоощущение.
Продуманный внешний вид играет важную роль в создании образа.
Она помогает передать личный стиль и выглядеть гармонично.
Современный стиль формирует мнение окружающих.
В повседневной жизни одежда может придавать уверенность.
https://graph.org/Versace-Home-01-12
Стильный образ облегчает деловые контакты.
При выборе вещей важно учитывать личные предпочтения и контекст.
Актуальные стили дают возможность обновлять образ.
В итоге, умение стильно одеваться помогает чувствовать себя увереннее.
To be honest, I was looking for Stromectol medication and came across Ivermectin Express. They provide 3mg, 6mg & 12mg tablets with express shipping. For treating parasites quickly, check this out: https://ivermectinexpress.xyz/#. Cheers
Подбирать одежду со вкусом важно для самовыражения.
Внешний вид помогает показать личный вкус и повышает уверенность.
Продуманный стиль создаёт впечатление окружающих.
В повседневной жизни одежда может повышать самооценку.
https://telegra.ph/Off-White-12-29-3
Хорошо сочетаемая одежда упрощает социальные взаимодействия.
При выборе стиля важно учитывать личные предпочтения и контекст.
Мода позволяют экспериментировать.
В итоге, умение стильно одеваться делает образ завершённым.
Подбирать одежду со вкусом важно для формирования образа.
Внешний вид помогает показать личный вкус и повышает уверенность.
Продуманный стиль создаёт впечатление окружающих.
В повседневной жизни одежда может придавать внутреннюю собранность.
https://telegra.ph/Valentino-12-29-17
Грамотно подобранный гардероб упрощает общение.
При выборе стиля важно учитывать индивидуальные особенности и обстановку.
Актуальные направления позволяют обновлять образ.
Таким образом, умение стильно одеваться положительно влияет на самоощущение.
Гедонизм — это концепция, которое выдвигает наслаждение в центр человеческой жизни.
Согласно этому взгляду, стремление к удовольствию считается значимой частью существования.
Данная философия не всегда подразумевает чрезмерность.
Во многих трактовках он предполагает баланс и контроль желаний.
https://sites.google.com/view/brand-history/balenciaga
Актуальная интерпретация часто акцентирует внимание на качестве жизни.
При этом важную роль играет гармония между удовольствиями и обязанностями.
Данный взгляд может помогать лучше понимать себя.
В итоге, гедонизм рассматривается как философская перспектива, а не как отказ от ответственности.
п»їLately, I was looking for Ciprofloxacin quickly and stumbled upon a reliable pharmacy. They let you purchase generics online safely. For treating sinusitis, check this shop. Overnight shipping guaranteed. Visit here: [url=http://antibioticsexpress.com/#]z-pak no prescription[/url]. Hope you feel better.
Greetings! I found this site for those who need prescriptions fast. This store offers express shipping on all meds. If you want to save, take a look: online drugstore. Thanks.
Wow, amazing blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you made blogging look easy. The overall look of your site is great, as well as the content!
Actually, I wanted to get antibiotics for a tooth infection and came across Amoxicillin Express. They provide antibiotics without prescription cheaply. For fast relief, check this out: amoxicillin no prescription. Best prices.
What i discover troublesome is to find a weblog that may capture me for a minute however your blog is different. Bravo.
п»їJust now, I was looking for antibiotics quickly and found a great source. They let you purchase generics online safely. If you have UTI, try here. Fast shipping to USA. Go here: https://antibioticsexpress.com/#. Get well soon.
п»їRecently, I wanted to buy Amoxicillin without waiting and discovered a great source. You can purchase generics online safely. For treating UTI, I recommend this site. Fast shipping guaranteed. Visit here: [url=https://antibioticsexpress.com/#]Antibiotics Express Store[/url]. Cheers.
The best choice I made for trading. Smooth and wide token selection. My withdrawals were always smooth.
The post is absolutely fantastic! Lots of great info and inspiration, both of which we all need! Also like to admire the time and effort you put into your website and detailed info you offer! I will bookmark your website!
Great blog here! Additionally your website rather a lot up very fast! What host are you the usage of? Can I get your associate link for your host? I desire my website loaded up as fast as yours lol
I’ve been surfing online more than 3 hours today, yet I never found any interesting article like yours. It’s pretty worth enough for me. In my view, if all web owners and bloggers made good content as you did, the net will be much more useful than ever before.
I was suggested this website by my cousin. I am not sure whether this post is written by him as no one else know such detailed about my difficulty. You are wonderful! Thanks!
Glad to be one of several visitors on this awful internet site : D.
Hey all! Check out a great online drugstore if you need generics at a discount. The site has reliable delivery on all meds. For fast service, take a look: https://pharmiexpress.xyz/#. Hope this helps.
I imagine so. Very good stuff, I agree totally.
Actually, I needed medication for an infection and came across this source. They provide effective treatment fast. If you are in pain, visit this link: https://amoxicillinexpress.xyz/#. Get well soon.
To be honest, I wanted to buy scabies treatment for humans and discovered this reliable site. They provide generic Stromectol without a prescription. For treating scabies effectively, visit this link: IvermectinExpress Store. Safe and secure
https://shorturl.fm/zgs7o
To be honest, I wanted to get medication for a toothache and discovered this source. They provide antibiotics without prescription with express shipping. If you are in pain, highly recommended: https://amoxicillinexpress.com/#. Cheers.
Surprisingly good post. I really found your primary webpage and additionally wanted to suggest that have essentially enjoyed searching your website blog posts. Whatever the case I’ll always be subscribing to your entire supply and I hope you jot down ever again soon!
Just now, I wanted to buy Ivermectin pills and found Ivermectin Express. It offers human grade meds no script needed. If you need to treat parasites safely, this is the best place: ivermectin for humans. Hope it helps
Woh I enjoy your content , saved to bookmarks!
Greetings! Just wanted to share a useful resource to buy medications at a discount. This store offers reliable delivery on Rx drugs. To save money, check it out: [url=http://pharmiexpress.com/#]pharmiexpress.com[/url]. Hope this helps.
Регулярное обращение к средствам массовой информации играет важную роль в повседневной жизни.
Оно помогает быть в курсе событий и ориентироваться в ситуации.
Актуальные новости позволяют принимать взвешенные решения.
Чтение СМИ способствует повышению осознанности.
https://telegra.ph/Novosibirsk-12-25-8
Разные источники помогают анализировать информацию.
В профессиональной сфере СМИ дают возможность быстро реагировать на изменения.
Осознанное потребление информации формирует навыки анализа.
В итоге, чтение СМИ помогает лучше понимать мир.
Знакомство с новостными источниками играет важную роль в информационном пространстве.
Оно помогает следить за актуальными новостями и понимать происходящее.
Свежие материалы позволяют оценивать события.
Чтение СМИ способствует развитию критического мышления.
https://telegra.ph/Moskva-12-25-7
Разнообразные медиа помогают анализировать информацию.
В профессиональной сфере СМИ дают возможность оставаться конкурентоспособным.
Осознанное потребление информации формирует информационную грамотность.
В итоге, чтение СМИ делает человека более информированным.
I personally find that fees are easy onboarding, and the execution is always smooth. The dashboard gives a complete view of my holdings.
Hi! I discovered a great pharmacy online to order prescriptions cheaply. This store provides the best prices on Rx drugs. If you want to save, take a look: https://pharmiexpress.xyz/#. Hope this helps.
What’s up to all, the contents present at this web site are genuinely awesome for people knowledge, well, keep up the good work fellows.
https://outdoor.od.ua/hyundai-kona-nezvychna-optyka-kona-nyuansy.html
Dressing stylishly is significant for self-expression.
A thoughtful appearance helps express personality.
Well-chosen outfits can increase self-assurance.
In everyday life, appearance often affects social interactions.
https://rentry.co/qd75kad9
Carefully selected clothing make communication easier.
It is important to consider personal preferences as well as the occasion.
Current trends give people the chance to discover new ideas.
Overall, dressing stylishly helps people feel confident.
Dressing stylishly is essential for self-expression.
A thoughtful appearance helps show personal taste.
A neat look can increase self-assurance.
In everyday life, appearance often influences how others perceive you.
https://graph.org/Levis-01-12
Carefully selected clothing make professional interactions smoother.
It is important to consider individual taste as well as the context.
Current trends give people the chance to refresh their image.
In conclusion, dressing stylishly supports a complete personal image.
https://shorturl.fm/OJfVX
Being well-dressed is essential for creating a positive impression.
A thoughtful appearance helps express personality.
Stylish clothing can increase self-assurance.
In everyday life, appearance often shapes first impressions.
https://telegra.ph/Salvatore-Ferragamo-12-25
A well-planned wardrobe make communication easier.
It is important to consider personal preferences as well as the occasion.
Modern styles give people the chance to experiment with looks.
In conclusion, dressing stylishly helps people feel confident.
Having a sense of style is important for creating a positive impression.
A thoughtful appearance helps highlight individuality.
Stylish clothing can boost confidence.
In everyday life, appearance often affects social interactions.
https://telegra.ph/Celine-12-25-8
Balanced style choices make professional interactions smoother.
It is important to consider individual taste as well as the situation.
Modern styles give people the chance to discover new ideas.
Overall, dressing stylishly positively affects perception.
Lately, I was looking for anti-parasitic meds for humans and stumbled upon this reliable site. It offers human grade meds delivered fast. If you need to treat lice safely, visit this link: [url=http://ivermectinexpress.com/#]buy stromectol generic[/url]. Fast delivery
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas
deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2
en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis
apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc
apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas
android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para
hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas
de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de
apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas
perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones
de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app
android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas
android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas
ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas
deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas
sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de
apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas
argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app
de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app
de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de
apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas
para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de
apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer
apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para
llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas
deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps
de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para
apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas
a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas
altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo
nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina
campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas
argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina
francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas
argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas
argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina
vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic
manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic
osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic
real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de
madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico
de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid
real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico
madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real
madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto
hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas
baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca
athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca
bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas
barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas
barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas
barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona
inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas
barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas
barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas
barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket
hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas
beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol
venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas
betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas
betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas
betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono
de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono
gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos
sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo
hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil
colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil
vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions
league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de
liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas
campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas
campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de
caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras
de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino
barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino
madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas
celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions
league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions
league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas
chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas
colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia
vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas
para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas
combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas
seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap
baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas
con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas
copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas
copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas
copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa
del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa
del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa
europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas
copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas
croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de
1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para
hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de
boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas
de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de
caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas
de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos
pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de
carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas
de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de
deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de
futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de
futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas
de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas
de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de
futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de
futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como
ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de
hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas
de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de
la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de
la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga
española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de
mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas
de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros
en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema
explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de
tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas
de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del
clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas
del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real
madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas
deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca
madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas
casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas
com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas
para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas
comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos
para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa
del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es
la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas
de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas
deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas
en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas
deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas
deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas
españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas
foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro
tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas
deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas
futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas
gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas
gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la
liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales
en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas
deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas
mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas
deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas
mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores
paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas
nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas
deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online
mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas
online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para
hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas
deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas
deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas
deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas
deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas
deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas
tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas
deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas
deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1
euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso
primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas
doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund
barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas
en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo
futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas
en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas
en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea
chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de
fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas
en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas
en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas
en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol
en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas
en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas
en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas
en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo
peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos
de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa
gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas
españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas
españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa
italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas
español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol
villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas
esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas
euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas
eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa
final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa
hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1
china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1
las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para
ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos
eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final
champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa
del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa
del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de
conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina
betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas
futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas
futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol
consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol
femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas
futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol
virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas
galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas
gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas
ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas
ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey
baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador
liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial
baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas
ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona
athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona
gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas
gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis
hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis
sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis
sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas
hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy
champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas
impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter
barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas
juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas
juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos
virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas
kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga
hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las
vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales
en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas
licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga
santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas
linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid
arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid
barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid
betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid
vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca
osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester
athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo
goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores
casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas
múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas
multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas
mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial
campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de
baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de
futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial
f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas
mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas
mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp
eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas
nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas
nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba
gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas
nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas
nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas
nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas
nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online
bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online
boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas
online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online
foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas
online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online
nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online
uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico
golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna
valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos
ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas
países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas
para el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas
para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar
la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa
league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para
hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas
para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas
para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para la final de la
eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido
aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas
partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas
partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos
eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos
mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff
ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por
ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera
division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas
pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas
pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas
pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas
puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas
que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que
siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas
quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el
mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas
rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real
madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real
madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid
atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid
atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid
bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid
borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real
madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid
hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real
sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid
villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas
real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid
vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real
sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas
hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas
rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world
cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la
ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras
foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras
gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras
para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para
hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas
seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico
de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas
sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas
sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas
simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas
sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas
sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas
sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas
stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl
favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga
argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis
femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas
tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas
tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos
de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas
ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc
telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas
uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia
barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas
valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas
valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas
villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas
villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas
villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas
vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y
pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos
deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia
apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs
chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona
apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs
real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto
apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid
apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico
de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter
apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real
sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia
apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base
de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best
america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas
en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de
tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas
sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas
sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono
bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono
bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida
casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida
marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de
apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa
de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa
de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono
sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas
deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos
apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos
apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida
casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de
apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de
apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas
gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de
bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos
de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas
de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos
gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos
paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito
apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia
apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas
seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de
cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas
deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora
apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora
de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora
de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de
arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora
para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para
apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake
apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular
apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular
cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular
cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios
apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas
gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras
de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de
caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras
de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa
apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas
betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca
de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas
nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas
peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas
10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas
atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de
apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de
bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa
de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa
de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa
de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa
de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de
apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa
de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa
de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas
de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de
apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de
apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa
de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de
apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa
de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de
apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de
apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de
apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de
apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de
apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de
apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa
de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de
apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial
del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa
de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online
chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas
online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas
perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas
promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real
madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de
apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de
apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas
apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas
apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia
españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas
apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas
sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de
apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas
bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos
gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas
boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas
de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas
de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas
con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos
sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de
apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas
con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas
con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas
de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de
fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas
asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas
en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas
de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas
de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas
españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas
madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas
deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas
de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de
apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de
apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de
apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas
españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas
españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas
españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas
de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera
de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de
apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso
minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas
legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de
apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de
apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de
apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de
apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas
mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas
de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de
apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas
online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de
apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas
de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de apuestas peru bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas presenciales en españa|casas de apuestas promociones|casas
If wings are your thing, Tinker Bell’s sexy Halloween costume design is all grown up.
A thoughtful insight and ideas I will use on my blog. You’ve obviously spent some time on this. Congratulations
Greetings! I found an awesome site if you need pills at a discount. The site has reliable delivery on all meds. If you want to save, visit here: [url=https://pharmiexpress.com/#]buy meds online[/url]. Cheers.
I was able to find good info from your blog posts.
igre dece od 12 godina
This is an awesome entry. Thank you very much for the supreme post provided! I was looking for this entry for a long time, but I wasn’t able to find a honest source.
This is something that will need all of our combined efforts to address.
Do you offer workshops?
п»їLately, I had to find Doxycycline fast and came across this amazing site. It allows you to order meds no script safely. For treating sinusitis, try here. Overnight shipping guaranteed. Link: buy antibiotics online. Hope you feel better.
п»їTo be honest, I wanted to buy antibiotics without waiting and came across a reliable pharmacy. They let you order meds no script legally. If you have a bacterial infection, try here. Express delivery guaranteed. Link: source. Cheers.
It’s continually awesome when you can not only be informed, but also entertained! I’m sure you had fun writing this article. Regards, Clotilde.
You write Formidable articles, keep up good work.
Tips and tools you offer are so helpful to agencies in our community.
Lately, I had to find anti-parasitic meds medication and found this reliable site. They sell 3mg, 6mg & 12mg tablets delivered fast. If you need to treat infections effectively, visit this link: Ivermectin Express. Safe and secure
I like what you have to offer. Keep up the good work!
Recently, I needed anti-parasitic meds for humans and came across this reliable site. They sell 3mg, 6mg & 12mg tablets delivered fast. If you need to treat scabies safely, visit this link: https://ivermectinexpress.xyz/#. Cheers
Actually, I was looking for anti-parasitic meds for humans and found a great pharmacy. You can get genuine Ivermectin delivered fast. For treating infections effectively, highly recommended: order stromectol 12mg. Best prices
I am glad to be a visitor on this website!, regards for this rare information!
Петербург является важным городом России.
Город расположен на северо-западе страны и обладает богатым прошлым.
Архитектура Петербурга сочетает классические постройки и актуальные районы.
Санкт-Петербург славится музеями и насыщенной программой.
Исторический центр создают неповторимое настроение.
Туристы приезжают сюда в любое время года, чтобы познакомиться с культурой.
Санкт-Петербург также является крупным транспортным узлом.
В итоге, Санкт-Петербург остаётся одним из самых привлекательных городов.
https://beteiligung.hafencity.com/profile/wixafaf511/
Петербург является значимым мегаполисом России.
Город расположен на берегах Невы и известен своей историей.
Архитектурный стиль сочетает величественные дворцы и современные кварталы.
Санкт-Петербург славится музеями и разнообразием событий.
Петербургские улицы создают неповторимое настроение.
Гости города приезжают сюда круглый год, чтобы познакомиться с культурой.
Санкт-Петербург также является значимой деловой площадкой.
Таким образом, Санкт-Петербург считается особенным местом.
https://mentorship.healthyseminars.com/members/yebibaf720/
What i discover troublesome is to find a weblog that may capture me for a minute however your blog is different. Bravo.
I’m partial to blogs and i actually respect your content. The article has actually peaks my interest. I am going to bookmark your site and preserve checking for new information.
Умение стильно одеваться имеет большое значение в формировании первого впечатления.
Одежда помогает подчеркнуть индивидуальность.
Аккуратный внешний вид повышает уверенность.
В повседневной жизни внешний вид часто влияет на восприятие окружающих.
https://www.vevioz.com/read-blog/390919
Продуманный гардероб упрощают социальное взаимодействие.
При выборе стиля важно учитывать собственный комфорт и контекст.
Актуальные стили дают возможность экспериментировать.
Таким образом, умение стильно одеваться помогает чувствовать себя увереннее.
Стильный внешний вид является значимым фактором в формировании первого впечатления.
Одежда помогает выразить характер.
Гармоничный стиль повышает уверенность.
В повседневной жизни внешний вид часто формирует мнение окружающих.
https://mypungi.com/read-blog/33615
Продуманный гардероб упрощают социальное взаимодействие.
При выборе стиля важно учитывать индивидуальные особенности и уместность ситуации.
Современные тенденции дают возможность экспериментировать.
Таким образом, умение стильно одеваться положительно отражается на самоощущении.
Гедонизм — это направление в философии, которое выдвигает наслаждение в центр человеческой жизни.
Согласно этому взгляду, стремление к удовольствию считается значимой частью существования.
Этот подход не всегда подразумевает отсутствие ограничений.
Во многих трактовках он предполагает баланс и контроль желаний.
https://telegra.ph/Loro-Piana-12-25
Сегодняшнее восприятие этой идеи часто акцентирует внимание на эмоциональном благополучии.
При этом важную роль играет гармония между удовольствиями и ценностями.
Гедонистический подход может поддерживать психологическое равновесие.
В итоге, гедонизм рассматривается как философская перспектива, а не как отказ от ответственности.
Traditional mechanical timepieces will always hold lasting appeal despite the growth of digital technology.
They represent skilled workmanship built on precision.
Unlike electronic alternatives, mechanical watches rely on intricate movements.
Timepiece lovers value them for their history.
https://www.globaldemocracy.com/user/44435
High-quality mechanical watches are often made using premium materials.
Their elegant appearance allows them to stay relevant over time.
Beyond telling time, these watches serve as expressions of personal style.
As a result, mechanical watches continue to attract admiration.
Traditional mechanical timepieces will always remain relevant despite the growth of smart devices.
They represent craftsmanship built on technical mastery.
Unlike electronic alternatives, mechanical watches rely on mechanical precision.
Watch enthusiasts value them for their history.
https://www.vevioz.com/read-blog/366921
High-quality mechanical watches are often made using carefully selected components.
Their classic aesthetics allows them to stay relevant over time.
Beyond telling time, these watches serve as refined accessories.
Ultimately, mechanical watches continue to appeal to new generations.
Abnormal this put up is totaly unrelated to what I was searching google for, but it surely used to be listed at the first page. I suppose your doing one thing proper if Google likes you adequate to place you at the first page of a non similar search.
I had highly recommend this blog to my good friend, it’s so good
I concur with your conclusions and will eagerly look forward to your future updates. The usefulness and significance is overwhelming and has been invaluable to me!
I came across an article that talks about the same thing but even more and when you go deeper.
I’ve thought about posting something about this before. Good job! Can I use part of your post in my blog?
That is really fascinating, You’re an excessively skilled blogger. I’ve joined your rss feed and look forward to in the hunt for extra of your magnificent post. Additionally, I’ve shared your website in my social networks!
Dressing stylishly is significant for building a personal image.
A thoughtful appearance helps express personality.
A neat look can improve self-esteem.
In everyday life, appearance often influences how others perceive you.
https://graph.org/Patagonia-01-12
A well-planned wardrobe make communication easier.
It is important to consider individual taste as well as the situation.
Fashion trends give people the chance to discover new ideas.
In conclusion, dressing stylishly positively affects perception.
A handbag is an important accessory in everyday life.
It combines practicality with visual appeal.
A good bag helps carry daily essentials.
At the same time, it can enhance a look.
https://egomoda.ru/read/2024-06-26-dzhennifer-lopes-vpechatlyaet-na-pokaze-dior-na-nedele-mody-v-parizhe/
Various styles allow people to match different occasions.
A carefully selected bag often reflects individual style.
High-quality materials and design contribute to long-term use.
In conclusion, a bag remains a valuable element of a modern wardrobe.
A well-chosen bag is an key accessory in everyday life.
It combines usefulness with style.
A good bag helps organize personal items.
At the same time, it can enhance a look.
https://kambadyami.net/read-blog/42185
Various styles allow people to express personal taste.
A carefully selected bag often reflects a sense of fashion.
High-quality materials and design contribute to durability.
Overall, a bag remains a valuable element of a modern wardrobe.
Great write-up, I am a big believer in placing comments on sites to inform the blog writers know that they’ve added something advantageous to the world wide web!
Модно одеваться значимо, потому что внешний вид задаёт образ.
Одежда помогает выразить индивидуальность.
Стильный образ усиливает самооценку и хорошо сказывается на настроении.
Модные вещи делают человека опрятным.
https://penposh.com/blogs/328910/%D0%9C%D0%BE%D0%B4%D0%BD%D1%8B%D0%B5-%D1%82%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B4%D1%8B-2025-%D1%87%D1%82%D0%BE-%D0%B1%D1%83%D0%B4%D0%B5%D1%82-%D0%B0%D0%BA%D1%82%D1%83%D0%B0%D0%BB%D1%8C%D0%BD%D0%BE-%D0%B2-%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%BE%D0%BC-%D1%81%D0%B5%D0%B7%D0%BE%D0%BD%D0%B5
В деловой и социальной среде внешний вид играет важную роль.
Мода позволяет соответствовать обстановке.
Кроме того, стильная одежда помогает чувствовать комфорт.
В результате, умение модно одеваться становится важной частью самовыражения.
Продуманный внешний вид имеет большое значение в создании образа.
Она помогает выразить характер и ощущать комфорт.
Грамотно подобранный образ формирует мнение окружающих.
В повседневной жизни одежда может придавать уверенность.
https://graph.org/Fendi-01-12-4
Продуманный гардероб облегчает деловые контакты.
При выборе вещей важно учитывать собственный вкус и обстановку.
Актуальные стили дают возможность обновлять образ.
В целом, умение стильно одеваться помогает чувствовать себя увереннее.
Модно одеваться важно, потому что внешний вид задаёт образ.
Одежда помогает выразить индивидуальность.
Стильный образ повышает уверенность и хорошо сказывается на настроении.
Модные вещи делают человека опрятным.
https://chatterchat.com/read-blog/40810
В деловой и социальной среде внешний вид играет важную роль.
Мода позволяет соответствовать обстановке.
Кроме того, стильная одежда помогает чувствовать комфорт.
В итоге, умение модно одеваться становится частью современного образа жизни.
Умение стильно одеваться является значимым фактором в создании образа.
Она помогает передать личный стиль и ощущать комфорт.
Современный стиль создаёт первое впечатление окружающих.
В повседневной жизни одежда может придавать уверенность.
https://rentry.co/g2ouupzn
Продуманный гардероб облегчает деловые контакты.
При выборе вещей важно учитывать собственный вкус и контекст.
Мода дают возможность экспериментировать.
В целом, умение стильно одеваться положительно влияет на самоощущение.
Traditional mechanical timepieces will always stay fashionable despite the growth of digital technology.
They represent craftsmanship built on technical mastery.
Unlike electronic alternatives, mechanical watches rely on intricate movements.
Timepiece lovers value them for their history.
https://hub.docker.com/u/arabicbezel
High-quality mechanical watches are often made using durable metals.
Their elegant appearance allows them to transcend trends.
Beyond telling time, these watches serve as symbols of taste.
Ultimately, mechanical watches continue to appeal to new generations.
Traditional mechanical timepieces will always hold lasting appeal despite the growth of smart devices.
They represent fine engineering built on technical mastery.
Unlike electronic alternatives, mechanical watches rely on mechanical precision.
Many collectors value them for their history.
https://www.rcuniverse.com/forum/members/arabicbezel.html
High-quality mechanical watches are often made using premium materials.
Their classic aesthetics allows them to remain stylish.
Beyond telling time, these watches serve as refined accessories.
Ultimately, mechanical watches continue to maintain their iconic status.
Умение стильно одеваться является значимым фактором в создании образа.
Она помогает подчеркнуть индивидуальность и чувствовать себя увереннее.
Грамотно подобранный образ формирует мнение окружающих.
В повседневной жизни одежда может придавать уверенность.
https://rentry.co/nvm2vvpu
Хорошо подобранная одежда облегчает общение.
При выборе вещей важно учитывать собственный вкус и обстановку.
Актуальные стили дают возможность находить новые решения.
В целом, умение стильно одеваться делает образ завершённым.
Продуманный внешний вид является значимым фактором в формировании впечатления.
Она помогает подчеркнуть индивидуальность и выглядеть гармонично.
Современный стиль создаёт первое впечатление окружающих.
В повседневной жизни одежда может помогать собранности.
https://graph.org/Saint-Laurent-01-12-2
Хорошо подобранная одежда облегчает общение.
При выборе вещей важно учитывать собственный вкус и обстановку.
Мода дают возможность находить новые решения.
В целом, умение стильно одеваться помогает чувствовать себя увереннее.
Sneakers have become extremely popular in recent years due to their convenience.
They bring together practicality with stylish looks.
Many people choose sneakers because they are suitable for everyday wear.
Fashion brands have made sneakers a core piece of modern wardrobes.
https://social.japrime.id/read-blog/26194
In addition, sneakers easily work with many looks.
Their popularity is also driven by dynamic daily lives.
High-quality sneakers offer reliable performance and support for the feet.
Overall, sneakers have become a go-to option for people of all ages.
Sneakers have become incredibly popular in recent years due to their comfort.
They blend practicality with stylish looks.
Many people choose sneakers because they are suitable for everyday wear.
Fashion brands have made sneakers a key element of modern wardrobes.
https://payhip.com/MaxBezel/blog/news/top-7-sneakers-to-buy-in-2024-style-and-comfort-combined
In addition, sneakers easily fit various styles.
Their popularity is also driven by busy routines.
High-quality sneakers offer long-lasting comfort and support for the feet.
Therefore, sneakers have become a universal footwear choice for people of all ages.
Регулярное обращение к средствам массовой информации имеет большое значение в современном обществе.
Оно помогает оставаться информированным и разбираться в текущих процессах.
Оперативная информация позволяют оценивать события.
Чтение СМИ способствует расширению кругозора.
https://telegra.ph/Moskva-12-25-7
Разные источники помогают анализировать информацию.
В профессиональной сфере СМИ дают возможность оставаться конкурентоспособным.
Внимательное чтение новостей формирует навыки анализа.
В итоге, чтение СМИ поддерживает осведомлённость.
Чтение СМИ играет важную роль в современном обществе.
Оно помогает следить за актуальными новостями и понимать происходящее.
Актуальные новости позволяют формировать собственное мнение.
Чтение СМИ способствует повышению осознанности.
https://telegra.ph/Moskva-12-25-7
Разные источники помогают анализировать информацию.
В профессиональной сфере СМИ дают возможность следить за тенденциями.
Регулярное изучение материалов формирует навыки анализа.
В итоге, чтение СМИ помогает лучше понимать мир.
Looking stylish plays an important role in modern society.
The way a person dresses often forms a strong impression.
Stylish clothing can boost confidence and help people feel at ease.
A well-chosen outfit also reflects personality and individual taste.
https://followmylive.com/read-blog/27937
In professional settings, style may influence how others perceive a person.
Fashionable clothing does not always mean expensive items, but rather thoughtful choices.
When people dress well, they often feel more motivated.
Overall, dressing stylishly helps create a confident look in different situations.
Having a good sense of style plays an important role in daily life.
The way a person dresses often forms a positive impression.
Stylish clothing can improve confidence and help people feel confident.
A well-chosen outfit also expresses personality and individual taste.
https://naijamatta.com/read-blog/55073
In professional settings, style may impact how others judge a person.
Fashionable clothing does not always mean expensive items, but rather thoughtful choices.
When people dress well, they often feel more motivated.
In the end, dressing stylishly helps create a confident look in different situations.
Thanks for some other great post. Where else may anybody get that kind of information in such an ideal method of writing? I’ve a presentation next week, and I am at the look for such information.
Dressing stylishly is important for self-expression.
A thoughtful appearance helps show personal taste.
Well-chosen outfits can boost confidence.
In everyday life, appearance often influences how others perceive you.
https://telegra.ph/Salvatore-Ferragamo-12-25
A well-planned wardrobe make social situations more comfortable.
It is important to consider individual taste as well as the situation.
Fashion trends give people the chance to discover new ideas.
Overall, dressing stylishly supports a complete personal image.
Having a sense of style is significant for building a personal image.
A thoughtful appearance helps express personality.
Well-chosen outfits can boost confidence.
In everyday life, appearance often influences how others perceive you.
https://telegra.ph/Dior-12-25-3
Balanced style choices make professional interactions smoother.
It is important to consider personal preferences as well as the situation.
Fashion trends give people the chance to discover new ideas.
In conclusion, dressing stylishly helps people feel confident.
This article actually helped me with a report I was doing.
Choosing the right fragrance is an important part of individual style.
A suitable scent can enhance personality and reflect mood.
Fragrance often leaves a lasting impression.
The right aroma can strengthen confidence and make a person feel relaxed.
https://medium.com/@litecat/top-10-online-stores-for-buying-perfume-c54af8c1c838
Scents also react to skin chemistry, making each fragrance personal.
In social and professional settings, a well-chosen perfume may improve how others perceive you.
It is important to consider occasion when selecting a fragrance.
Overall, the right scent helps create a balanced impression.
I have to say this post was certainly informative and contains useful content for enthusiastic visitors. I will definitely bookmark this website for future reference and further viewing. cheers a bunch for sharing this with us!
Стильно одеваться необходимо для формирования образа.
Внешний вид помогает подчеркнуть индивидуальность и даёт чувство комфорта.
Аккуратный образ влияет на восприятие окружающих.
В повседневной жизни одежда может придавать внутреннюю собранность.
https://telegra.ph/Dior-12-29
Хорошо сочетаемая одежда упрощает деловые контакты.
При выборе стиля важно учитывать индивидуальные особенности и уместность ситуации.
Мода позволяют экспериментировать.
Таким образом, умение стильно одеваться делает образ завершённым.
真实的人类第二季高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
真实的人类第三季高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Merhaba arkadaşlar, güvenilir casino siteleri arıyorsanız, bu siteye kesinlikle göz atın. Lisanslı firmaları ve bonusları sizin için listeledik. Güvenli oyun için doğru adres: listeyi gör bol şanslar.
Online slot oynamak isteyenler için rehber niteliğinde bir site: https://cassiteleri.us.org/# siteyi incele Nerede oynanır diye düşünmeyin. Onaylı bahis siteleri listesi ile sorunsuz oynayın. Tüm liste linkte.
Salam dostlar, siz də etibarlı kazino axtarırsınızsa, mütləq Pin Up saytını yoxlayasınız. Yüksək əmsallar və sürətli ödənişlər burada mövcuddur. İndi qoşulun və ilk depozit bonusunu götürün. Daxil olmaq üçün link: [url=https://pinupaz.jp.net/#]Pinup[/url] uğurlar hər kəsə!
Situs Bonaslot adalah agen judi slot online terpercaya di Indonesia. Banyak member sudah mendapatkan Jackpot sensasional disini. Transaksi super cepat hanya hitungan menit. Situs resmi п»ї[url=https://bonaslotind.us.com/#]login sekarang[/url] gas sekarang bosku.
Salamlar, əgər siz keyfiyyətli kazino axtarırsınızsa, məsləhətdir ki, Pin Up saytını yoxlayasınız. Yüksək əmsallar və rahat pul çıxarışı burada mövcuddur. Qeydiyyatdan keçin və bonus qazanın. Sayta keçmək üçün link: Pin Up AZ uğurlar hər kəsə!
2026 yılında en çok kazandıran casino siteleri hangileri? Cevabı platformumuzda mevcuttur. Bedava bahis veren siteleri ve güncel giriş linklerini paylaşıyoruz. Hemen tıklayın [url=https://cassiteleri.us.org/#]en iyi casino siteleri[/url] kazanmaya başlayın.
Merhaba arkadaşlar, güvenilir casino siteleri arıyorsanız, bu siteye kesinlikle göz atın. En iyi firmaları ve fırsatları sizin için inceledik. Güvenli oyun için doğru adres: en iyi casino siteleri bol şanslar.
Bonaslot adalah agen judi slot online terpercaya di Indonesia. Ribuan member sudah mendapatkan Jackpot sensasional disini. Transaksi super cepat kilat. Link alternatif п»їBonaslot daftar gas sekarang bosku.
Главный город страны — это один из самых больших городов с богатой историей.
Город органично соединяет архитектурную классику и современную инфраструктуру.
Здесь расположены крупные компании и культурные учреждения.
Москва дает большой выбор для работы и образования.
https://www.oranjo.eu/c/car/730969/
Город отличается удобной логистикой.
Парки и зеленые зоны обеспечивают уют в ритме мегаполиса.
Каждый район сохраняет уникальную атмосферу.
В итоге Москва остается притягательным городом для новых возможностей.
Главный город страны — это крупнейший мегаполис с уникальным прошлым.
Город гармонично объединяет историческое наследие и динамичную застройку.
Здесь сосредоточены крупные компании и театры и музеи.
Москва дает большой выбор для профессионального роста и обучения.
https://forums.maxperformanceinc.com/forums/member.php?u=235474
Город славится разнообразием транспорта.
Парки и зоны отдыха формируют комфорт в ритме мегаполиса.
Каждый район сохраняет особое настроение.
В целом Москва остается притягательным городом для жизни.
Bonaslot adalah bandar judi slot online terpercaya di Indonesia. Ribuan member sudah merasakan Maxwin sensasional disini. Proses depo WD super cepat kilat. Link alternatif https://bonaslotind.us.com/# login sekarang gas sekarang bosku.
Pin-Up AZ Azərbaycanda ən populyar platformadır. Saytda çoxlu slotlar və canlı dilerlər var. Qazancı kartınıza tez köçürürlər. Mobil tətbiqi də var, telefondan oynamaq çox rahatdır. Rəsmi sayt [url=https://pinupaz.jp.net/#]Pin Up AZ[/url] tövsiyə edirəm.
Pin Up Casino Azərbaycanda ən populyar platformadır. Saytda minlərlə oyun və Aviator var. Qazancı kartınıza tez köçürürlər. Mobil tətbiqi də var, telefondan oynamaq çox rahatdır. Giriş linki bura daxil olun tövsiyə edirəm.
Info slot gacor malam ini: mainkan Gate of Olympus atau Mahjong Ways di Bonaslot. Website ini anti rungkad dan resmi. Promo menarik menanti anda. Kunjungi: [url=https://bonaslotind.us.com/#]bonaslotind.us.com[/url] raih kemanangan.
Pin-Up AZ Azərbaycanda ən populyar platformadır. Saytda çoxlu slotlar və Aviator var. Pulu kartınıza anında köçürürlər. Mobil tətbiqi də var, telefondan oynamaq çox rahatdır. Giriş linki burada yoxlayın.
п»їHalo Bosku, lagi nyari situs slot yang hoki? Coba main di Bonaslot. Winrate tertinggi hari ini dan pasti bayar. Deposit bisa pakai OVO tanpa potongan. Daftar sekarang: п»ї[url=https://bonaslotind.us.com/#]Bonaslot daftar[/url] salam jackpot.
Info slot gacor malam ini: mainkan Gate of Olympus atau Mahjong Ways di Bonaslot. Situs ini gampang menang dan resmi. Promo menarik menanti anda. Akses link: [url=https://bonaslotind.us.com/#]daftar situs judi slot[/url] dan menangkan.
Pin-Up AZ Azərbaycanda ən populyar platformadır. Saytda çoxlu slotlar və canlı dilerlər var. Pulu kartınıza tez köçürürlər. Mobil tətbiqi də var, telefondan oynamaq çox rahatdır. Rəsmi sayt [url=https://pinupaz.jp.net/#]Pin Up giriş[/url] tövsiyə edirəm.
Info slot gacor malam ini: mainkan Gate of Olympus atau Mahjong Ways di Bonaslot. Situs ini anti rungkad dan aman. Bonus new member menanti anda. Akses link: п»ї[url=https://bonaslotind.us.com/#]situs slot resmi[/url] raih kemanangan.
Bonaslot adalah agen judi slot online terpercaya di Indonesia. Banyak member sudah mendapatkan Maxwin sensasional disini. Transaksi super cepat kilat. Link alternatif https://bonaslotind.us.com/# slot gacor gas sekarang bosku.
Online slot oynamak isteyenler için rehber niteliğinde bir site: [url=https://cassiteleri.us.org/#]buraya tıkla[/url] Hangi site güvenilir diye düşünmeyin. Onaylı bahis siteleri listesi ile sorunsuz oynayın. Detaylar linkte.
Bonaslot adalah bandar judi slot online terpercaya di Indonesia. Ribuan member sudah merasakan Jackpot sensasional disini. Transaksi super cepat kilat. Link alternatif п»їhttps://bonaslotind.us.com/# Bonaslot rtp jangan sampai ketinggalan.
I concur with your conclusions and will eagerly look forward to your future updates. The usefulness and significance is overwhelming and has been invaluable to me!
Salam Gacor, cari situs slot yang gacor? Rekomendasi kami adalah Bonaslot. Winrate tertinggi hari ini dan terbukti membayar. Deposit bisa pakai Pulsa tanpa potongan. Login disini: [url=https://bonaslotind.us.com/#]bonaslotind.us.com[/url] salam jackpot.
Bonaslot adalah bandar judi slot online nomor 1 di Indonesia. Ribuan member sudah mendapatkan Maxwin sensasional disini. Proses depo WD super cepat kilat. Situs resmi п»їhttps://bonaslotind.us.com/# Bonaslot rtp jangan sampai ketinggalan.
Pin Up Casino Azərbaycanda ən populyar kazino saytıdır. Saytda minlərlə oyun və canlı dilerlər var. Pulu kartınıza anında köçürürlər. Proqramı də var, telefondan oynamaq çox rahatdır. Giriş linki [url=https://pinupaz.jp.net/#]bura daxil olun[/url] yoxlayın.
Canlı casino oynamak isteyenler için kılavuz niteliğinde bir site: https://cassiteleri.us.org/# en iyi casino siteleri Hangi site güvenilir diye düşünmeyin. Editörlerimizin seçtiği bahis siteleri listesi ile sorunsuz oynayın. Detaylar linkte.
Thanks for a Interesting item; I enjoyed it very much. Regards Sang Magistrale
Salamlar, əgər siz etibarlı kazino axtarırsınızsa, mütləq Pin Up saytını yoxlayasınız. Canlı oyunlar və rahat pul çıxarışı burada mövcuddur. İndi qoşulun və ilk depozit bonusunu götürün. Sayta keçmək üçün link: [url=https://pinupaz.jp.net/#]rəsmi sayt[/url] uğurlar hər kəsə!
п»їSalam Gacor, lagi nyari situs slot yang gacor? Coba main di Bonaslot. RTP Live tertinggi hari ini dan pasti bayar. Deposit bisa pakai Dana tanpa potongan. Login disini: п»їhttps://bonaslotind.us.com/# Bonaslot rtp salam jackpot.
Merhaba arkadaşlar, sağlam casino siteleri bulmak istiyorsanız, bu siteye kesinlikle göz atın. En iyi firmaları ve fırsatları sizin için listeledik. Güvenli oyun için doğru adres: [url=https://cassiteleri.us.org/#]siteyi incele[/url] iyi kazançlar.
Selamlar, sağlam casino siteleri arıyorsanız, bu siteye mutlaka göz atın. En iyi firmaları ve fırsatları sizin için inceledik. Dolandırılmamak için doğru adres: [url=https://cassiteleri.us.org/#]en iyi casino siteleri[/url] bol şanslar.
從英超、西甲、德甲到中超,全球各大足球聯盟的livescore官方即時比分都在這裡。
Pin Up Casino Azərbaycanda ən populyar platformadır. Saytda minlərlə oyun və Aviator var. Qazancı kartınıza anında köçürürlər. Mobil tətbiqi də var, telefondan oynamaq çox rahatdır. Giriş linki https://pinupaz.jp.net/# Pinup baxın.
п»їSalam Gacor, cari situs slot yang mudah menang? Rekomendasi kami adalah Bonaslot. RTP Live tertinggi hari ini dan pasti bayar. Isi saldo bisa pakai Dana tanpa potongan. Login disini: п»ї[url=https://bonaslotind.us.com/#]Bonaslot daftar[/url] semoga maxwin.
Info slot gacor malam ini: mainkan Gate of Olympus atau Mahjong Ways di Bonaslot. Website ini anti rungkad dan resmi. Promo menarik menanti anda. Akses link: п»їsitus slot resmi raih kemanangan.
Регулярное выполнение домашних заданий играет важную роль в образовательном процессе.
Домашняя работа способствует закрепить знания и лучше понять темы.
В результате ученики формируют самоорганизацию.
Регулярные задания учат грамотно распределять нагрузку.
https://gdzlol.net/6-klass/russkij-yazyk/ladyzhenskaya-baranov-trostencova/
Кроме того, домашняя работа формирует навыки анализа.
Школьники чувствуют себя спокойными на уроках.
Со временем выполнение заданий благоприятно сказывается на качество обучения.
В итоге домашние задания остаются неотъемлемым элементом школьного обучения.
Mindful play plays an important role of a healthy entertainment experience.
It allows people to maintain balance while enjoying interactive activities.
Establishing clear limits reduces risks.
Responsible play also supports smart behavior.
daily bonus / free spins
By managing time and budget, players can reduce pressure.
This approach supports a sustainable long-term experience.
Awareness of personal habits is very important.
Ultimately, responsible gaming helps preserve fun for everyone.
Responsible play is a key element of a healthy entertainment experience.
It allows people to maintain balance while enjoying interactive activities.
Defining boundaries minimizes negative outcomes.
Responsible play also supports thoughtful choices.
social casinos
By tracking personal limits, players can prevent frustration.
This approach supports a comfortable long-term experience.
Awareness of personal habits makes a real difference.
As a result, responsible gaming keeps entertainment enjoyable for everyone.
Responsible gaming plays an important role of a balanced entertainment experience.
It enables users to maintain balance while enjoying interactive activities.
Setting limits minimizes negative outcomes.
Responsible play also supports smart behavior.
https://dosweeps.com/game-categories/arcade-casual
By controlling spending and time, players can prevent frustration.
This approach creates a comfortable long-term experience.
Understanding of personal habits plays a major role.
Ultimately, responsible gaming keeps entertainment enjoyable for everyone.
Bu sene popüler olan casino siteleri hangileri? Cevabı web sitemizde mevcuttur. Deneme bonusu veren siteleri ve yeni adres linklerini paylaşıyoruz. Hemen tıklayın bonus veren siteler fırsatı kaçırmayın.
Mindful play plays an important role of a healthy entertainment experience.
It helps players to keep awareness while enjoying interactive activities.
Establishing clear limits reduces risks.
Responsible play also promotes thoughtful choices.
https://dosweeps.com/game-categories/live-dealer
By managing time and budget, players can reduce pressure.
This approach builds a comfortable long-term experience.
Understanding of personal habits makes a real difference.
Ultimately, responsible gaming helps preserve fun for everyone.
Pin Up Casino ölkəmizdə ən populyar platformadır. Burada minlərlə oyun və canlı dilerlər var. Pulu kartınıza anında köçürürlər. Proqramı də var, telefondan oynamaq çox rahatdır. Giriş linki Pinup yoxlayın.
2026 yılında en çok kazandıran casino siteleri hangileri? Cevabı platformumuzda mevcuttur. Deneme bonusu veren siteleri ve yeni adres linklerini paylaşıyoruz. İncelemek için https://cassiteleri.us.org/# buraya tıkla kazanmaya başlayın.
Online slot oynamak isteyenler için kılavuz niteliğinde bir site: türkçe casino siteleri Nerede oynanır diye düşünmeyin. Editörlerimizin seçtiği bahis siteleri listesi ile sorunsuz oynayın. Detaylar linkte.
Система iQOS представляет собой технологичной системой для использования табачных стиков.
В отличие от традиционного курения, устройство работает без горения.
Такой подход дает возможность снизить образование дыма.
Система выделяется компактным дизайном.
TEREA Bronze
Простота эксплуатации делает устройство популярным выбором для многих пользователей.
Также iQOS обеспечивает стабильную работу.
Наличие разных вкусов позволяет подобрать подходящий формат.
В итоге, система iQOS заняла свое место на рынке среди взрослых пользователей.
Система iQOS представляет собой технологичной системой для использования табачных стиков.
В отличие от традиционного курения, устройство нагревает табак.
Такой подход позволяет избежать процесса сгорания.
Система отличается современным внешним видом.
TEREA вкусы табака
Простота эксплуатации делает устройство удобным вариантом для многих пользователей.
Также iQOS предоставляет предсказуемый результат.
Наличие разных вкусов помогает найти подходящий формат.
Таким образом, система iQOS получила широкое распространение среди взрослых пользователей.
Canlı casino oynamak isteyenler için rehber niteliğinde bir site: https://cassiteleri.us.org/# cassiteleri.us.org Hangi site güvenilir diye düşünmeyin. Editörlerimizin seçtiği casino siteleri listesi ile sorunsuz oynayın. Tüm liste linkte.
Bu sene popüler olan casino siteleri hangileri? Cevabı platformumuzda mevcuttur. Deneme bonusu veren siteleri ve güncel giriş linklerini paylaşıyoruz. İncelemek için https://cassiteleri.us.org/# türkçe casino siteleri kazanmaya başlayın.
Online slot oynamak isteyenler için rehber niteliğinde bir site: https://cassiteleri.us.org/# cassiteleri.us.org Nerede oynanır diye düşünmeyin. Onaylı casino siteleri listesi ile sorunsuz oynayın. Tüm liste linkte.
Yeni Pin Up giriş ünvanını axtaranlar, bura baxa bilərsiniz. Bloklanmayan link vasitəsilə qeydiyyat olun və oynamağa başlayın. Pulsuz fırlanmalar sizi gözləyir. Keçid: https://pinupaz.jp.net/# Pin Up kazino uğurlar.
Salamlar, əgər siz yaxşı kazino axtarırsınızsa, mütləq Pin Up saytını yoxlayasınız. Canlı oyunlar və rahat pul çıxarışı burada mövcuddur. Qeydiyyatdan keçin və bonus qazanın. Sayta keçmək üçün link: [url=https://pinupaz.jp.net/#]Pinup[/url] uğurlar hər kəsə!
2026 yılında en çok kazandıran casino siteleri hangileri? Detaylı liste platformumuzda mevcuttur. Deneme bonusu veren siteleri ve güncel giriş linklerini paylaşıyoruz. İncelemek için [url=https://cassiteleri.us.org/#]cassiteleri.us.org[/url] kazanmaya başlayın.
Hər vaxtınız xeyir, əgər siz keyfiyyətli kazino axtarırsınızsa, mütləq Pin Up saytını yoxlayasınız. Canlı oyunlar və sürətli ödənişlər burada mövcuddur. Qeydiyyatdan keçin və bonus qazanın. Oynamaq üçün link: [url=https://pinupaz.jp.net/#]Pinup[/url] uğurlar hər kəsə!
п»їHalo Bosku, lagi nyari situs slot yang gacor? Rekomendasi kami adalah Bonaslot. RTP Live tertinggi hari ini dan terbukti membayar. Isi saldo bisa pakai Dana tanpa potongan. Daftar sekarang: п»ї[url=https://bonaslotind.us.com/#]Bonaslot login[/url] semoga maxwin.
Aktual Pin Up giriş ünvanını axtaranlar, bura baxa bilərsiniz. Bloklanmayan link vasitəsilə qeydiyyat olun və qazanmağa başlayın. Pulsuz fırlanmalar sizi gözləyir. Keçid: [url=https://pinupaz.jp.net/#]Pin Up online[/url] qazancınız bol olsun.
Situs Bonaslot adalah agen judi slot online nomor 1 di Indonesia. Ribuan member sudah merasakan Maxwin sensasional disini. Proses depo WD super cepat kilat. Link alternatif п»їbonaslotind.us.com jangan sampai ketinggalan.
Info slot gacor malam ini: mainkan Gate of Olympus atau Mahjong Ways di Bonaslot. Website ini anti rungkad dan resmi. Promo menarik menanti anda. Akses link: п»їslot gacor raih kemanangan.
Merhaba arkadaşlar, sağlam casino siteleri bulmak istiyorsanız, hazırladığımız listeye mutlaka göz atın. En iyi firmaları ve bonusları sizin için listeledik. Güvenli oyun için doğru adres: [url=https://cassiteleri.us.org/#]casino siteleri[/url] bol şanslar.
п»їSalam Gacor, cari situs slot yang hoki? Coba main di Bonaslot. Winrate tertinggi hari ini dan terbukti membayar. Isi saldo bisa pakai Pulsa tanpa potongan. Login disini: п»їlogin sekarang salam jackpot.
Selamlar, güvenilir casino siteleri arıyorsanız, hazırladığımız listeye kesinlikle göz atın. Lisanslı firmaları ve bonusları sizin için inceledik. Güvenli oyun için doğru adres: güvenilir casino siteleri iyi kazançlar.
Salamlar, əgər siz etibarlı kazino axtarırsınızsa, məsləhətdir ki, Pin Up saytını yoxlayasınız. Canlı oyunlar və sürətli ödənişlər burada mövcuddur. Qeydiyyatdan keçin və bonus qazanın. Daxil olmaq üçün link: https://pinupaz.jp.net/# bura daxil olun uğurlar hər kəsə!
Yeni Pin Up giriş ünvanını axtarırsınızsa, bura baxa bilərsiniz. Bloklanmayan link vasitəsilə hesabınıza girin və qazanmağa başlayın. Xoş gəldin bonusu sizi gözləyir. Keçid: https://pinupaz.jp.net/# Pin Up rəsmi sayt uğurlar.
Yeni Pin Up giriş ünvanını axtarırsınızsa, bura baxa bilərsiniz. Bloklanmayan link vasitəsilə qeydiyyat olun və qazanmağa başlayın. Xoş gəldin bonusu sizi gözləyir. Keçid: Pin-Up Casino qazancınız bol olsun.
Earn your airdrop on Aster https://is.gd/ZceEI6
This is valuable stuff.In my opinion, if all website owners and bloggers developed their content they way you have, the internet will be a lot more useful than ever before.
Good day! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my previous room mate! He always kept chatting about this. I will forward this post to him. Pretty sure he will have a good read. Thanks for sharing!
byueuropaviagraonline
2026 yılında popüler olan casino siteleri hangileri? Cevabı web sitemizde mevcuttur. Deneme bonusu veren siteleri ve yeni adres linklerini paylaşıyoruz. İncelemek için [url=https://cassiteleri.us.org/#]siteyi incele[/url] fırsatı kaçırmayın.
Very Interesting Information! Thank You For Thi Information!
Selam, sağlam casino siteleri arıyorsanız, bu siteye mutlaka göz atın. Lisanslı firmaları ve bonusları sizin için inceledik. Güvenli oyun için doğru adres: https://cassiteleri.us.org/# en iyi casino siteleri bol şanslar.
Canlı casino oynamak isteyenler için kılavuz niteliğinde bir site: en iyi casino siteleri Nerede oynanır diye düşünmeyin. Editörlerimizin seçtiği bahis siteleri listesi ile rahatça oynayın. Detaylar linkte.
My issues have been very similar, with my family. But, we made some different decisions. It’s complex.
Greetings, I just found a useful source for meds where you can buy pills securely. If you are looking for no prescription drugs, OnlinePharm is very good. Secure shipping and huge selection. Visit here: [url=https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#]read more[/url]. Have a nice day.
Hello everyone, Lately discovered a great website to save on Rx. For those seeking and want generic drugs, this site is highly recommended. Great prices plus secure. Check it out: https://pharm.mex.com/#. Be well.
Hello. Great job. I did not expect this on a Wednesday. This is a great story. Thanks!
Like the way you’ve outlined things. Easy to follow. Not cluttered.
I have been curious about these trends, and you have really helped me. I have just told a few of my friends about this on FaceBook and they love your content just as much as I do.
Hey guys, Just now discovered a useful source from India to save on Rx. If you want to buy medicines from India without prescription, IndiaPharm is highly recommended. You get secure delivery worldwide. Visit here: https://indiapharm.in.net/#. Hope it helps.
Hi all, I recently discovered an amazing source from India for cheap meds. For those looking for generic pills at factory prices, this site is the best place. They offer lowest prices worldwide. Check it out: https://indiapharm.in.net/#. Cheers.
Hey there, I wanted to share a reliable online drugstore to order generics cheaply. If you need no prescription drugs, this site is highly recommended. Secure shipping and it is very affordable. Link here: [url=https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#]OnlinePharm[/url]. Cya.
Hi guys, I just found a reliable online source to buy medication. If you want to save money and need cheap antibiotics, Pharm Mex is a game changer. Fast shipping plus secure. Check it out: mexican pharmacy online. I hope you find what you need.
Hi, I just found a reliable international pharmacy for purchasing generics online. For those who need safe pharmacy delivery, OnlinePharm is the best choice. Great prices and it is very affordable. See for yourself: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Thx.
Hi all, Just now discovered an amazing online drugstore for cheap meds. For those looking for medicines from India safely, this store is worth checking. They offer lowest prices to USA. More info here: order medicines from india. Cheers.
Greetings, I wanted to share a reliable source for meds for purchasing pills hassle-free. For those who need antibiotics, this site is very good. Great prices and it is very affordable. See for yourself: OnlinePharm. Have a great week.
To be honest, I just found a reliable website to buy medication. If you are tired of high prices and need cheap antibiotics, this store is the best option. No prescription needed and secure. Check it out: check availability. Hope this helps!
Claim 5% Rebate and Exclusive Bonuses on AsterDEX https://is.gd/CGTnqR
Hello, I wanted to share a reliable online drugstore to order medications securely. For those who need cheap meds, this store is very good. Secure shipping and no script needed. Visit here: read more. Hope this was useful.
Hi all, I just found an amazing source from India for cheap meds. If you need ED meds without prescription, this store is worth checking. It has lowest prices to USA. Visit here: indiapharm.in.net. Best regards.
Hello, I wanted to share a reliable international pharmacy where you can buy medications hassle-free. If you need antibiotics, this site is the best choice. They ship globally plus no script needed. Visit here: online pharmacy usa. Cheers.
Hello everyone, I recently discovered a trusted online source for cheap meds. If you are tired of high prices and want meds from Mexico, this store is the best option. Great prices plus it is safe. Take a look: cheap antibiotics mexico. Have a good one.
Greetings, I wanted to share an excellent international pharmacy to order generics online. For those who need safe pharmacy delivery, this store is the best choice. Great prices and it is very affordable. Visit here: buy meds online. Best regards.
Το στοίχημα αποτελεί αναπόσπαστο κομμάτι της ψυχαγωγίας για πολλούς Έλληνες παίκτες. Καθώς η εγχώρια αγορά υπόκειται σε αυστηρή ρύθμιση και περιορισμούς, ένα μεγάλο μέρος των παικτών στρέφεται προς ξένες στοιχηματικές εταιρείες που προσφέρουν μεγαλύτερη ευελιξία, καλύτερες αποδόσεις, περισσότερες επιλογές και καινοτόμα χαρακτηριστικά. Ειδικά για όσους αναζητούν μια πιο πλούσια στοιχηματική εμπειρία, οι πλατφόρμες του εξωτερικού προσφέρουν σημαντικά πλεονεκτήματα. Ο όρος ξένες στοιχηματικές εταιρείες που δέχονται Έλληνες δεν αφορά απαραίτητα αδειοδοτημένους παρόχους στην Ελλάδα, αλλά ιστοσελίδες που λειτουργούν νόμιμα υπό διεθνείς άδειες όπως της Κουρασάο, της Ανζουάν ή της Κόστα Ρίκα και επιτρέπουν εγγραφή και στοιχηματισμό από Έλληνες χρήστες. Το ενδιαφέρον για τέτοιου είδους εταιρείες αυξάνεται συνεχώς, καθώς προσφέρουν όχι μόνο καλύτερα μπόνους και προωθητικές ενέργειες, αλλά και υποστήριξη σε κρυπτονομίσματα, μηδενική γραφειοκρατία και πιο φιλικές προς τον χρήστη εμπειρίες.
Hi guys, Just now found a great online source for affordable pills. If you are tired of high prices and need generic drugs, this store is worth checking out. No prescription needed plus secure. Visit here: read more. Get well soon.
Greetings, I just found an excellent website to order pills online. If you are looking for safe pharmacy delivery, this store is worth a look. Secure shipping and it is very affordable. Visit here: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Good luck with everything.
Greetings, I recently found a great resource to save on Rx. If you want to save money and need affordable prescriptions, this site is the best option. Fast shipping plus very reliable. Check it out: [url=https://pharm.mex.com/#]read more[/url]. Have a great week.
Hey everyone, I recently discovered a great international pharmacy where you can buy generics securely. For those who need antibiotics, this site is highly recommended. Great prices and huge selection. See for yourself: online pharmacy no prescription. Be well.
To be honest, I recently found the best source from India for cheap meds. If you want to buy generic pills without prescription, IndiaPharm is the best place. They offer wholesale rates worldwide. Take a look: [url=https://indiapharm.in.net/#]indiapharm.in.net[/url]. Cheers.
Pretty nice post. I just stumbled upon your weblog and wanted to say that I’ve really enjoyed surfing around your blog posts. After all I’ll be subscribing in your feed and I am hoping you write again very soon!
Το στοίχημα αποτελεί αναπόσπαστο κομμάτι της ψυχαγωγίας για πολλούς Έλληνες παίκτες. Καθώς η εγχώρια αγορά υπόκειται σε αυστηρή ρύθμιση και περιορισμούς, ένα μεγάλο μέρος των παικτών στρέφεται προς ξένες στοιχηματικές εταιρείες που προσφέρουν μεγαλύτερη ευελιξία, καλύτερες αποδόσεις, περισσότερες επιλογές και καινοτόμα χαρακτηριστικά. Ειδικά για όσους αναζητούν μια πιο πλούσια στοιχηματική εμπειρία, οι πλατφόρμες του εξωτερικού προσφέρουν σημαντικά πλεονεκτήματα. Ο όρος ξένες στοιχηματικές εταιρείες που δέχονται Έλληνες δεν αφορά απαραίτητα αδειοδοτημένους παρόχους στην Ελλάδα, αλλά ιστοσελίδες που λειτουργούν νόμιμα υπό διεθνείς άδειες όπως της Κουρασάο, της Ανζουάν ή της Κόστα Ρίκα και επιτρέπουν εγγραφή και στοιχηματισμό από Έλληνες χρήστες. Το ενδιαφέρον για τέτοιου είδους εταιρείες αυξάνεται συνεχώς, καθώς προσφέρουν όχι μόνο καλύτερα μπόνους και προωθητικές ενέργειες, αλλά και υποστήριξη σε κρυπτονομίσματα, μηδενική γραφειοκρατία και πιο φιλικές προς τον χρήστη εμπειρίες.
Hey there, I recently discovered a useful international pharmacy for purchasing generics securely. If you are looking for cheap meds, this store is worth a look. Fast delivery and no script needed. See for yourself: [url=https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#]Online Pharm Store[/url]. Cya.
Glad to be one of many visitants on this amazing site : D.
Does it look like we’re in for a big ride here?
To be honest, I just came across a great Mexican pharmacy to save on Rx. If you are tired of high prices and need meds from Mexico, Pharm Mex is the best option. No prescription needed plus secure. Visit here: [url=https://pharm.mex.com/#]click here[/url]. Sincerely.
Hey everyone, I just found a reliable online drugstore for purchasing pills online. For those who need cheap meds, this site is highly recommended. They ship globally and no script needed. Link here: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Hope this helps!
Regards for helping out, superb info.
Hi all, I recently discovered the best website for cheap meds. If you need generic pills at factory prices, IndiaPharm is worth checking. It has lowest prices to USA. Visit here: [url=https://indiapharm.in.net/#]indian pharmacy[/url]. Hope it helps.
How do I subscribe to your blog? Thanks for your help.
I have to say this post was certainly informative and contains useful content for enthusiastic visitors. I will definitely bookmark this website for future reference and further viewing. cheers a bunch for sharing this with us!
Greetings, To be honest, I found a reliable online drugstore for purchasing medications online. If you need safe pharmacy delivery, this site is highly recommended. Great prices and no script needed. Link here: [url=https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#]OnlinePharm[/url]. Many thanks.
One more thing. I think that there are many travel insurance sites of reputable companies that let you enter your journey details and find you the quotations. You can also purchase this international holiday insurance policy on the web by using your credit card. All you need to do will be to enter all your travel information and you can see the plans side-by-side. Just find the package that suits your budget and needs and use your credit card to buy the item. Travel insurance on the internet is a good way to check for a reputable company regarding international travel cover. Thanks for revealing your ideas.
Hey guys, Lately came across a great Indian pharmacy to buy generics. If you want to buy ED meds at factory prices, this store is very reliable. They offer wholesale rates guaranteed. Visit here: [url=https://indiapharm.in.net/#]indiapharm.in.net[/url]. Best regards.
Hey everyone, To be honest, I found a reliable online drugstore where you can buy medications online. If you are looking for safe pharmacy delivery, OnlinePharm is the best choice. Secure shipping and huge selection. Visit here: onlinepharm.jp.net. All the best.
nicee content keep writing
To be honest, I just ran into a reliable Mexican pharmacy to save on Rx. If you want to save money and need cheap antibiotics, this site is highly recommended. Fast shipping plus secure. Take a look: https://pharm.mex.com/#. Be well.
Hi, I wanted to share a reliable international pharmacy where you can buy medications online. If you are looking for safe pharmacy delivery, this store is the best choice. Fast delivery plus huge selection. See for yourself: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Warmly.
To be honest, Lately stumbled upon a useful Indian pharmacy to buy generics. If you want to buy generic pills cheaply, this store is worth checking. They offer lowest prices worldwide. More info here: https://indiapharm.in.net/#. Good luck.
Hey everyone, I wanted to share a reliable website for purchasing prescription drugs cheaply. If you are looking for cheap meds, this store is the best choice. They ship globally plus huge selection. Visit here: [url=https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#]Trust Pharmacy online[/url]. Thanks!
To be honest, I recently discovered a great online drugstore to save on Rx. If you need cheap antibiotics at factory prices, this store is worth checking. You get lowest prices guaranteed. Check it out: https://indiapharm.in.net/#. Good luck.
okmark your weblog and check again here regularly. I’m quite certain I will learn lots of new stuff right here! Best of luck for the next!
爱一帆会员多少钱海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频平台,支持全球加速观看。
To be honest, I just stumbled upon a great Indian pharmacy for affordable pills. For those looking for medicines from India cheaply, this site is the best place. You get secure delivery guaranteed. More info here: [url=https://indiapharm.in.net/#]indian pharmacy online[/url]. Best regards.
Hi, I recently discovered a reliable online drugstore for purchasing generics hassle-free. For those who need safe pharmacy delivery, this site is worth a look. Secure shipping and no script needed. Link here: [url=https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#]click here[/url]. Have a good one.
I switched from another service because of the fast transactions and quick deposits.
Hello, I just found a useful source for meds for purchasing medications securely. For those who need no prescription drugs, OnlinePharm is highly recommended. They ship globally plus huge selection. Visit here: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Hope this helps!
Fast indexing of website pages and backlinks on Google https://is.gd/r7kPlC
Hi all, I recently found the best Indian pharmacy to buy generics. If you need medicines from India at factory prices, this site is the best place. It has fast shipping worldwide. Visit here: [url=https://indiapharm.in.net/#]check availability[/url]. Cheers.
Hi, To be honest, I found a great online drugstore to order generics online. For those who need cheap meds, OnlinePharm is worth a look. They ship globally plus no script needed. See for yourself: safe online drugstore. Be well.
Great ? I should certainly pronounce, impressed with your website. I had no trouble navigating through all tabs and related info ended up being truly easy to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it at all. Reasonably unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or anything, web site theme . a tones way for your customer to communicate. Excellent task..
Hey guys, I recently discovered an amazing website for affordable pills. If you need ED meds without prescription, IndiaPharm is worth checking. They offer wholesale rates guaranteed. Visit here: read more. Best regards.
Hello, I recently discovered a reliable website to order generics securely. For those who need no prescription drugs, this store is highly recommended. Great prices and no script needed. Link here: [url=https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#]visit website[/url]. Hope this was useful.
Hi guys, I recently came across a reliable Mexican pharmacy to save on Rx. For those seeking and need meds from Mexico, this site is highly recommended. Great prices plus it is safe. Link is here: click here. Hope this helps!
Hey everyone, I just found a useful website where you can buy medications online. If you need cheap meds, this store is very good. They ship globally and no script needed. Visit here: onlinepharm.jp.net. I hope you find what you need.
Hi, I just found a great international pharmacy to order medications hassle-free. If you need safe pharmacy delivery, OnlinePharm is very good. Secure shipping plus it is very affordable. Visit here: [url=https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#]international pharmacy online[/url]. Best regards.
Hello, I just found a useful international pharmacy to order prescription drugs cheaply. For those who need cheap meds, this site is very good. Fast delivery and it is very affordable. Link here: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Hope this was useful.
To be honest, Just now found a useful source from India to buy generics. If you need generic pills at factory prices, this site is very reliable. It has fast shipping guaranteed. Visit here: [url=https://indiapharm.in.net/#]visit website[/url]. Best regards.
Greetings, Lately discovered an awesome online source for cheap meds. If you are tired of high prices and need generic drugs, this site is a game changer. They ship to USA and secure. Link is here: https://pharm.mex.com/#. Hope this helps!
Hi, I recently discovered a useful online drugstore where you can buy pills online. If you need safe pharmacy delivery, this store is very good. Secure shipping and it is very affordable. Check it out: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. I hope you find what you need.
Hi guys, I recently came across a reliable resource for affordable pills. If you are tired of high prices and want meds from Mexico, this store is highly recommended. Fast shipping plus it is safe. Visit here: [url=https://pharm.mex.com/#]mexican pharmacy online[/url]. Cheers.
It is perfect time to make some plans for the future and it is time to be happy. I’ve read this post and if I could I want to suggest you some interesting things or suggestions. Perhaps you can write next articles referring to this article. I wish to read more things about it!
This is something that will need all of our combined efforts to address.
Woh I enjoy your content , saved to bookmarks!
Hello, I wanted to share a reliable website to order generics hassle-free. If you are looking for safe pharmacy delivery, this store is worth a look. Great prices and no script needed. Visit here: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Stay healthy.
Hey there, To be honest, I found an excellent online drugstore to order generics securely. If you are looking for no prescription drugs, this site is very good. Secure shipping and huge selection. Check it out: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Sincerely.
Greetings, Just now ran into an awesome online source for affordable pills. For those seeking and need cheap antibiotics, Pharm Mex is highly recommended. They ship to USA plus very reliable. Take a look: [url=https://pharm.mex.com/#]Pharm Mex Store[/url]. Best wishes.
Hey there, I just found a useful online drugstore where you can buy prescription drugs online. For those who need no prescription drugs, this site is highly recommended. They ship globally and huge selection. Check it out: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Appreciate it.
You are my inspiration , I possess few web logs and very sporadically run out from to brand 🙁
Hello everyone, Just now came across an awesome website to buy medication. If you are tired of high prices and want affordable prescriptions, this store is highly recommended. No prescription needed and it is safe. Visit here: https://pharm.mex.com/#. Good luck with everything.
Greetings, To be honest, I found a great international pharmacy to order prescription drugs cheaply. If you need cheap meds, this site is the best choice. Great prices and huge selection. Check it out: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Best wishes.
nicee content keep writing
What an insightful and meticulously-researched article! The author’s thoroughness and capability to present complex ideas in a digestible manner is truly commendable. I’m totally impressed by the scope of knowledge showcased in this piece. Thank you, author, for sharing your expertise with us. This article has been a game-changer!
Hey everyone, I recently discovered a great source for meds for purchasing medications securely. If you need cheap meds, this site is the best choice. Fast delivery plus it is very affordable. Visit here: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Stay healthy.
How long does it take you to write an article like this?
Greetings, Just now found a trusted website for cheap meds. If you want to save money and want meds from Mexico, this site is worth checking out. Great prices plus secure. Link is here: mexican pharmacy. All the best.
Thank you a lot for sharing this with all folks you actually recognize what you’re speaking about! Bookmarked. Please additionally visit my site =). We can have a hyperlink trade contract among us!
Hey there, I wanted to share a useful online drugstore where you can buy prescription drugs securely. For those who need no prescription drugs, OnlinePharm is the best choice. They ship globally plus huge selection. Link here: [url=https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#]check availability[/url]. Best of luck.
Hey there, To be honest, I found a useful international pharmacy to order prescription drugs hassle-free. If you need safe pharmacy delivery, OnlinePharm is the best choice. Secure shipping plus huge selection. Check it out: cheap pharmacy online. Best regards.
Hello everyone, Lately found a reliable resource to save on Rx. If you are tired of high prices and need affordable prescriptions, Pharm Mex is highly recommended. They ship to USA plus it is safe. Check it out: https://pharm.mex.com/#. Have a good one.
Greetings, I recently ran into an awesome resource for cheap meds. If you want to save money and need meds from Mexico, this site is the best option. Great prices and secure. Check it out: https://pharm.mex.com/#. Peace.
Hey there, I just found a reliable source for meds to order prescription drugs online. For those who need cheap meds, OnlinePharm is the best choice. Secure shipping and no script needed. Link here: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Have a good one.
Hello everyone, Just now came across a great Mexican pharmacy to save on Rx. For those seeking and need generic drugs, this site is worth checking out. They ship to USA plus secure. Link is here: this site. Hope this helps!
I really like your wordpress theme, wherever do you get a hold of it through?
Hi, I wanted to share an excellent international pharmacy where you can buy medications securely. For those who need cheap meds, this store is worth a look. Fast delivery and it is very affordable. Visit here: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Hope it helps.
Hello, To be honest, I found a reliable website to order generics online. If you are looking for cheap meds, this site is the best choice. Secure shipping plus no script needed. Check it out: [url=https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#]safe online drugstore[/url]. Best wishes.
We absolutely love your blog and find the majority of your post’s to be exactly what I’m looking for. Do you offer guest writers to write content to suit your needs? I wouldn’t mind composing a post or elaborating on a number of the subjects you write about here. Again, awesome weblog!
Hey guys, I recently came across an amazing website to save on Rx. If you want to buy ED meds cheaply, IndiaPharm is worth checking. It has secure delivery to USA. Take a look: indian pharmacy online. Hope it helps.
Hey there, To be honest, I found an excellent online drugstore to order generics securely. If you need no prescription drugs, OnlinePharm is highly recommended. Secure shipping and no script needed. Visit here: [url=https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#]read more[/url]. I hope you find what you need.
Система IQOS представляет собой инновационным решением для работы с табачными изделиями.
В отличие от обычных методов, устройство использует нагрев.
Такой подход дает возможность уменьшить количество продуктов горения.
Система выделяется эргономичной формой.
лучшие куки TEREA стики
Удобство использования делает устройство удобным вариантом для многих пользователей.
Также iQOS предоставляет предсказуемый результат.
Выбор вариантов дает возможность выбрать подходящий формат.
Таким образом, система iQOS заняла свое место на рынке среди взрослых пользователей.
Система IQOS считается технологичной системой для работы с табачными изделиями.
В отличие от традиционного курения, устройство работает без горения.
Такой подход позволяет уменьшить количество продуктов горения.
Система отличается эргономичной формой.
https://terea777.shop/category/mofee/
Комфорт в применении делает устройство популярным выбором для многих пользователей.
Также iQOS предоставляет контролируемый процесс.
Разнообразие стиков дает возможность выбрать подходящий формат.
В целом, система iQOS заняла свое место на рынке среди взрослых пользователей.
Hi all, I recently found an amazing website to save on Rx. For those looking for generic pills cheaply, IndiaPharm is the best place. It has fast shipping to USA. Visit here: order medicines from india. Cheers.
Thanks for your write-up on this blog. From my own personal experience, there are times when softening upwards a photograph might provide the photo shooter with a chunk of an artsy flare. More often than not however, this soft clouds isn’t what exactly you had as the primary goal and can sometimes spoil an otherwise good picture, especially if you intend on enlarging the item.
Arkadaşlar, Grandpashabet son linki belli oldu. Giremeyenler şu linkten giriş yapabilir Grandpashabet İndir
Grandpashabet guncel linki ar?yorsan?z dogru yerdesiniz. Sorunsuz erisim icin t?kla [url=https://grandpashabet.in.net/#]Grandpashabet Mobil[/url] Deneme bonusu bu sitede.
Matbet giriş linki arıyorsanız işte burada. Maç izlemek için tıkla: [url=https://matbet.jp.net/#]Matbet TV Giriş[/url] Canlı maçlar bu sitede. Gençler, Matbet yeni adresi belli oldu.
Arkadaşlar, Grandpashabet yeni adresi belli oldu. Adresi bulamayanlar buradan devam edebilir Siteye Git
My partner and I stumbled over here coming from a different website and thought I might check things out. I like what I see so now i am following you. Look forward to looking over your web page again.
Arkadaslar selam, Vaycasino kullan?c?lar? ad?na onemli bir duyuru yapmak istiyorum. Bildiginiz gibi platform adresini yine degistirdi. Giris hatas? varsa panik yapmay?n. Cal?san Vay Casino giris adresi su an burada: [url=https://vaycasino.us.com/#]Vay Casino Guvenilir mi[/url] Bu link uzerinden vpn kullanmadan siteye girebilirsiniz. Guvenilir bahis keyfi icin Vaycasino tercih edebilirsiniz. Tum forum uyelerine bol sans dilerim.
Arkadaşlar, Grandpashabet Casino yeni adresi belli oldu. Giremeyenler şu linkten giriş yapabilir [url=https://grandpashabet.in.net/#]Resmi Site[/url]
Matbet TV guncel adresi laz?msa iste burada. H?zl? icin: Matbet Apk Canl? maclar bu sitede. Gencler, Matbet bahis son linki ac?kland?.
If you don’t mind, where do you host your weblog? I am looking for a very good web host and your webpage seams to be extremely fast and up most the time…
Took me time to read all the comments, but I really enjoyed the article. It proved to be Very helpful to me and I am sure to all the commenters here It’s always nice when you can not only be informed, but also entertained I’m sure you had fun writing this article.
Grandpasha giriş linki lazımsa işte burada. Hızlı giriş yapmak için tıkla [url=https://grandpashabet.in.net/#]Grandpashabet Twitter[/url] Deneme bonusu bu sitede.
Matbet TV güncel adresi arıyorsanız doğru yerdesiniz. Sorunsuz için: Matbet Apk Yüksek oranlar burada. Gençler, Matbet bahis son linki açıklandı.
Arkadaslar, Grandpashabet son linki belli oldu. Adresi bulamayanlar su linkten giris yapabilir [url=https://grandpashabet.in.net/#]Grandpashabet Guvenilir mi[/url]
Grandpasha giriş adresi lazımsa işte burada. Hızlı giriş yapmak için https://grandpashabet.in.net/# Deneme bonusu bu sitede.
Herkese merhaba, Casibom sitesi oyuncuları adına kısa bir paylaşım paylaşıyorum. Bildiğiniz gibi bahis platformu domain adresini erişim kısıtlaması nedeniyle yine taşıdı. Siteye ulaşım hatası yaşıyorsanız link aşağıda. Güncel siteye erişim linki artık aşağıdadır https://casibom.mex.com/# Bu link üzerinden vpn kullanmadan siteye erişebilirsiniz. Ek olarak yeni üyelere verilen hoşgeldin bonusu kampanyalarını mutlaka kaçırmayın. En iyi slot deneyimi için Casibom tercih edebilirsiniz. Tüm forum üyelerine bol şans dilerim.
Dostlar selam, Vay Casino kullan?c?lar? icin k?sa bir duyuru paylas?yorum. Bildiginiz gibi site giris linkini yine guncelledi. Erisim sorunu varsa endise etmeyin. Yeni siteye erisim linki su an burada: T?kla Git Bu link uzerinden direkt siteye erisebilirsiniz. Lisansl? casino deneyimi surdurmek icin Vaycasino dogru adres. Herkese bol sans dilerim.
Dostlar selam, Vaycasino kullan?c?lar? icin onemli bir duyuru yapmak istiyorum. Bildiginiz gibi site adresini tekrar guncelledi. Giris sorunu varsa endise etmeyin. Guncel Vaycasino giris adresi art?k asag?dad?r: https://vaycasino.us.com/# Bu link uzerinden vpn kullanmadan hesab?n?za girebilirsiniz. Lisansl? casino deneyimi surdurmek icin Vaycasino tercih edebilirsiniz. Tum forum uyelerine bol kazanclar dilerim.
Dostlar selam, Casibom sitesi kullanıcıları için önemli bir duyuru yapmak istiyorum. Bildiğiniz gibi bahis platformu domain adresini erişim kısıtlaması nedeniyle sürekli taşıdı. Erişim hatası varsa doğru yerdesiniz. Son siteye erişim adresi şu an paylaşıyorum https://casibom.mex.com/# Bu link üzerinden vpn kullanmadan hesabınıza erişebilirsiniz. Ayrıca kayıt olanlara verilen yatırım bonusu kampanyalarını da inceleyin. Güvenilir slot deneyimi sürdürmek için Casibom tercih edebilirsiniz. Herkese bol kazançlar dilerim.
Arkadaşlar selam, bu site kullanıcıları için önemli bir duyuru yapmak istiyorum. Bildiğiniz gibi platform giriş linkini yine değiştirdi. Erişim sorunu varsa endişe etmeyin. Yeni siteye erişim adresi şu an aşağıdadır: Vaycasino Bonus Paylaştığım bağlantı üzerinden vpn kullanmadan hesabınıza girebilirsiniz. Güvenilir casino deneyimi için Vaycasino tercih edebilirsiniz. Tüm forum üyelerine bol kazançlar temenni ederim.
Grandpasha giriş adresi arıyorsanız doğru yerdesiniz. Hızlı erişim için tıkla https://grandpashabet.in.net/# Yüksek oranlar burada.
Gençler, Grandpashabet son linki belli oldu. Giremeyenler şu linkten devam edebilir [url=https://grandpashabet.in.net/#]Siteye Git[/url]
Matbet giriş adresi arıyorsanız işte burada. Maç izlemek için tıkla: https://matbet.jp.net/# Canlı maçlar burada. Gençler, Matbet son linki açıklandı.
My issues have been very similar, with my family. But, we made some different decisions. It’s complex.
Arkadaslar selam, Vay Casino oyuncular? ad?na k?sa bir duyuru paylas?yorum. Malum site giris linkini yine guncelledi. Erisim hatas? varsa endise etmeyin. Son Vaycasino giris adresi art?k asag?dad?r: [url=https://vaycasino.us.com/#]Vaycasino Uyelik[/url] Paylast?g?m baglant? ile vpn kullanmadan siteye girebilirsiniz. Guvenilir bahis deneyimi icin Vay Casino tercih edebilirsiniz. Tum forum uyelerine bol kazanclar temenni ederim.
Have you given any kind of thought at all with converting your current web-site into French? I know a couple of of translaters here that will would certainly help you do it for no cost if you want to get in touch with me personally.
Thank you for this great piece of content. Best Regards
OK, you outline what is a big issue. But, can’t we develop more answers in the private sector?
Arkadaşlar selam, Casibom üyeleri için kısa bir paylaşım paylaşıyorum. Bildiğiniz gibi Casibom giriş linkini BTK engeli yüzünden tekrar değiştirdi. Giriş problemi varsa doğru yerdesiniz. Güncel siteye erişim adresi artık burada https://casibom.mex.com/# Bu link üzerinden vpn kullanmadan siteye erişebilirsiniz. Ayrıca yeni üyelere sunulan hoşgeldin bonusu fırsatlarını mutlaka kaçırmayın. Güvenilir casino deneyimi için Casibom tercih edebilirsiniz. Herkese bol kazançlar dilerim.
Hey very cool site!! Man .. Beautiful .. Amazing .. I will bookmark your website and take the feeds also…I’m happy to find so many useful information here in the post, we need develop more strategies in this regard, thanks for sharing. . . . . .
Gençler, Grandpashabet son linki belli oldu. Adresi bulamayanlar buradan devam edebilir Grandpashabet Güncel
Matbet TV guncel linki laz?msa iste burada. H?zl? icin: Matbet Twitter Yuksek oranlar burada. Gencler, Matbet bahis yeni adresi belli oldu.
I am glad to be a visitor of this thoroughgoing web blog ! , regards for this rare information! .
Im impressed. I dont think Ive met anyone who knows as much about this subject as you do. Youre truly well informed and very intelligent. You wrote something that people could understand and made the subject intriguing for everyone. Really, great blog youve got here.
Grandpasha güncel linki lazımsa işte burada. Sorunsuz giriş yapmak için tıkla https://grandpashabet.in.net/# Yüksek oranlar burada.
Grandpashabet giriş adresi arıyorsanız işte burada. Sorunsuz erişim için tıkla Grandpashabet Mobil Yüksek oranlar bu sitede.
I really love this article.
Gençler, Grandpashabet Casino yeni adresi belli oldu. Giremeyenler şu linkten devam edebilir [url=https://grandpashabet.in.net/#]Grandpashabet Mobil[/url]
it is a really nice point of view. I usually meet people who rather say what they suppose others want to hear. Good and well written! I will come back to your site for sure!
Grandpashabet guncel linki laz?msa iste burada. H?zl? giris yapmak icin t?kla [url=https://grandpashabet.in.net/#]Grandpashabet Twitter[/url] Deneme bonusu burada.
Matbet giris adresi laz?msa iste burada. Mac izlemek icin t?kla: Buraya T?kla Canl? maclar bu sitede. Arkadaslar, Matbet son linki belli oldu.
Grandpasha güncel linki arıyorsanız doğru yerdesiniz. Sorunsuz erişim için tıkla Grandpasha Giriş Yüksek oranlar burada.
Arkadaşlar selam, bu popüler site üyeleri adına kısa bir paylaşım yapmak istiyorum. Bildiğiniz gibi Casibom domain adresini erişim kısıtlaması nedeniyle sürekli taşıdı. Erişim problemi varsa çözüm burada. Güncel siteye erişim adresi artık aşağıdadır https://casibom.mex.com/# Paylaştığım bağlantı üzerinden doğrudan hesabınıza girebilirsiniz. Ayrıca kayıt olanlara verilen yatırım bonusu fırsatlarını mutlaka inceleyin. Güvenilir bahis keyfi sürdürmek için Casibom doğru adres. Tüm forum üyelerine bol şans dilerim.
Arkadaslar, Grandpashabet Casino yeni adresi belli oldu. Giremeyenler buradan devam edebilir https://grandpashabet.in.net/#
Arkadaşlar selam, bu site oyuncuları için önemli bir bilgilendirme paylaşıyorum. Bildiğiniz gibi platform adresini yine güncelledi. Erişim hatası yaşıyorsanız panik yapmayın. Son Vay Casino giriş adresi şu an burada: Buraya Tıkla Paylaştığım bağlantı ile vpn kullanmadan siteye girebilirsiniz. Lisanslı casino keyfi için Vaycasino tercih edebilirsiniz. Herkese bol kazançlar dilerim.
Herkese merhaba, Vay Casino oyuncuları için kısa bir duyuru paylaşıyorum. Malum site adresini tekrar değiştirdi. Erişim hatası varsa panik yapmayın. Son Vay Casino giriş adresi artık aşağıdadır: https://vaycasino.us.com/# Bu link ile doğrudan hesabınıza girebilirsiniz. Lisanslı bahis deneyimi için Vay Casino tercih edebilirsiniz. Herkese bol kazançlar dilerim.
Arkadaşlar selam, Casibom sitesi üyeleri adına önemli bir duyuru yapmak istiyorum. Herkesin bildiği üzere Casibom domain adresini erişim kısıtlaması nedeniyle yine güncelledi. Siteye ulaşım sorunu varsa çözüm burada. Yeni Casibom giriş adresi şu an aşağıdadır Giriş Yap Paylaştığım bağlantı üzerinden vpn kullanmadan hesabınıza girebilirsiniz. Ek olarak yeni üyelere verilen freespin fırsatlarını da kaçırmayın. Lisanslı casino keyfi için Casibom tercih edebilirsiniz. Herkese bol kazançlar dilerim.
Awareness of health issues is steadily increasing.Increased exposure rarely ensures meaningful insight.Nuance is commonly lost in popular explanations.Context is often minimized or excluded.Body signals may be misunderstood without context.The problem stems from oversimplified framing.Physiological systems respond differently under similar conditions.Long-term observation provides clarity.Attention allows patterns to become visible.Editorial discussion helps organize this complexity.Continuity strengthens insight.Ideas are presented without pressure.Rather than offering immediate conclusions, reflection is encouraged.It aligns with thoughtful health decision-making.For those who value medical clarity.To engage with an editorial health overview of vibramycin side effects.
Virtual phone number rental is a convenient service for modern communication needs.
It enables people to get verification codes without using a physical SIM card.
Such a service is widely used for account verification.
Renting a virtual number supports personal privacy.
https://www.technologistan.pk/how-to-save-money-and-stay-connected-with-cheap-virtual-phone-numbers/
The process is simple and usually works almost instantly.
Virtual numbers are suitable across multiple services.
This solution offers flexibility for both short-term and ongoing tasks.
In general, virtual number rental is highly valued among users worldwide.
Virtual number rental is a convenient service for modern communication needs.
It allows users to handle calls without using a physical SIM card.
Such a service is widely used for temporary communication.
Choosing this service helps protect personal privacy.
https://www.latestupdatedtricks.com/how-to-safely-buy-phone-numbers-with-crypto/
The process is easy to understand and usually requires minimal time.
Virtual numbers are suitable across various online tools.
This solution provides convenience for both temporary and extended tasks.
As a result, virtual number rental remains a popular choice among users worldwide.
Arkadaslar, Grandpashabet Casino son linki ac?kland?. Giremeyenler su linkten devam edebilir Grandpasha Giris
Matbet TV giriş linki lazımsa doğru yerdesiniz. Sorunsuz için tıkla: Matbet Canlı Canlı maçlar burada. Gençler, Matbet son linki belli oldu.
Matbet güncel adresi lazımsa doğru yerdesiniz. Maç izlemek için: https://matbet.jp.net/# Yüksek oranlar burada. Gençler, Matbet bahis yeni adresi belli oldu.
Herkese merhaba, bu populer site uyeleri ad?na onemli bir bilgilendirme yapmak istiyorum. Herkesin bildigi uzere Casibom domain adresini erisim k?s?tlamas? nedeniyle surekli guncelledi. Erisim problemi cekenler icin cozum burada. Resmi siteye erisim baglant?s? su an burada https://casibom.mex.com/# Paylast?g?m baglant? uzerinden vpn kullanmadan hesab?n?za baglanabilirsiniz. Ayr?ca kay?t olanlara sunulan freespin f?rsatlar?n? mutlaka inceleyin. Lisansl? slot deneyimi icin Casibom tercih edebilirsiniz. Tum forum uyelerine bol sans dilerim.
Grandpashabet guncel adresi ar?yorsan?z iste burada. Sorunsuz giris yapmak icin t?kla https://grandpashabet.in.net/# Yuksek oranlar bu sitede.
апартаменты в краби краби ко ланта
Arkadaşlar, Grandpashabet son linki açıklandı. Adresi bulamayanlar buradan devam edebilir Grandpasha Giriş
Dostlar selam, Vay Casino oyuncuları için kısa bir duyuru yapmak istiyorum. Bildiğiniz gibi site adresini tekrar güncelledi. Giriş hatası varsa panik yapmayın. Son siteye erişim linki şu an aşağıdadır: https://vaycasino.us.com/# Paylaştığım bağlantı ile vpn kullanmadan siteye erişebilirsiniz. Güvenilir bahis keyfi için Vaycasino tercih edebilirsiniz. Tüm forum üyelerine bol şans temenni ederim.
Herkese selam, Casibom sitesi uyeleri icin k?sa bir paylas?m yapmak istiyorum. Herkesin bildigi uzere bahis platformu giris linkini BTK engeli yuzunden yine degistirdi. Erisim hatas? yas?yorsan?z link asag?da. Cal?san Casibom guncel giris baglant?s? su an paylas?yorum Hemen Oyna Paylast?g?m baglant? uzerinden vpn kullanmadan hesab?n?za girebilirsiniz. Ek olarak kay?t olanlara sunulan freespin f?rsatlar?n? da inceleyin. En iyi bahis keyfi icin Casibom dogru adres. Tum forum uyelerine bol sans dilerim.
Herkese selam, Casibom sitesi üyeleri için önemli bir paylaşım paylaşıyorum. Herkesin bildiği üzere Casibom domain adresini erişim kısıtlaması nedeniyle tekrar değiştirdi. Siteye ulaşım sorunu yaşıyorsanız doğru yerdesiniz. Güncel Casibom giriş adresi şu an burada Hemen Oyna Paylaştığım bağlantı ile vpn kullanmadan siteye erişebilirsiniz. Ayrıca yeni üyelere verilen freespin kampanyalarını da inceleyin. En iyi casino deneyimi sürdürmek için Casibom doğru adres. Tüm forum üyelerine bol kazançlar dilerim.
Dostlar selam, bu popüler site kullanıcıları için önemli bir paylaşım yapmak istiyorum. Bildiğiniz gibi bahis platformu adresini erişim kısıtlaması nedeniyle sürekli değiştirdi. Siteye ulaşım sorunu varsa doğru yerdesiniz. Yeni Casibom giriş adresi şu an burada Giriş Yap Paylaştığım bağlantı üzerinden vpn kullanmadan hesabınıza erişebilirsiniz. Ayrıca yeni üyelere sunulan yatırım bonusu kampanyalarını da kaçırmayın. Lisanslı bahis deneyimi için Casibom tercih edebilirsiniz. Tüm forum üyelerine bol kazançlar dilerim.
Dostlar selam, bu popüler site kullanıcıları için kısa bir bilgilendirme paylaşıyorum. Bildiğiniz gibi site giriş linkini BTK engeli yüzünden yine değiştirdi. Erişim sorunu varsa doğru yerdesiniz. Son Casibom güncel giriş adresi şu an burada [url=https://casibom.mex.com/#]Casibom İndir[/url] Paylaştığım bağlantı üzerinden direkt siteye girebilirsiniz. Ayrıca kayıt olanlara sunulan yatırım bonusu kampanyalarını mutlaka inceleyin. En iyi casino deneyimi sürdürmek için Casibom doğru adres. Tüm forum üyelerine bol kazançlar dilerim.
Herkese merhaba, Vaycasino oyuncular? icin onemli bir bilgilendirme yapmak istiyorum. Malum platform adresini yine guncelledi. Erisim sorunu yas?yorsan?z endise etmeyin. Guncel Vaycasino giris linki art?k asag?dad?r: [url=https://vaycasino.us.com/#]Vaycasino Indir[/url] Paylast?g?m baglant? uzerinden direkt hesab?n?za erisebilirsiniz. Lisansl? bahis keyfi icin Vaycasino dogru adres. Tum forum uyelerine bol kazanclar dilerim.
Very nice post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wanted to say that I’ve really enjoyed browsing your blog posts. In any case I’ll be subscribing to your rss feed and I hope you write again soon!
Arkadaşlar, Grandpashabet Casino son linki açıklandı. Adresi bulamayanlar şu linkten giriş yapabilir [url=https://grandpashabet.in.net/#]Grandpashabet Giriş[/url]
This platform provides a wide range of valuable and helpful information.
Visitors can find content on many topics.
All materials are thoughtfully arranged and easy to understand.
The site gets frequent updates with relevant information.
https://danghung.vn/%E2%9D%97%EF%B8%8Fdam-dan-than-chu-dong-la-duc-tinh-cua-nguoi-thanh-cong/
This makes it a trustworthy resource for everyday use.
Whether you are looking for quick answers or useful tips, the platform has something to offer.
The information is presented in a accessible and convenient format.
Overall, this site continues to be helpful for a wide audience.
This online resource features a variety of engaging and useful information.
Visitors will discover content on different areas.
All materials are clearly organized and easy to understand.
The site stays current with relevant information.
https://pestcontrolbatam.com/selamat-datang/
This makes it a reliable source for everyday use.
When searching for quick answers or detailed explanations, the platform meets different needs.
The information is delivered in a concise and reader-friendly format.
Overall, this site stands out for a wide audience.
Gencler, Grandpashabet Casino yeni adresi belli oldu. Giremeyenler su linkten giris yapabilir Resmi Site
Grandpashabet giriş linki lazımsa doğru yerdesiniz. Sorunsuz erişim için tıkla [url=https://grandpashabet.in.net/#]Grandpashabet Twitter[/url] Yüksek oranlar bu sitede.
Grandpashabet guncel adresi ar?yorsan?z dogru yerdesiniz. H?zl? giris yapmak icin t?kla https://grandpashabet.in.net/# Yuksek oranlar bu sitede.
Grandpasha giriş adresi arıyorsanız işte burada. Sorunsuz giriş yapmak için https://grandpashabet.in.net/# Deneme bonusu bu sitede.
Grandpashabet giris adresi ar?yorsan?z dogru yerdesiniz. Sorunsuz giris yapmak icin t?kla [url=https://grandpashabet.in.net/#]Grandpashabet Guvenilir mi[/url] Deneme bonusu burada.
Arkadaşlar selam, Vay Casino kullanıcıları için kısa bir bilgilendirme yapmak istiyorum. Malum Vaycasino adresini yine güncelledi. Giriş hatası yaşıyorsanız endişe etmeyin. Güncel Vay Casino giriş linki şu an burada: Giriş Yap Bu link ile direkt hesabınıza erişebilirsiniz. Güvenilir bahis deneyimi sürdürmek için Vaycasino tercih edebilirsiniz. Tüm forum üyelerine bol kazançlar temenni ederim.
Bahis severler selam, Casibom uyeleri icin k?sa bir duyuru paylas?yorum. Herkesin bildigi uzere bahis platformu domain adresini erisim k?s?tlamas? nedeniyle surekli degistirdi. Erisim sorunu cekenler icin dogru yerdesiniz. Son siteye erisim linki art?k paylas?yorum [url=https://casibom.mex.com/#]Casibom[/url] Bu link uzerinden direkt siteye girebilirsiniz. Ek olarak kay?t olanlara sunulan freespin f?rsatlar?n? mutlaka inceleyin. Lisansl? bahis deneyimi icin Casibom tercih edebilirsiniz. Herkese bol sans dilerim.
Hi các bác, ai đang tìm chỗ nạp rút nhanh để gỡ gạc Casino thì vào ngay trang này nhé. Tốc độ bàn thờ: Tải Sunwin. Chúc anh em may mắn.
Well, I don’t know if that’s going to work for me, but definitely worked for you! 🙂 Excellent post!
Hello mọi người, nếu anh em đang kiếm nhà cái uy tín để giải trí Casino đừng bỏ qua con hàng này. Nạp rút 1-1: https://homemaker.org.in/#. Chúc anh em may mắn.
The sketch is tasteful, your authored material stylish.
Could not disagree with the main ideas. Wonder how things will develop over the coming years.
I favored your idea there, I tell you blogs are so helpful sometimes like looking into people’s private life’s and work.At times this world has too much information to grasp. Every new comment wonderful in its own right.
Most often since i look for a blog Document realize that the vast majority of blog pages happen to be amateurish. Not so,We can honestly claim for which you writen is definitely great and then your webpage rock solid.
Simply wish to say the frankness in your article is surprising.
Hello m?i ngu?i, ngu?i anh em nao c?n nha cai uy tin d? g? g?c Game bai thi xem th? ch? nay. Uy tin luon: [url=https://pacebhadrak.org.in/#]bj88[/url]. Hup l?c d?y nha.
Pretty nice post. I just stumbled upon your weblog and wanted to say that I’ve really enjoyed surfing around your blog posts. After all I’ll be subscribing in your feed and I am hoping you write again very soon!
Hello mọi người, nếu anh em đang kiếm cổng game không bị chặn để giải trí Tài Xỉu đừng bỏ qua chỗ này. Nạp rút 1-1: [url=https://gramodayalawcollege.org.in/#]Link không bị chặn[/url]. Húp lộc đầy nhà.
Hello mọi người, người anh em nào cần chỗ nạp rút nhanh để cày cuốc Nổ Hũ thì tham khảo chỗ này. Uy tín luôn: [url=https://homemaker.org.in/#]Sunwin web[/url]. Chiến thắng nhé.
My brother suggested I might like this websiteHe was once totally rightThis post truly made my dayYou can not imagine simply how a lot time I had spent for this information! Thanks!
I want to see your book when it comes out.
Hi cac bac, n?u anh em dang ki?m c?ng game khong b? ch?n d? gi?i tri Casino d?ng b? qua ch? nay. N?p rut 1-1: https://pacebhadrak.org.in/#. Hup l?c d?y nha.
Boost your income effortlessly—join our affiliate network now!
Hi các bác, ai đang tìm nhà cái uy tín để chơi Tài Xỉu thì tham khảo trang này nhé. Nạp rút 1-1: [url=https://pacebhadrak.org.in/#]Tải app BJ88[/url]. Về bờ thành công.
Chao anh em, ngu?i anh em nao c?n ch? n?p rut nhanh d? g? g?c Da Ga thi tham kh?o con hang nay. T?c d? ban th?: https://gramodayalawcollege.org.in/#. Chuc anh em may m?n.
Advanced reading here!
This text is invaluable. Where can I find out more?
официальный сайт рио бет казино
Chào cả nhà, bác nào muốn tìm sân chơi đẳng cấp để gỡ gạc Đá Gà thì xem thử trang này nhé. Nạp rút 1-1: BJ88. Về bờ thành công.
Chào cả nhà, nếu anh em đang kiếm sân chơi đẳng cấp để cày cuốc Đá Gà thì tham khảo con hàng này. Tốc độ bàn thờ: [url=https://pacebhadrak.org.in/#]Tải app BJ88[/url]. Húp lộc đầy nhà.
Xin chao 500 anh em, n?u anh em dang ki?m ch? n?p rut nhanh d? choi Game bai d?ng b? qua con hang nay. Khong lo l?a d?o: https://pacebhadrak.org.in/#. Chuc cac bac r?c r?.
Hello mọi người, nếu anh em đang kiếm nhà cái uy tín để cày cuốc Game bài thì vào ngay con hàng này. Nạp rút 1-1: https://gramodayalawcollege.org.in/#. Chúc các bác rực rỡ.
Xin chào 500 anh em, nếu anh em đang kiếm sân chơi đẳng cấp để cày cuốc Nổ Hũ thì xem thử chỗ này. Tốc độ bàn thờ: [url=https://gramodayalawcollege.org.in/#]Tải app Dola789[/url]. Về bờ thành công.
Xin chao 500 anh em, ngu?i anh em nao c?n nha cai uy tin d? g? g?c Da Ga thi tham kh?o trang nay nhe. N?p rut 1-1: [url=https://gramodayalawcollege.org.in/#]Nha cai Dola789[/url]. Chuc anh em may m?n.
Xin chao 500 anh em, n?u anh em dang ki?m ch? n?p rut nhanh d? gi?i tri Tai X?u thi xem th? d?a ch? nay. Khong lo l?a d?o: https://gramodayalawcollege.org.in/#. Chi?n th?ng nhe.
Chào cả nhà, ai đang tìm sân chơi đẳng cấp để gỡ gạc Game bài đừng bỏ qua địa chỉ này. Tốc độ bàn thờ: https://homemaker.org.in/#. Chiến thắng nhé.
Chao anh em, ngu?i anh em nao c?n nha cai uy tin d? cay cu?c Da Ga thi tham kh?o trang nay nhe. Khong lo l?a d?o: Nha cai BJ88. V? b? thanh cong.
Thank you for the auspicious writeup.
Hi các bác, bác nào muốn tìm trang chơi xanh chín để chơi Game bài thì vào ngay địa chỉ này. Nạp rút 1-1: https://gramodayalawcollege.org.in/#. Về bờ thành công.
Hi các bác, ai đang tìm trang chơi xanh chín để gỡ gạc Tài Xỉu thì xem thử trang này nhé. Không lo lừa đảo: [url=https://pacebhadrak.org.in/#]Tải app BJ88[/url]. Chiến thắng nhé.
How come you do not have your website viewable in mobile format? cant see anything in my Droid.
That’s some inspirational stuff. Never knew that opinions might be this varied. Thanks for all the enthusiasm to supply such helpful information here.
The swapping tokens tools are fast transactions and low fees.
Chao anh em, n?u anh em dang ki?m c?ng game khong b? ch?n d? choi Game bai thi tham kh?o ch? nay. Dang co khuy?n mai: https://homemaker.org.in/#. Hup l?c d?y nha.
Hi các bác, ai đang tìm trang chơi xanh chín để gỡ gạc Đá Gà đừng bỏ qua con hàng này. Uy tín luôn: https://gramodayalawcollege.org.in/#. Chúc anh em may mắn.
Hi các bác, bác nào muốn tìm chỗ nạp rút nhanh để chơi Casino thì xem thử địa chỉ này. Không lo lừa đảo: [url=https://pacebhadrak.org.in/#]bj88[/url]. Chiến thắng nhé.
Chào anh em, bác nào muốn tìm trang chơi xanh chín để chơi Casino đừng bỏ qua địa chỉ này. Nạp rút 1-1: https://gramodayalawcollege.org.in/#. Húp lộc đầy nhà.
While this issue can vexed most people, my thought is that there has to be a middle or common ground that we all can find. I do value that you’ve added pertinent and sound commentary here though. Thank you!
Public policy is key here, and our states need to develop some strategies – – soon.
I wrote down your blog in my bookmark. I hope that it somehow did not fall and continues to be a great place for reading texts.
Cherished is likely to be what people say about your comments.
Hi cac bac, bac nao mu?n tim c?ng game khong b? ch?n d? gi?i tri Game bai d?ng b? qua con hang nay. Khong lo l?a d?o: nha cai dola789. Chuc anh em may m?n.
Loving the info on this website , you have done outstanding job on the blog posts.
Hi các bác, ai đang tìm cổng game không bị chặn để chơi Game bài đừng bỏ qua trang này nhé. Nạp rút 1-1: Link vào Dola789. Chúc các bác rực rỡ.
Chào cả nhà, ai đang tìm nhà cái uy tín để giải trí Casino thì vào ngay con hàng này. Đang có khuyến mãi: https://pacebhadrak.org.in/#. Chúc các bác rực rỡ.
I encountered your site after doing a search for new contesting using Google, and decided to stick around and read more of your articles. Thanks for posting, I have your site bookmarked now.
Hello mọi người, bác nào muốn tìm nhà cái uy tín để giải trí Game bài đừng bỏ qua địa chỉ này. Đang có khuyến mãi: https://homemaker.org.in/#. Chúc anh em may mắn.
You need to really control the comments listed here
Just a quick note to express my appreciation. Take care
Xin chao 500 anh em, ngu?i anh em nao c?n nha cai uy tin d? g? g?c Game bai d?ng b? qua d?a ch? nay. Khong lo l?a d?o: https://gramodayalawcollege.org.in/#. Chuc cac bac r?c r?.
Hi there, just became aware of your blog through Google, and found that it’s truly informative. It’s important to cover these trends.
Xin chào 500 anh em, nếu anh em đang kiếm sân chơi đẳng cấp để gỡ gạc Game bài thì tham khảo chỗ này. Đang có khuyến mãi: [url=https://gramodayalawcollege.org.in/#]Link không bị chặn[/url]. Húp lộc đầy nhà.
Chào anh em, ai đang tìm nhà cái uy tín để giải trí Casino đừng bỏ qua con hàng này. Uy tín luôn: Dola789 đăng nhập. Húp lộc đầy nhà.
This has to be one of my favorite posts! And on top of thats its also very helpful topic for newbies. thank a lot for the information!
Hi cac bac, bac nao mu?n tim trang choi xanh chin d? g? g?c Game bai thi xem th? con hang nay. T?c d? ban th?: https://gramodayalawcollege.org.in/#. Chuc anh em may m?n.
With this issue, it’s important to have someone like you with something to say that really matters.
Hello m?i ngu?i, ngu?i anh em nao c?n nha cai uy tin d? g? g?c Casino thi tham kh?o ch? nay. Khong lo l?a d?o: https://homemaker.org.in/#. V? b? thanh cong.
Chào cả nhà, bác nào muốn tìm cổng game không bị chặn để giải trí Casino đừng bỏ qua con hàng này. Uy tín luôn: Dola789 đăng nhập. Chúc các bác rực rỡ.
I appreciate your work, thanks for all the great blog posts.
Its like you read my mind! You seem to know a lot about this, like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you can do with some pics to drive the message home a bit, but other than that, this is wonderful blog. A great read. I’ll certainly be back.
Hey, I simply hopped over to your website by way of StumbleUpon. No longer one thing I’d normally learn, but I preferred your thoughts none the less. Thanks for making one thing worth reading.
you’re in reality a just right webmaster. The web site loading velocity is incredible. It sort of feels that you’re doing any distinctive trick. In addition, The contents are masterpiece. you’ve performed a great process on this topic!
Chào cả nhà, người anh em nào cần sân chơi đẳng cấp để giải trí Tài Xỉu thì xem thử trang này nhé. Nạp rút 1-1: [url=https://gramodayalawcollege.org.in/#]Dola789[/url]. Húp lộc đầy nhà.
Hi cac bac, ngu?i anh em nao c?n trang choi xanh chin d? cay cu?c Game bai thi xem th? trang nay nhe. T?c d? ban th?: https://pacebhadrak.org.in/#. Chuc anh em may m?n.
I like this weblog very much so much great info .
Could not disagree with the main ideas. Wonder how things will develop over the coming years.
Hi các bác, ai đang tìm nhà cái uy tín để cày cuốc Nổ Hũ đừng bỏ qua con hàng này. Uy tín luôn: [url=https://gramodayalawcollege.org.in/#]Link không bị chặn[/url]. Húp lộc đầy nhà.
Im impressed. I dont think Ive met anyone who knows as much about this subject as you do. Youre truly well informed and very intelligent. You wrote something that people could understand and made the subject intriguing for everyone. Really, great blog youve got here.
Chào anh em, người anh em nào cần nhà cái uy tín để giải trí Casino thì xem thử địa chỉ này. Uy tín luôn: Nhà cái Dola789. Chúc các bác rực rỡ.
Hello mọi người, người anh em nào cần nhà cái uy tín để chơi Casino đừng bỏ qua địa chỉ này. Tốc độ bàn thờ: Sunwin web. Húp lộc đầy nhà.
Xin chao 500 anh em, ngu?i anh em nao c?n c?ng game khong b? ch?n d? cay cu?c Da Ga thi tham kh?o d?a ch? nay. Khong lo l?a d?o: Nha cai Dola789. Chuc cac bac r?c r?.
Xin chao 500 anh em, ai dang tim trang choi xanh chin d? gi?i tri N? Hu thi xem th? ch? nay. Dang co khuy?n mai: Dola789 dang nh?p. V? b? thanh cong.
Xin chào 500 anh em, người anh em nào cần trang chơi xanh chín để chơi Nổ Hũ thì xem thử địa chỉ này. Nạp rút 1-1: Nhà cái Dola789. Chiến thắng nhé.
Умение одеваться со вкусом играет важную роль в создании образа.
Она помогает подчеркнуть индивидуальность.
Удачный внешний вид усиливает уверенность в себе.
Одежда нередко является инструментом визуального контакта.
https://angelina-podium.blogspot.com/2026/01/7-zimmermann.html
Кроме того, продуманный гардероб экономит время в повседневных делах.
В долгосрочной перспективе внимание к стилю развивает вкус.
В результате стильная одежда играет значимую роль современного образа жизни.
Amitriptyline: AmiTrip – AmiTrip
https://fertilitypctguide.us.com/# clomid pill
Умение одеваться со вкусом является значимым фактором в создании образа.
Она позволяет подчеркнуть индивидуальность.
Гармоничный стиль усиливает самооценку.
Одежда нередко является важным элементом визуального контакта.
https://sites.google.com/view/luisaspagnoli2026/main
Кроме того, продуманный гардероб упрощает выбор в повседневных делах.
В долгосрочной перспективе внимание к стилю воспитывает чувство меры.
В результате стильная одежда становится важной частью современного образа жизни.
Умение одеваться со вкусом является значимым фактором в создании образа.
Она помогает выразить характер.
Удачный внешний вид поддерживает внутренний комфорт.
Одежда может быть важным элементом первого восприятия.
https://angelina-podium.blogspot.com/2026/01/luisa-spagnoli.html
Кроме того, продуманный гардероб делает сборы быстрее в повседневных делах.
В долгосрочной перспективе внимание к стилю формирует привычку.
В итоге стильная одежда становится важной частью современного образа жизни.
https://fertilitypctguide.us.com/# where can i buy generic clomid pills
Follicle Insight: Follicle Insight – Follicle Insight
https://fertilitypctguide.us.com/# how to get cheap clomid online
buy generic propecia no prescription: cost generic propecia – Follicle Insight
When are you going to post again? You really entertain me!
Curating a stylish outfit is essential.
It serves as a powerful mode of non-verbal communication.
Your apparel defines first impressions almost immediately.
Feeling confident in your clothes significantly boosts your confidence.
https://sites.google.com/view/guccibags2026/gucci
A well-chosen style can create opportunities in both career and social contexts.
It allows you to project your personal identity without uttering a word.
Ultimately, investing in your personal style is an act of valuing your own potential.
Curating a polished outfit is essential.
It serves as a powerful mode of non-verbal communication.
Your attire shapes first impressions almost immediately.
Feeling self-assured in your ensemble greatly enhances your confidence.
https://angelina-podium.blogspot.com/2026/01/gucci-2026.html
A deliberate style can open doors in both professional and social contexts.
It enables you to express your personal identity before saying a single word.
Ultimately, focusing on your personal style is an act of valuing yourself.
Follicle Insight [url=https://follicle.us.com/#]order propecia without rx[/url] Follicle Insight
What’s Happening i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve found It positively useful and it has aided me out loads. I hope to contribute & help other users like its aided me. Great job.
A cool post there mate ! Thank you for posting.
Hey! awesome blog! I happen to be a daily visitor to your site (somewhat more like addict 😛 ) of this website. Just wanted to say I appreciate your blogs and am looking forward for more!
I Am Going To have to come back again when my course load lets up – however I am taking your Rss feed so i can go through your site offline. Thanks.
fertility pct guide: can you get generic clomid without rx – fertility pct guide
https://amitrip.us.com/# Generic Elavil
AmiTrip Relief Store: AmiTrip – AmiTrip
https://iver.us.com/# Iver Protocols Guide
Generic Elavil: AmiTrip Relief Store – AmiTrip Relief Store
https://follicle.us.com/# Follicle Insight
Amitriptyline [url=https://amitrip.us.com/#]Generic Elavil[/url] Elavil
Generic Elavil: buy Elavil – AmiTrip Relief Store
We’re developing a conference, and it looks like you would be a great speaker.
https://follicle.us.com/# Follicle Insight
https://fertilitypctguide.us.com/# where to get cheap clomid for sale
where to buy ivermectin: ivermectin 50ml – ivermectin 50
https://fertilitypctguide.us.com/# can you get generic clomid without insurance
Follicle Insight: Follicle Insight – Follicle Insight
https://iver.us.com/# cost of stromectol medication
Generic Elavil: AmiTrip Relief Store – AmiTrip
Follicle Insight [url=https://follicle.us.com/#]Follicle Insight[/url] Follicle Insight
ivermectin 400 mg brands: ivermectin price uk – Iver Protocols Guide
Follicle Insight: Follicle Insight – Follicle Insight
https://iver.us.com/# ivermectin lotion cost
https://follicle.us.com/# Follicle Insight
Day after day, health quietly steers how we feel, choose, and respond.
We’re told what to eat, how to train, what to cut out—yet understanding rarely deepens.
Promises sound simple, while uniqueness gets ignored.
Every change is a form of communication from within.
Our systems adapt and recalibrate day by day.
When we observe, we learn what our body is actually asking for.
Over time, health stops feeling like an outside target and becomes part of identity.
By watching patterns, we learn how health responds to stress, time, and emotion.
When slowing down feels like the missing step forward.
To move with awareness instead of fighting your own rhythm.
It’s about understanding rather than urgency.
Each insight brings us closer to what health actually means.
When we understand those patterns, sensations start to make sense.
These deeper processes become easier to see through tadalafil bioavailability.
buy Elavil: Elavil – AmiTrip
Iver Protocols Guide [url=https://iver.us.com/#]stromectol order online[/url] Iver Protocols Guide
https://amitrip.us.com/# Amitriptyline
Generic Elavil: AmiTrip – Amitriptyline
https://fertilitypctguide.us.com/# fertility pct guide
This has to be one of my favorite posts! And on top of thats its also very helpful topic for newbies. thank a lot for the information!
Follicle Insight: Follicle Insight – cost cheap propecia tablets
https://follicle.us.com/# Follicle Insight
Продуманный внешний вид является значимым фактором в создании образа.
Она дает возможность произвести хорошее впечатление.
Правильно подобранный образ усиливает самооценку.
Одежда часто становится частью невербального общения.
https://n2.vladtoday.ru/redirect.php?id=vPduii5MymnG
Кроме того, продуманный гардероб упрощает выбор в повседневных делах.
В долгосрочной перспективе внимание к стилю развивает вкус.
Таким образом стильная одежда играет значимую роль современного образа жизни.
Iver Protocols Guide: Iver Protocols Guide – Iver Protocols Guide
buy Elavil: Elavil – AmiTrip Relief Store
https://iver.us.com/# ivermectin generic cream
https://iver.us.com/# Iver Protocols Guide
fertility pct guide: fertility pct guide – fertility pct guide
buy Elavil: Generic Elavil – Amitriptyline
https://follicle.us.com/# Follicle Insight
AmiTrip Relief Store: AmiTrip – AmiTrip Relief Store
Volume shooters, players who take most shots per game tracked
Iver Protocols Guide: Iver Protocols Guide – Iver Protocols Guide
https://amitrip.us.com/# AmiTrip Relief Store
cost of propecia for sale: Follicle Insight – Follicle Insight
The portfolio tracking process is simple and the responsive team makes it even better. The updates are frequent and clear.
Hello there! I really enjoy reading your blog! If you keep making amazing posts like this I will come back every day to keep reading.
fertility pct guide [url=https://fertilitypctguide.us.com/#]where can i buy generic clomid[/url] fertility pct guide
Умение стильно одеваться играет важную роль в формировании образа.
Она помогает выразить характер и выглядеть гармонично.
Аккуратный стиль влияет на то, как человека оценивают другие люди.
В повседневной жизни одежда может повышать самооценку.
https://teletype.in/@maxbezel/dngGPS_YD7V
Хорошо подобранная одежда облегчает социальные контакты.
При этом важно учитывать собственный вкус и уместность ситуации.
Стиль дают возможность обновлять образ.
В итоге, умение стильно одеваться влияет на общее восприятие личности.
Follicle Insight: Follicle Insight – propecia sale
https://iver.us.com/# ivermectin human
https://amitrip.us.com/# buy Elavil
cost of propecia without a prescription: get generic propecia online – Follicle Insight
Join our affiliate community and maximize your profits!
https://follicle.us.com/# Follicle Insight
Our communities really need to deal with this.
Generic Elavil: buy Elavil – Generic Elavil
What’s Happening i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve found It positively useful and it has aided me out loads. I hope to contribute & help other users like its aided me. Great job.
Generic Elavil: Generic Elavil – buy Elavil
In terms of proper usage instructions, you can consult the detailed guide on: https://magmaxhealth.com/toradol.html to ensure correct administration.
Твердосплавной инструмент изготавливается из особо твёрдых сплавов.
Его базу составляют тугоплавкие карбиды вольфрама и тантала.
Это даёт высокую прочность и устойчивость перед истиранию.
promgrupp.ru
Такой инструмент способен работать при высоких температурных режимах.
Данный материал превосходит по своей прочности классическую инструментальную сталь.
Твёрдосплавные вставки очень используются в обработке металлов.
Твердосплавной инструмент производится на основе особо твёрдых сплавов.
Данный инструмент основу составляют тугоплавкие карбиды титана или кобальта.
Данное решение обеспечивает исключительную прочность а также стойкость к износу.
https://www.vse-pishut.ru/kompaniya-promgrupp-oficialnyjj-predstavitel-gesa-6ki7/
Такой инструмент может работать в условиях высоких температурах.
Он уступает в своей прочности классическую инструментальную сталь.
Твердосплавные пластины очень применяются при обработке твёрдых материалов.
Hi, if you are looking for a useful article about various medications, I found this medical reference. It explains usage and risks clearly. Reference: https://magmaxhealth.com/Flonase. Thanks.
Hey everyone, if you are looking for an affordable drugstore to order health products cheaply. I recommend this site: clarinex. Stocking generic tablets at the best prices. Thanks.
Greetings, if anyone needs a useful article about common medicines, I recommend this drug database. It covers how to take meds clearly. See details: https://magmaxhealth.com. Very informative.
If you are looking for I recommend this reliable site super pharmacy for the best prices. Stop overpaying and save big.
Does it look like we’re in for a big ride here?
Hello, for those searching for dosage instructions regarding health treatments, check out this online directory. You can read about usage and risks clearly. See details: https://magmaxhealth.com/Rosuvastatin. Hope this is useful.
Ответственная игра — это набор строгих правил и подходов.
Данная концепция ориентирована на обеспечение безопасности игроков от вредоносного воздействия.
Ключевая цель — сохранить развлекательную сущность без ущерба для личного состояния участника.
https://t.me/s/top_onlajn_kazino_rossii
Это подразумевает установление лимитов над длительностью и бюджетом, потраченными на игру.
Существенным компонентом является понимание игроком имеющихся возможных рисков.
Платформы должны обеспечивать честную информацию и инструменты с целью контроля за игрой.
Таким образом, безопасная деятельность создаёт здоровую игровую атмосферу со стороны всех сторон.
I imagine so. Very good stuff, I agree totally.
Hello, if you are looking for an affordable health store to order medicines online. I found MagMaxHealth: buspar. Selling high quality drugs and huge discounts. Cheers.
To start saving, visit this reliable site here for fast USA shipping. Take control of your health hassle-free.
Hi, if anyone needs a medical guide about various medications, check out this useful resource. It explains how to take meds clearly. Source: https://magmaxhealth.com/Prilosec. Thanks.
A good web site with interesting content, that’s what I need. Thank you for making this web site, and I will be visiting again. Do you do newsletters? I Can’t find it.
For a complete overview of side effects and interactions, data is available at the official information page at: https://magmaxhealth.com/lamictal.html which covers risk management.
regarding the medical specifications, please review the detailed guide on: https://magmaxhealth.com/clarinex.html for safe treatment.
Greetings, have tried to subscribe to this websites rss feed but I am having a bit of a problem. Can anyone kindly tell me what to do?’
Hello, if you are looking for an affordable source for meds to order prescription drugs online. I recommend MagMaxHealth: meclizine. Selling high quality drugs with fast shipping. Hope this helps.
We’re developing a conference, and it looks like you would be a great speaker.
Hi all, if you are looking for side effects info on common medicines, I recommend this health wiki. It explains drug interactions clearly. Read more here: https://magmaxhealth.com/Flonase. Good info.
Hello there, just became aware of your blog through Google, and found that it is truly informative. I am going to watch out for brussels. I will appreciate if you continue this in future. Lots of people will be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
Saw your material, and hope you publish more soon.
This website has lots of really useful stuff on it. Thanks for informing me.
It’s continually awesome when you can not only be informed, but also entertained! I’m sure you had fun writing this article. Regards, Clotilde.
Hello, I think your blog might be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your website in Chrome, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other than that, awesome blog!
Hello, I wanted to share a trusted drugstore to buy medicines securely. Take a look at this site: prilosec. They offer a wide range of meds and huge discounts. Hope this helps.
Hello, if you are looking for side effects info regarding common medicines, check out this health wiki. You can read about usage and risks very well. See details: https://magmaxhealth.com/Allopurinol. Hope it helps.
Hi all, if anyone needs side effects info regarding health treatments, check out this useful resource. It covers drug interactions in detail. See details: https://magmaxhealth.com/Flonase. Very informative.
For a complete overview of safety protocols, you can consult the medical directory at: https://magmaxhealth.com/buspar.html for safe treatment.
Hello, I recently found detailed information about health treatments, check out this online directory. It explains safety protocols clearly. Source: https://magmaxhealth.com/Clarinex. Very informative.
regarding the dosage guidelines, it is recommended to check the official information page at: https://magmaxhealth.com/lamictal.html which covers risk management.
월드카지노
This platform exceeded my expectations with robust security and responsive team. Charts are accurate and load instantly.
Твердосплавный инструментальная оснастка изготавливается из особо прочных сплавов.
Его основу составляют тугоплавкие карбиды вольфрама и кобальта.
Данное решение даёт высокую прочность и устойчивость перед истиранию.
ПромГрупп
Подобный инвентарь способен работать при повышенных температурных режимах.
Данный материал превосходит в своей прочности обычную инструментальную сталь HSS.
Твёрдосплавные пластины широко применяются в обработке металлов.
Твердосплавной инструмент изготавливается на основе особо прочных материалов.
Данный инструмент основу образуют карбиды титана или кобальта.
Это обеспечивает исключительную прочность а также устойчивость к истиранию.
promgrupp.ru
Подобный инструмент может функционировать при повышенных температурах.
Он уступает в своей долговечности классическую быстрорежущую сталь HSS.
Твердосплавные пластины широко применяются при обработке металлов.
Hey everyone, I recently found side effects info about common medicines, I found this online directory. You can read about safety protocols in detail. See details: https://magmaxhealth.com/Naltrexone. Very informative.
Hi guys, I wanted to share a reliable source for meds to order health products online. I found this site: rosuvastatin. Stocking a wide range of meds at the best prices. Hope this helps.
omeprazole generic: prilosec generic – Gastro Health Monitor
of course like your web-site however you have to check the spelling on several of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling problems and I find it very troublesome to tell the reality then again I will surely come back again.
Hiya, I am really glad I have found this information. Nowadays bloggers publish only about gossip and net stuff and this is actually frustrating.
Makes sense to me.
https://gastrohealthmonitor.shop/# Gastro Health Monitor
buy zofran: Nausea Care US – zofran side effects
I think it is a nice point of view. I most often meet people who rather say what they suppose others want to hear. Good and well written! I will come back to your site for sure!
muscle relaxers over the counter: Spasm Relief Protocols – tizanidine hcl
zofran medication: zofran dosage – Nausea Care US
There is so much to try to understand
Hello there! I really enjoy reading your blog! If you keep making amazing posts like this I will come back every day to keep reading.
A thoughtful insight and ideas I will use on my blog. You’ve obviously spent some time on this. Congratulations
Great blog right here! You seem to put a significant amount of material on the site rather quickly.
This article actually helped me with a report I was doing.
robaxin: Spasm Relief Protocols – tizanidine hcl
Gastro Health Monitor [url=https://gastrohealthmonitor.com/#]Gastro Health Monitor[/url] Gastro Health Monitor
antispasmodic medication: buy methocarbamol – methocarbamol dosing
http://spasmreliefprotocols.com/# robaxin generic
Earn passive income with every click—sign up today!
buy zofran online: Nausea Care US – zofran medication
OK, you outline what is a big issue. But, can’t we develop more answers in the private sector?
muscle relaxant drugs: Spasm Relief Protocols – zanaflex
Nausea Care US: zofran generic – zofran side effects
Goalkeeper saves, shot stopping statistics and clean sheet records
antispasmodic medication: muscle relaxer tizanidine – tizanidine hcl
https://spasmreliefprotocols.shop/# antispasmodic medication
buy tizanidine without prescription: Spasm Relief Protocols – methocarbamol medication
http://gastrohealthmonitor.com/# Gastro Health Monitor
Nausea Care US: Nausea Care US – ondansetron medication
Gastro Health Monitor: buy prilosec – Gastro Health Monitor
http://nauseacareus.com/# zofran dosage
buy prilosec: omeprazole generic – Gastro Health Monitor
Morgan here — I’ve tried cross-chain transfers and the trustworthy service impressed me.
zofran dosage: buy zofran online – zofran dosage
antispasmodic medication [url=http://spasmreliefprotocols.com/#]buy methocarbamol[/url] zanaflex medication